Electret microphones and MEMS microphones differ significantly in capturing heart sounds, with MEMS offering superior sensitivity, low power consumption, and compact size ideal for precise medical applications. Explore the rest of this article to understand how these technologies impact your heart sound monitoring choices.
Table of Comparison
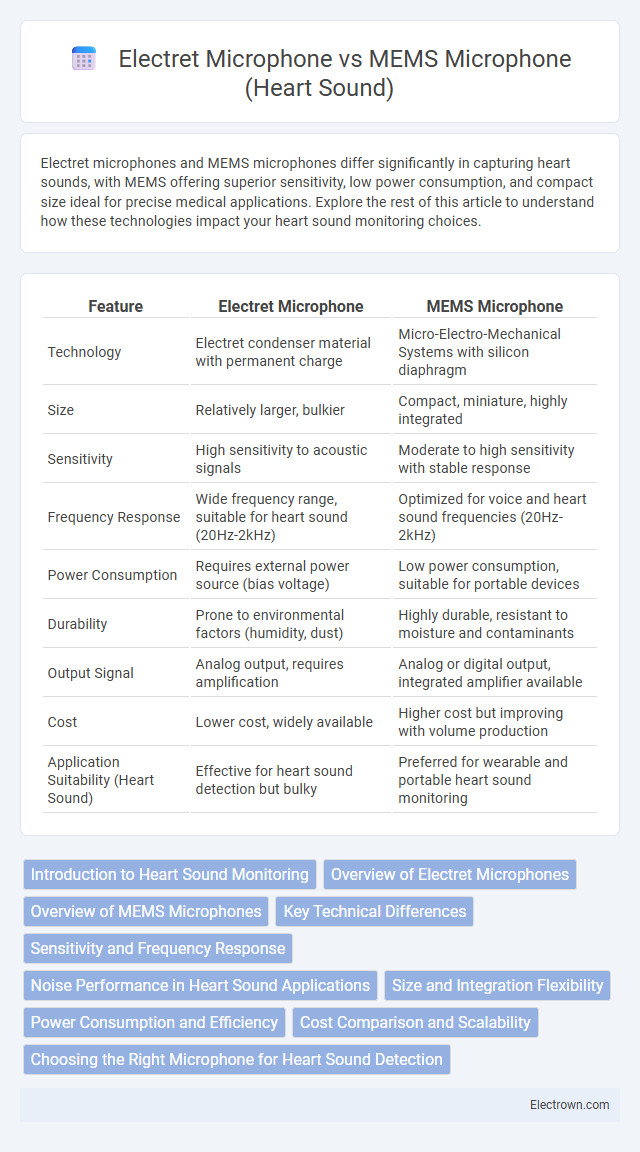
| Feature | Electret Microphone | MEMS Microphone |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Electret condenser material with permanent charge | Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems with silicon diaphragm |
| Size | Relatively larger, bulkier | Compact, miniature, highly integrated |
| Sensitivity | High sensitivity to acoustic signals | Moderate to high sensitivity with stable response |
| Frequency Response | Wide frequency range, suitable for heart sound (20Hz-2kHz) | Optimized for voice and heart sound frequencies (20Hz-2kHz) |
| Power Consumption | Requires external power source (bias voltage) | Low power consumption, suitable for portable devices |
| Durability | Prone to environmental factors (humidity, dust) | Highly durable, resistant to moisture and contaminants |
| Output Signal | Analog output, requires amplification | Analog or digital output, integrated amplifier available |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost but improving with volume production |
| Application Suitability (Heart Sound) | Effective for heart sound detection but bulky | Preferred for wearable and portable heart sound monitoring |
Introduction to Heart Sound Monitoring
Heart sound monitoring relies on precise audio capture technologies like Electret microphones and MEMS microphones to detect cardiac signals. Electret microphones offer robust sensitivity and low noise, suitable for traditional stethoscope integration, while MEMS microphones provide miniaturization and enhanced durability ideal for wearable heart sound devices. Your choice of microphone directly impacts the accuracy and quality of heart sound recordings for effective diagnosis and monitoring.
Overview of Electret Microphones
Electret microphones use a permanently charged dielectric material to convert acoustic signals into electrical signals, making them highly sensitive and widely used in medical applications like heart sound monitoring. Their analog output and simple design enable reliable detection of low-frequency heart sounds, but they are generally larger and more susceptible to environmental noise compared to MEMS microphones. Electret microphones remain a cost-effective choice for auscultation devices requiring robust performance in diverse clinical settings.
Overview of MEMS Microphones
MEMS microphones utilize micro-electromechanical systems technology to convert acoustic signals into electrical signals with high precision and reliability, making them ideal for capturing subtle heart sounds. Their compact size, low power consumption, and robustness against environmental noise enhance performance in medical devices like digital stethoscopes. Compared to electret microphones, MEMS microphones offer superior sensitivity and frequency response, crucial for accurate heart sound analysis.
Key Technical Differences
Electret microphones utilize a permanently charged diaphragm and backplate to capture heart sounds with high sensitivity but are more susceptible to environmental noise and aging effects. MEMS microphones feature microfabricated silicon structures offering improved durability, lower power consumption, and better noise immunity, making them highly suitable for precise heart sound detection. The key technical differences involve MEMS devices' advanced fabrication techniques enabling miniaturization and integration with digital electronics, whereas electret microphones rely on mechanical components and analog output.
Sensitivity and Frequency Response
Electret microphones typically offer high sensitivity with a frequency response suitable for capturing low-frequency heart sounds, often ranging from 20 Hz to 20 kHz, making them effective for detailed auscultation. MEMS microphones provide a more consistent frequency response with sensitivity optimized for mid to high-frequency sounds, generally around 100 Hz to 10 kHz, which can limit their ability to capture the full range of heart sound nuances. Your choice depends on whether higher sensitivity at low frequencies or compact, stable performance in medium frequency ranges is more critical for accurate heart sound detection.
Noise Performance in Heart Sound Applications
Electret microphones typically exhibit higher self-noise levels, which can interfere with the detection of low-amplitude heart sounds, reducing diagnostic accuracy. MEMS microphones offer superior noise performance due to their smaller diaphragm and integrated circuitry, enabling clearer capture of subtle acoustic signals in cardiac monitoring. This enhanced sensitivity and lower inherent noise of MEMS technology make it preferable for precise heart sound recordings in medical applications.
Size and Integration Flexibility
Electret microphones typically have a larger size due to their traditional components, limiting their integration flexibility in compact heart sound monitoring devices. MEMS microphones offer a significantly smaller form factor with high integration versatility, enabling seamless embedding in wearable cardiac sensors and portable stethoscopes. Their miniaturized design supports advanced signal processing and enhanced user comfort in continuous heart sound analysis.
Power Consumption and Efficiency
Electret microphones typically consume more power due to the need for a built-in preamplifier and continuous polarization voltage, impacting battery life in heart sound monitoring devices. MEMS microphones offer higher efficiency with significantly lower power consumption, often in the range of microwatts, making them ideal for portable and wearable heart sound applications. The advanced MEMS technology provides consistent performance with less energy, enhancing overall device longevity and reliability in continuous cardiac monitoring.
Cost Comparison and Scalability
Electret microphones generally offer lower initial costs due to established manufacturing processes and widely available materials, making them suitable for budget-conscious heart sound monitoring projects. MEMS microphones, despite higher upfront expenses, provide superior scalability with miniaturized designs and integration capabilities, enabling mass production and consistent performance in complex medical devices. Your choice depends on balancing cost constraints with long-term scalability needs for heart sound detection technology.
Choosing the Right Microphone for Heart Sound Detection
Electret microphones offer reliable sensitivity and cost-effectiveness for heart sound detection, making them suitable for basic auscultation devices. MEMS microphones provide superior noise immunity, smaller form factor, and enhanced frequency response, critical for accurate heart sound acquisition in portable and wearable health monitors. Selecting between these technologies depends on application requirements for signal clarity, device size, and integration complexity in cardiac diagnostics.
Electret Microphone vs MEMS Microphone (Heart Sound) Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com