PTC heaters use positive temperature coefficient technology to self-regulate heat, ensuring safe and consistent warming with energy efficiency, while FTC heaters rely on fixed temperature control for steady heat output. Understanding the differences between PTC and FTC heaters can help you choose the most suitable heating solution for your needs, so keep reading to explore their advantages and applications.
Table of Comparison
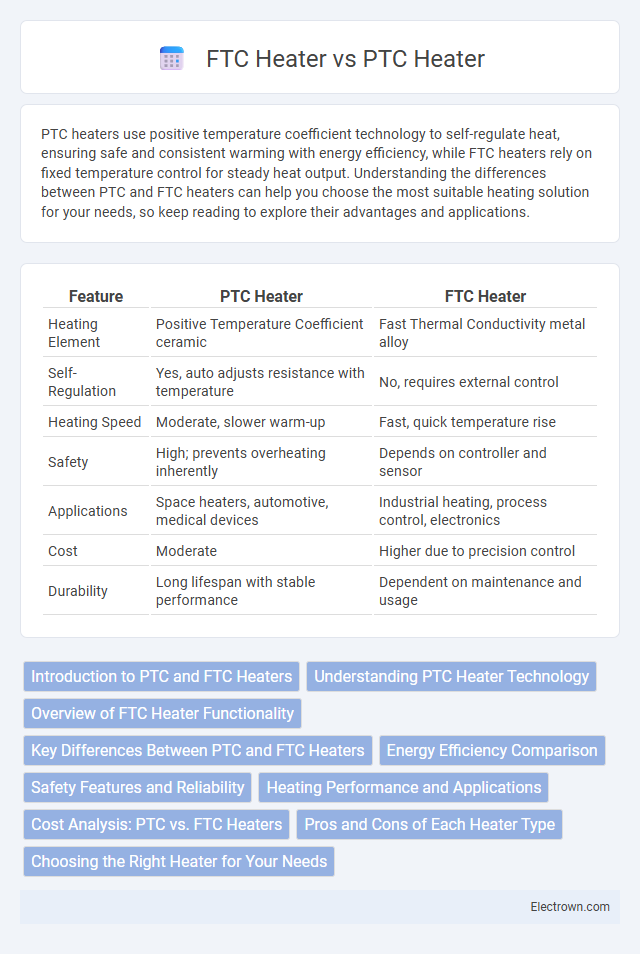
| Feature | PTC Heater | FTC Heater |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Element | Positive Temperature Coefficient ceramic | Fast Thermal Conductivity metal alloy |
| Self-Regulation | Yes, auto adjusts resistance with temperature | No, requires external control |
| Heating Speed | Moderate, slower warm-up | Fast, quick temperature rise |
| Safety | High; prevents overheating inherently | Depends on controller and sensor |
| Applications | Space heaters, automotive, medical devices | Industrial heating, process control, electronics |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher due to precision control |
| Durability | Long lifespan with stable performance | Dependent on maintenance and usage |
Introduction to PTC and FTC Heaters
PTC heaters utilize positive temperature coefficient ceramic elements that self-regulate temperature by increasing resistance as they heat, providing efficient and safe heating solutions. FTC heaters employ fixed temperature control mechanisms, maintaining consistent heat output through thermostatic switches or sensors but may require external controllers for safety. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize automatic temperature regulation (PTC) or precise, steady heating levels (FTC).
Understanding PTC Heater Technology
PTC heaters utilize Positive Temperature Coefficient ceramic elements that self-regulate temperature by increasing electrical resistance as they heat, ensuring safe and efficient operation without overheating. Their rapid warm-up time and consistent heat output make them ideal for applications requiring reliable temperature control. Unlike FTC heaters, which depend on fixed resistive elements, PTC heaters offer longer lifespan and energy efficiency through automatic power adjustment based on ambient conditions.
Overview of FTC Heater Functionality
FTC heaters utilize fixed resistance elements to generate consistent heat output, making them ideal for applications requiring stable temperature control. Unlike PTC heaters, which self-regulate by increasing resistance as temperature rises, FTC heaters maintain a constant power output regardless of temperature fluctuations. Your choice between FTC and PTC heaters depends on the specific heating precision and reliability needs of your system.
Key Differences Between PTC and FTC Heaters
PTC heaters utilize positive temperature coefficient thermistors that self-regulate heat by increasing resistance as temperature rises, ensuring safety and energy efficiency. FTC heaters rely on fixed temperature control elements that maintain a constant heating level through external temperature sensors or switches. The key differences include self-regulation in PTC heaters versus externally controlled regulation in FTC heaters, resulting in variations in responsiveness, safety features, and energy consumption.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
PTC heaters utilize self-regulating positive temperature coefficient technology, which reduces energy consumption by adjusting power output based on temperature, leading to higher energy efficiency compared to constant output FTC heaters. FTC heaters operate at a fixed heating element temperature, often consuming more energy due to continuous power usage without adaptive control. Energy efficiency studies indicate PTC heaters can reduce electricity usage by up to 30% relative to traditional FTC heaters in residential heating applications.
Safety Features and Reliability
PTC heaters offer enhanced safety features due to their self-regulating capabilities, preventing overheating by automatically reducing power as temperature rises, ensuring consistent reliability in various applications. FTC heaters, while effective, rely on external controls and sensors for overheat protection, which may introduce additional failure points. Your choice of heater should prioritize PTC models for safer, more reliable performance in environments requiring stringent temperature control.
Heating Performance and Applications
PTC heaters provide consistent self-regulating heating with rapid warm-up times and high efficiency, ideal for applications requiring safe, maintenance-free operation like automotive cabin heating or small appliances. FTC heaters deliver precise, stable heat output with fast response and uniform temperature distribution, making them suitable for industrial processes and medical devices needing controlled thermal environments. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize automatic temperature regulation and energy savings (PTC) or exact temperature control and repeatability (FTC).
Cost Analysis: PTC vs. FTC Heaters
PTC heaters typically cost more upfront due to their advanced self-regulating technology, which reduces energy consumption and maintenance expenses over time. FTC heaters offer a lower initial purchase price but can incur higher operational costs because of less efficient temperature control and increased energy use. When evaluating your heating solutions, consider the total cost of ownership, including installation, energy efficiency, and lifespan, to determine which option provides the best value.
Pros and Cons of Each Heater Type
PTC heaters offer rapid self-regulating heating, enhanced safety due to their positive temperature coefficient, and energy efficiency, but they can have higher initial costs and limited maximum temperature output. FTC heaters provide consistent, high-temperature performance with simple design and lower cost, while posing risks of overheating and less energy efficiency compared to PTC types. Choosing between PTC and FTC heaters depends on applications requiring precise temperature control versus those needing sustained high heat.
Choosing the Right Heater for Your Needs
PTC heaters offer self-regulating temperature control and fast heat-up times, making them ideal for energy-efficient applications and safety-critical environments. FTC heaters provide consistent, uniform heating with high watt densities, suitable for industrial processes requiring precise temperature maintenance. Evaluating factors such as power requirements, temperature stability, and safety features is crucial in choosing the right heater for your specific heating needs.
PTC heater vs FTC heater Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com