Capacitive touch sensing uses the electrical properties of the human body to detect touch, providing high accuracy and multi-touch capabilities, while optical touch sensing relies on light interruptions or reflections, often enabling larger screen sizes and durability. Discover how understanding these differences can help you choose the best technology for your device by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
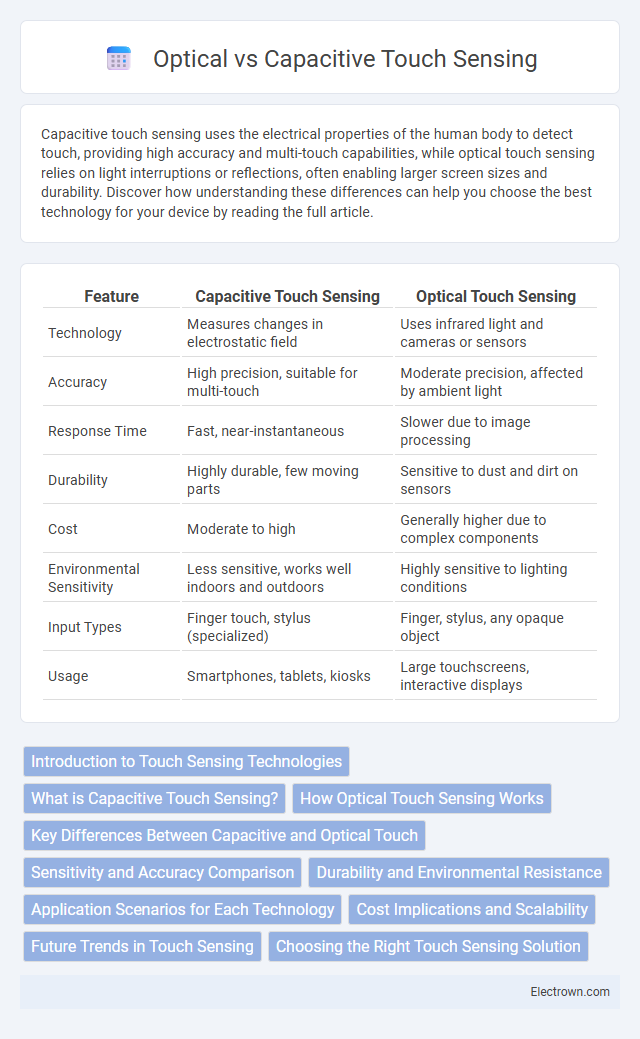
| Feature | Capacitive Touch Sensing | Optical Touch Sensing |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Measures changes in electrostatic field | Uses infrared light and cameras or sensors |
| Accuracy | High precision, suitable for multi-touch | Moderate precision, affected by ambient light |
| Response Time | Fast, near-instantaneous | Slower due to image processing |
| Durability | Highly durable, few moving parts | Sensitive to dust and dirt on sensors |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Generally higher due to complex components |
| Environmental Sensitivity | Less sensitive, works well indoors and outdoors | Highly sensitive to lighting conditions |
| Input Types | Finger touch, stylus (specialized) | Finger, stylus, any opaque object |
| Usage | Smartphones, tablets, kiosks | Large touchscreens, interactive displays |
Introduction to Touch Sensing Technologies
Capacitive touch sensing detects touch by measuring changes in the electrical field caused by the conductive properties of the human finger, offering high accuracy and multi-touch capabilities. Optical touch sensing uses infrared or camera-based technology to detect touch through disruptions in light beams or image analysis, providing versatility in screen size and stylus compatibility. Both technologies are integral in devices ranging from smartphones to interactive kiosks, each with distinct advantages in responsiveness and environmental adaptability.
What is Capacitive Touch Sensing?
Capacitive touch sensing detects touch input by measuring changes in electrical capacitance caused by a conductive object, such as a finger, on a sensor surface. This technology relies on an electrostatic field to accurately sense touch location, offering high sensitivity and multi-touch capabilities. Commonly found in smartphones, tablets, and interactive displays, capacitive touch sensors deliver fast response times and durable performance with minimal wear.
How Optical Touch Sensing Works
Optical touch sensing operates by detecting interruptions in infrared light beams or using cameras to track touch interactions on a screen's surface. When your finger or stylus disrupts the light paths or is recognized through image processing, the device accurately determines the touch location. This technology enables precise multi-touch capabilities and works well with various input types without pressure sensitivity.
Key Differences Between Capacitive and Optical Touch
Capacitive touch sensing detects touch through changes in the electrical field caused by the conductive properties of the human skin, offering high accuracy and multi-touch capabilities ideal for smartphones and tablets. Optical touch sensing employs infrared light sensors to detect touch by interruption or reflection of light beams, enabling large surface tracking with minimal wear and compatibility with gloves or stylus use. Key differences include capacitive's reliance on conductive touch for high precision versus optical's use of light for touch detection, influencing device design, durability, and user interaction methods.
Sensitivity and Accuracy Comparison
Capacitive touch sensing offers higher sensitivity by detecting changes in the electrical field caused by the human body, allowing for precise multi-touch input and superior responsiveness on smooth surfaces. Optical touch sensing relies on infrared light interruption, which provides good accuracy but may struggle with smaller or quick touches, leading to potential false inputs or reduced sensitivity in bright environments. Your choice depends on the need for fine accuracy and responsiveness, with capacitive technology generally outperforming optical in sensitive and precise touch applications.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Capacitive touch sensing offers high durability with its solid-state design, making it resistant to wear and tear from repeated use. Optical touch sensing excels in environmental resistance by functioning accurately under various conditions such as dirt, dust, and moisture without degradation. You can rely on capacitive technology for robust everyday use, while optical sensors provide superior performance in challenging environmental settings.
Application Scenarios for Each Technology
Capacitive touch sensing excels in smartphones, tablets, and interactive kiosks where multi-touch and high sensitivity are essential for user experience. Optical touch sensing is preferred in large-format displays, such as digital whiteboards, retail touchscreens, and outdoor kiosks, due to its ability to detect multiple touch points without physical contact or surface deformation. Each technology's suitability aligns with environmental conditions and interaction complexity, with capacitive favored for precision and optical for scalability and durability.
Cost Implications and Scalability
Capacitive touch sensing typically incurs lower costs due to simpler materials like indium tin oxide (ITO) and established manufacturing processes, making it cost-effective for mass production; however, scalability can be limited by the precision required for consistent sensitivity over larger surfaces. Optical touch sensing involves higher initial costs because of components such as cameras and infrared sensors, yet it offers superior scalability and flexibility for large or irregular touch areas without compromising accuracy. Choosing between these technologies depends on balancing upfront investment against long-term scalability and application requirements.
Future Trends in Touch Sensing
Capacitive touch sensing continues to advance with developments in multi-touch precision and integration with flexible displays, enhancing user interaction in smartphones and wearables. Optical touch sensing is evolving through improvements in infrared and gesture recognition technologies, enabling contactless control and expanded applications in automotive and healthcare sectors. Future trends in touch sensing emphasize seamless user experiences and increased sensor accuracy, allowing your devices to respond more intuitively and reliably.
Choosing the Right Touch Sensing Solution
Selecting the appropriate touch sensing technology depends on the application's environmental conditions and user interaction requirements. Capacitive touch sensing offers high accuracy, multi-touch capability, and durability, making it ideal for consumer electronics and devices with frequent finger input. Optical touch sensing excels in large-scale interfaces and harsh environments by utilizing infrared light to detect touches, providing superior performance with stylus or gloved users and minimizing surface wear.
Capacitive vs Optical Touch Sensing Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com