Proper ECG lead placement directly influences the accuracy of your cardiac readings by ensuring electrodes capture precise electrical signals from the heart. Understanding the distinction between lead placement and electrode positioning is essential for accurate diagnostics; explore the rest of the article to deepen your knowledge and improve your ECG technique.
Table of Comparison
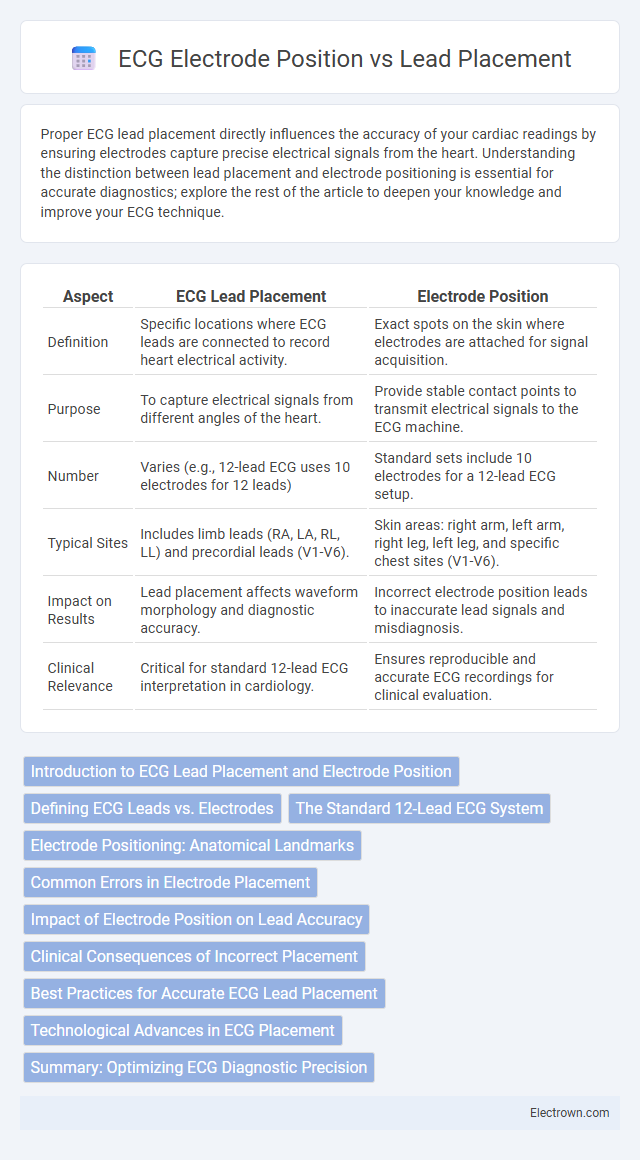
| Aspect | ECG Lead Placement | Electrode Position |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Specific locations where ECG leads are connected to record heart electrical activity. | Exact spots on the skin where electrodes are attached for signal acquisition. |
| Purpose | To capture electrical signals from different angles of the heart. | Provide stable contact points to transmit electrical signals to the ECG machine. |
| Number | Varies (e.g., 12-lead ECG uses 10 electrodes for 12 leads) | Standard sets include 10 electrodes for a 12-lead ECG setup. |
| Typical Sites | Includes limb leads (RA, LA, RL, LL) and precordial leads (V1-V6). | Skin areas: right arm, left arm, right leg, left leg, and specific chest sites (V1-V6). |
| Impact on Results | Lead placement affects waveform morphology and diagnostic accuracy. | Incorrect electrode position leads to inaccurate lead signals and misdiagnosis. |
| Clinical Relevance | Critical for standard 12-lead ECG interpretation in cardiology. | Ensures reproducible and accurate ECG recordings for clinical evaluation. |
Introduction to ECG Lead Placement and Electrode Position
ECG lead placement refers to the specific locations on the body where leads are attached to record electrical activity of the heart, with standard configurations like 12-lead ECG involving precise electrode positioning on the chest and limbs. Electrode position directly impacts the accuracy and diagnostic quality of the ECG trace, as improper placement can result in misleading waveforms or missed cardiac abnormalities. Understanding the relationship between lead placement and electrode position is critical for obtaining reliable ECG recordings and accurate interpretation of cardiac function.
Defining ECG Leads vs. Electrodes
ECG leads represent the electrical viewpoint created by combining signals from specific electrode pairs placed on the body, whereas electrodes are the physical sensors attached to the skin to detect cardiac electrical activity. Your understanding of ECG lead placement depends on accurately positioning these electrodes, as improper electrode placement can distort the lead signals and affect diagnostic accuracy. Clear differentiation between leads and electrodes ensures precise ECG interpretation and effective cardiac monitoring.
The Standard 12-Lead ECG System
The Standard 12-Lead ECG System relies on precise lead placement combined with accurate electrode position to capture comprehensive cardiac electrical activity across multiple planes. Electrodes are strategically positioned on the limbs and chest to create 12 distinct leads, each providing unique diagnostic information for conditions like arrhythmias, ischemia, and myocardial infarction. Ensuring correct electrode placement enhances the accuracy of your ECG readings and improves the reliability of cardiac assessments.
Electrode Positioning: Anatomical Landmarks
Electrode positioning for ECG lead placement relies on precise anatomical landmarks to ensure accurate cardiac monitoring. Common reference points include the clavicle, sternum, and intercostal spaces, which guide the placement of electrodes on the chest and limbs. Accurate positioning relative to these landmarks is critical for reliable detection of cardiac electrical activity and optimal waveform interpretation.
Common Errors in Electrode Placement
Incorrect ECG lead placement often results from electrode mispositioning, such as placing limb electrodes too close to the torso or interchanging precordial leads V1 and V2. Common errors include symmetric electrode placement on opposite sides, leading to distorted waveforms and inaccurate cardiac readings. Ensuring your electrodes align precisely with anatomical landmarks like the fourth intercostal space and midclavicular line is essential for reliable ECG results.
Impact of Electrode Position on Lead Accuracy
Electrode position directly affects ECG lead accuracy by influencing signal quality and waveform interpretation. Incorrect electrode placement can result in altered QRS complex morphology, misdiagnosis of arrhythmias, and inaccurate ST segment evaluation. Ensuring precise electrode positioning is critical for your ECG to deliver reliable and clinically meaningful data.
Clinical Consequences of Incorrect Placement
Incorrect ECG lead placement can result in misinterpretation of cardiac rhythms, leading to inaccurate diagnoses such as myocardial infarction or arrhythmias. Electrode position errors may cause false ST-segment changes, altering clinical decisions and patient management. Precise placement is critical to ensure reliable ECG readings and prevent diagnostic errors that affect treatment outcomes.
Best Practices for Accurate ECG Lead Placement
Accurate ECG lead placement relies on precise electrode positioning following standardized anatomical landmarks, such as placing precordial leads in correct intercostal spaces to ensure reliable cardiac electrical activity recording. Consistent skin preparation, including cleaning and abrasion, minimizes impedance, improving signal quality and reducing artifacts. Adhering to best practices like symmetrical limb lead placement and securing electrodes firmly enhances reproducibility and diagnostic accuracy in electrocardiography.
Technological Advances in ECG Placement
Technological advances in ECG placement have enhanced accuracy in lead placement through the integration of wearable sensors and AI-guided electrode positioning systems. These innovations improve diagnostic precision by minimizing errors caused by incorrect electrode placement, ensuring that your cardiac data reflects true physiological signals. Modern devices also facilitate real-time monitoring and automated adjustments, optimizing the correlation between lead placement and electrode position.
Summary: Optimizing ECG Diagnostic Precision
Accurate ECG lead placement directly correlates with precise electrode positioning to enhance diagnostic reliability in cardiac assessments. Misplaced electrodes can cause significant deviations in waveforms, potentially leading to misinterpretation of myocardial ischemia, arrhythmias, or conduction abnormalities. Standardizing lead placement protocols ensures reproducible electrocardiographic data essential for effective diagnosis and patient care.
ECG Lead Placement vs Electrode Position Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com