Pinion sensors measure the rotational position of the steering column's pinion gear to accurately detect steering angle, while torque sensors gauge the amount of force applied by the driver on the steering wheel to assist with steering input and feedback. Understanding the differences between these sensors can help you optimize your vehicle's steering performance--read on to explore their functionalities in detail.
Table of Comparison
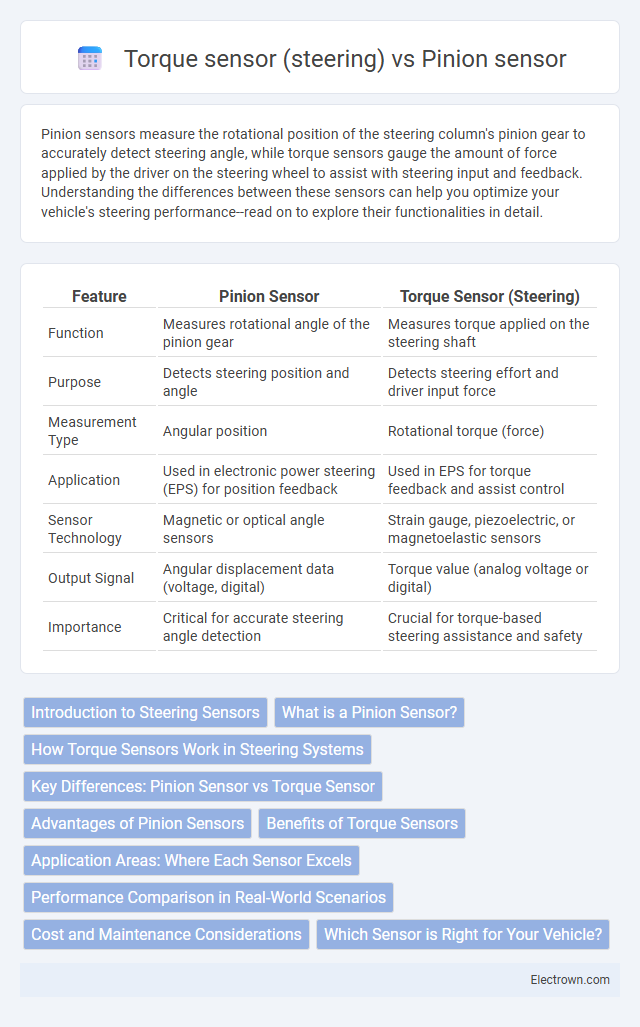
| Feature | Pinion Sensor | Torque Sensor (Steering) |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Measures rotational angle of the pinion gear | Measures torque applied on the steering shaft |
| Purpose | Detects steering position and angle | Detects steering effort and driver input force |
| Measurement Type | Angular position | Rotational torque (force) |
| Application | Used in electronic power steering (EPS) for position feedback | Used in EPS for torque feedback and assist control |
| Sensor Technology | Magnetic or optical angle sensors | Strain gauge, piezoelectric, or magnetoelastic sensors |
| Output Signal | Angular displacement data (voltage, digital) | Torque value (analog voltage or digital) |
| Importance | Critical for accurate steering angle detection | Crucial for torque-based steering assistance and safety |
Introduction to Steering Sensors
Steering sensors, including pinion sensors and torque sensors, play a crucial role in modern vehicle steering systems by providing precise input data for electronic control units. Pinion sensors measure the rotational position and speed of the steering pinion gear, enabling accurate angle detection and responsiveness. Torque sensors detect the force or torque applied by the driver on the steering wheel, allowing adaptive steering assistance and enhanced vehicle stability control.
What is a Pinion Sensor?
A Pinion sensor detects the rotational position and velocity of the pinion gear in a steering system, providing accurate feedback for electronic power steering (EPS) control. It measures the angular displacement of the pinion shaft to determine steering input and assist torque requirements. This sensor is essential for enhancing steering precision and responsiveness by enabling real-time adjustments based on driver input.
How Torque Sensors Work in Steering Systems
Torque sensors in steering systems measure the rotational force applied by the driver on the steering wheel, using strain gauges or magnetoelastic elements to detect twist or torsion in the steering column. These sensors convert mechanical torque into electrical signals, enabling electronic power steering (EPS) systems to adjust motor assistance based on real-time input. Compared to pinion sensors, torque sensors provide precise feedback for smoother, more responsive steering control by directly assessing driver input rather than relying on positional data.
Key Differences: Pinion Sensor vs Torque Sensor
Pinion sensors measure the angular position and speed of the steering shaft, providing real-time data on steering wheel rotation, while torque sensors detect the force or twisting applied by the driver to the steering wheel, essential for power-assisted steering systems. Torque sensors enable precise assistance adjustments by monitoring the amount of steering input force, whereas pinion sensors focus on the mechanical movement and position of the pinion gear in the steering system. Your vehicle's steering control relies on both sensors working together to ensure accurate and responsive handling.
Advantages of Pinion Sensors
Pinion sensors offer precise and direct measurement of the steering angle by monitoring the rotation of the pinion gear, resulting in faster response times and improved accuracy over torque sensors. Their design typically ensures reduced mechanical complexity and better resistance to interference, enhancing reliability in automotive steering systems. Pinion sensors contribute to more consistent feedback and refined vehicle control, making them advantageous in advanced driver-assistance and electric power steering applications.
Benefits of Torque Sensors
Torque sensors in steering systems provide precise real-time feedback on the amount of force applied, enhancing vehicle control and safety. Unlike pinion sensors that primarily measure rotational position, torque sensors offer improved responsiveness and smoother handling by directly detecting steering effort. Your driving experience benefits from increased accuracy and reduced steering effort, leading to better overall performance and reduced driver fatigue.
Application Areas: Where Each Sensor Excels
Pinion sensors excel in automotive steering systems by providing precise angular position data crucial for electronic power steering and stability control. Torque sensors are primarily used in electric and hybrid vehicles to measure applied steering force, enhancing driver feedback and adaptive assistance. Industrial machinery benefits more from torque sensors due to their ability to monitor load and stress for predictive maintenance and operational accuracy.
Performance Comparison in Real-World Scenarios
Pinion sensors offer precise angular position measurements crucial for responsive steering control, while torque sensors excel in detecting steering effort and driver intent through real-time torque feedback. In real-world scenarios, torque sensors deliver enhanced driver assistance system performance by accurately gauging steering load, improving stability and safety under variable road conditions. Pinion sensors, however, provide faster response times critical in high-performance or racing applications where steering angle accuracy directly affects vehicle dynamics.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Pinion sensors generally have lower upfront costs and simpler maintenance requirements compared to torque sensors, making them a cost-effective choice for steering applications. Torque sensors, while offering higher sensitivity and precision, often come with increased complexity that can lead to higher maintenance expenses and longer downtime. Choosing between the two depends on balancing initial investment with long-term operational costs and reliability needs.
Which Sensor is Right for Your Vehicle?
Choosing between a pinion sensor and a torque sensor for steering depends on vehicle type and driving conditions. Pinion sensors precisely measure the steering shaft angle, offering accurate feedback for electric power steering systems in passenger cars. Torque sensors gauge the applied force on the steering wheel, providing responsive input for adaptive steering in performance and off-road vehicles.
Pinion sensor vs Torque sensor (steering) Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com