CAN FD offers higher data rates and improved flexibility over classical CAN, while CAN XL extends these capabilities with even greater bandwidth and enhanced data capacity for next-generation automotive and industrial applications. Explore the rest of this article to understand how these protocols can optimize Your communication networks.
Table of Comparison
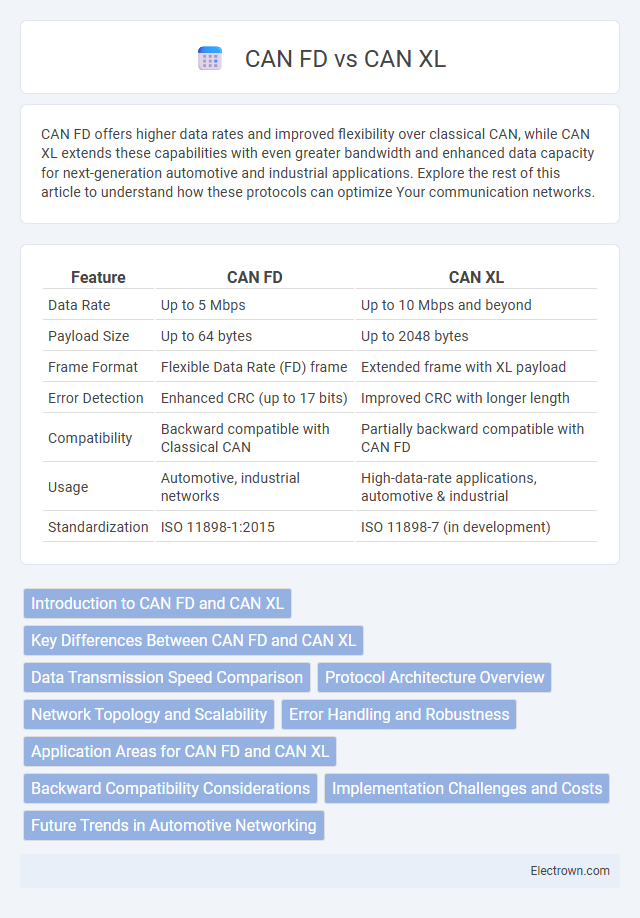
| Feature | CAN FD | CAN XL |
|---|---|---|
| Data Rate | Up to 5 Mbps | Up to 10 Mbps and beyond |
| Payload Size | Up to 64 bytes | Up to 2048 bytes |
| Frame Format | Flexible Data Rate (FD) frame | Extended frame with XL payload |
| Error Detection | Enhanced CRC (up to 17 bits) | Improved CRC with longer length |
| Compatibility | Backward compatible with Classical CAN | Partially backward compatible with CAN FD |
| Usage | Automotive, industrial networks | High-data-rate applications, automotive & industrial |
| Standardization | ISO 11898-1:2015 | ISO 11898-7 (in development) |
Introduction to CAN FD and CAN XL
CAN FD (Controller Area Network Flexible Data-Rate) enhances traditional CAN by increasing data throughput up to 8 Mbps and expanding payload size to 64 bytes, improving automotive and industrial communication efficiency. CAN XL (CAN Extra Long) represents the next generation, delivering even higher data rates beyond 10 Mbps and payloads up to 2048 bytes, enabling advanced applications requiring larger data transfers and lower latency. Both protocols maintain backward compatibility with classical CAN, ensuring seamless integration in existing network infrastructures while addressing evolving performance demands.
Key Differences Between CAN FD and CAN XL
CAN FD (Flexible Data-rate) supports data rates up to 8 Mbps and payloads up to 64 bytes, enhancing the classic CAN protocol's speed and capacity. CAN XL, the next-generation protocol, significantly increases data rates up to 10 Mbps and expands payload sizes to 2048 bytes, targeting high-bandwidth automotive and industrial applications. Key differences include CAN XL's improved error handling, flexible frame format, and scalability for future network demands compared to CAN FD's fixed frame structure and lower data throughput.
Data Transmission Speed Comparison
CAN FD supports data transmission speeds up to 8 Mbps, significantly improving over the classical CAN standard's 1 Mbps limit. In contrast, CAN XL offers even higher speeds, targeting up to 10 Mbps and beyond, enabling more efficient communication in complex automotive and industrial networks. This speed enhancement in CAN XL facilitates larger payload sizes and faster data throughput, making it suitable for future high-bandwidth applications.
Protocol Architecture Overview
CAN FD enhances traditional CAN protocol by increasing data payload up to 64 bytes and allowing faster bit rates during the data phase, improving real-time communication efficiency. CAN XL builds upon CAN FD by introducing an extended frame format with payloads up to 2048 bytes and a new protocol layer that supports higher throughput and complex applications in automotive and industrial networks. Your system can benefit from CAN XL's scalable architecture when requiring substantial data transfer and advanced diagnostics beyond CAN FD capabilities.
Network Topology and Scalability
CAN FD supports a simple linear bus topology allowing up to 30 nodes on a single network, which limits its scalability in complex or large automotive systems. CAN XL introduces enhanced scalability by accommodating more nodes and enabling flexible topologies, including star and mixed bus configurations, suitable for advanced vehicle architectures. This evolution facilitates higher data throughput and network expansion without compromising reliability or latency requirements.
Error Handling and Robustness
CAN FD enhances error handling with improved CRC length and flexible data rates, offering robust protection against data corruption in automotive and industrial networks. CAN XL further advances error detection by implementing stronger cyclic redundancy checks and enhanced fault confinement mechanisms, optimizing communication reliability in complex, high-throughput environments. Both protocols increase robustness, but CAN XL targets next-generation applications requiring ultra-reliable and scalable network performance.
Application Areas for CAN FD and CAN XL
CAN FD excels in automotive and industrial sectors where enhanced data rates up to 8 Mbps and flexible payload sizes improve real-time communication and diagnostics. CAN XL, with data rates reaching 10 Mbps and extended frame formats, targets advanced vehicle systems and next-generation industrial automation requiring higher bandwidth and more complex data structures. Both protocols enhance network efficiency, but CAN XL supports emerging applications like autonomous driving and high-definition sensor data integration.
Backward Compatibility Considerations
CAN XL maintains backward compatibility by supporting the CAN FD data link layer while introducing enhanced frame formats for higher throughput. Devices designed for CAN FD can interoperate with CAN XL networks, ensuring seamless integration during gradual technology upgrades. This compatibility facilitates network scalability without requiring complete replacement of existing CAN FD infrastructure.
Implementation Challenges and Costs
Implementing CAN FD presents fewer challenges and lower costs due to its backward compatibility with existing CAN infrastructure and simpler upgrade requirements for hardware and software. CAN XL, designed for higher data throughput and enhanced features, demands substantial investment in new transceiver designs, controllers, and robust protocol stack changes, increasing both complexity and overall implementation expenses. Organizations must weigh CAN FD's cost-efficiency against CAN XL's advanced capabilities when considering integration into automotive or industrial communication networks.
Future Trends in Automotive Networking
CAN FD (Flexible Data-Rate) enhances traditional CAN protocol by increasing data payloads up to 64 bytes and supporting faster bit rates, enabling improved real-time communication in automotive systems. CAN XL, the next-generation protocol, pushes this further with payloads up to 2048 bytes and data rates exceeding 10 Mbps, designed to meet the growing demands for high-bandwidth applications such as advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving. Future trends in automotive networking emphasize the integration of CAN XL to support complex sensor fusion, over-the-air updates, and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, facilitating safer and more connected vehicles.
CAN FD vs CAN XL Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com