CAN terminators and resistors both play crucial roles in Controller Area Network (CAN) communication by ensuring signal integrity and preventing message reflection. Understanding the difference between a dedicated CAN terminator and a general-purpose resistor can help you optimize your network setup for better performance; continue reading to explore their distinct functions and applications.
Table of Comparison
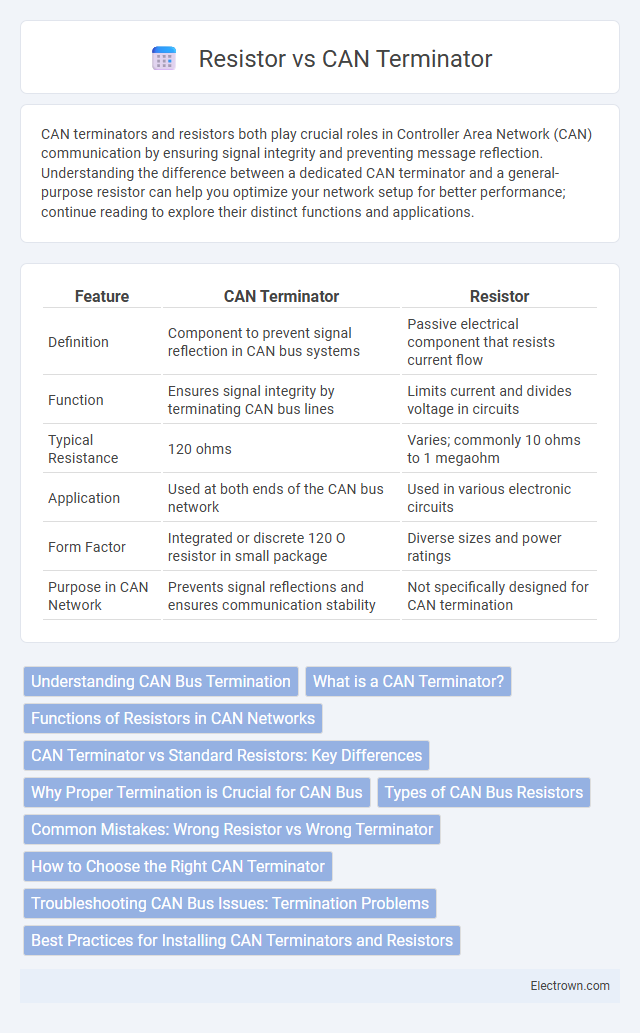
| Feature | CAN Terminator | Resistor |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Component to prevent signal reflection in CAN bus systems | Passive electrical component that resists current flow |
| Function | Ensures signal integrity by terminating CAN bus lines | Limits current and divides voltage in circuits |
| Typical Resistance | 120 ohms | Varies; commonly 10 ohms to 1 megaohm |
| Application | Used at both ends of the CAN bus network | Used in various electronic circuits |
| Form Factor | Integrated or discrete 120 O resistor in small package | Diverse sizes and power ratings |
| Purpose in CAN Network | Prevents signal reflections and ensures communication stability | Not specifically designed for CAN termination |
Understanding CAN Bus Termination
Proper CAN bus termination requires resistors to prevent signal reflections and ensure reliable communication. A standard CAN bus uses two 120-ohm terminating resistors placed at each end of the bus to match the characteristic impedance of the cable. Incorrect or missing termination causes data errors and communication failures in automotive and industrial CAN networks.
What is a CAN Terminator?
A CAN terminator is a specialized resistor, typically 120 ohms, placed at the ends of a Controller Area Network (CAN) bus to prevent signal reflections and ensure proper communication integrity. The terminator matches the characteristic impedance of the CAN bus, stabilizing voltage levels and minimizing electromagnetic interference. Without effective termination resistors, data transmission errors and network malfunctions can occur due to signal distortion on the bus lines.
Functions of Resistors in CAN Networks
Resistors in CAN networks primarily function to terminate the bus and prevent signal reflections, ensuring data integrity and reliable communication. A termination resistor, typically 120 ohms, matches the cable impedance and stabilizes the CAN signal by absorbing excess energy at the network edges. Properly placed resistors reduce electromagnetic interference and improve signal quality, unlike non-terminating resistors that fail to address these critical transmission issues.
CAN Terminator vs Standard Resistors: Key Differences
CAN terminators are specialized resistors with a fixed 120-ohm resistance designed to match the characteristic impedance of the CAN bus, minimizing signal reflections and ensuring reliable data transmission. Standard resistors may not have precise resistance values or the necessary power rating, leading to signal integrity issues and increased error rates in the CAN network. Proper CAN termination is critical for maintaining network stability and preventing communication failures in automotive and industrial applications.
Why Proper Termination is Crucial for CAN Bus
Proper termination in a CAN bus system prevents signal reflections and ensures clean data transmission, which is essential for network reliability and performance. A CAN terminator, typically a 120-ohm resistor, matches the characteristic impedance of the bus, minimizing noise and preventing data errors. Ensuring your CAN bus has correct termination with the proper resistor directly impacts the accuracy and stability of your communication network.
Types of CAN Bus Resistors
CAN bus systems utilize terminators and resistors to maintain signal integrity and reduce reflections along the network. Common types of CAN bus resistors include standard 120-ohm terminators placed at each end of the bus, zero-ohm jumpers for configuring network segments, and specialized terminating resistors with integrated ESD protection for enhanced reliability. Your choice of resistor type directly impacts communication stability and overall CAN bus performance.
Common Mistakes: Wrong Resistor vs Wrong Terminator
Using the wrong resistor value instead of a proper CAN terminator can cause signal reflections and communication errors on the CAN bus, leading to unreliable network performance. A common mistake is confusing a standard resistor with a 120-ohm terminator, which is specifically designed to match the impedance of the CAN bus and ensure proper signal integrity. Your CAN network requires precise termination to minimize noise and prevent data corruption, so using the correct 120-ohm terminator resistor at both ends of the bus is essential.
How to Choose the Right CAN Terminator
Choosing the right CAN terminator involves understanding the importance of a fixed 120-ohm resistor that matches the characteristic impedance of the CAN bus to prevent signal reflections and ensure data integrity. You should select a terminator based on the bus length, network topology, and the specific CAN transceiver requirements, as incorrect termination can lead to communication errors or bus failure. Evaluate the operating environment and select high-quality resistors with tight tolerance to maintain stable signal transmission in automotive or industrial CAN networks.
Troubleshooting CAN Bus Issues: Termination Problems
Termination problems in CAN bus networks often stem from incorrect or missing terminators, leading to signal reflections and communication errors. Properly implemented 120-ohm resistors at both ends of the CAN bus are critical to maintaining signal integrity and reducing noise interference. Troubleshooting steps include verifying resistor values with a multimeter and ensuring terminators are firmly connected to prevent data loss and bus faults.
Best Practices for Installing CAN Terminators and Resistors
Proper installation of CAN terminators and resistors is crucial for maintaining signal integrity and preventing data errors in Controller Area Network (CAN) systems. Use a 120-ohm resistor at each end of the CAN bus to match the characteristic impedance and reduce signal reflections effectively. Ensure terminators are placed only at the bus endpoints, and avoid inserting terminators or resistors in the middle of the bus to maintain reliable communication and minimize electromagnetic interference.
CAN terminator vs Resistor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com