Reflective PPG measures blood flow by detecting light reflected from tissues, making it ideal for wearable devices that monitor heart rate continuously, while transmissive PPG passes light through a part of the body like a fingertip, offering higher accuracy but limited to specific body sites. Discover how understanding these differences can improve Your choice of photoplethysmography technology by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
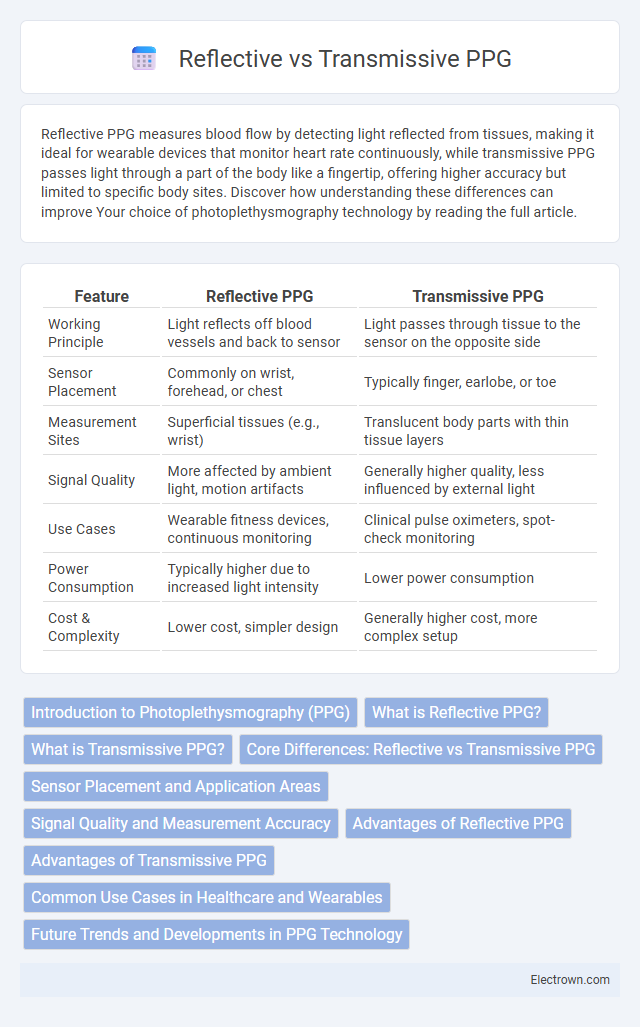
| Feature | Reflective PPG | Transmissive PPG |
|---|---|---|
| Working Principle | Light reflects off blood vessels and back to sensor | Light passes through tissue to the sensor on the opposite side |
| Sensor Placement | Commonly on wrist, forehead, or chest | Typically finger, earlobe, or toe |
| Measurement Sites | Superficial tissues (e.g., wrist) | Translucent body parts with thin tissue layers |
| Signal Quality | More affected by ambient light, motion artifacts | Generally higher quality, less influenced by external light |
| Use Cases | Wearable fitness devices, continuous monitoring | Clinical pulse oximeters, spot-check monitoring |
| Power Consumption | Typically higher due to increased light intensity | Lower power consumption |
| Cost & Complexity | Lower cost, simpler design | Generally higher cost, more complex setup |
Introduction to Photoplethysmography (PPG)
Photoplethysmography (PPG) measures blood volume changes in the microvascular bed of tissue, commonly using light-based sensors. Reflective PPG places both the light source and detector on the same side of the skin, capturing signals by light reflected from underlying blood vessels, ideal for wrist-worn devices. Transmissive PPG passes light through tissue with the detector on the opposite side, offering more direct signals typically used in fingertip pulse oximeters, enabling your devices to monitor cardiovascular health effectively.
What is Reflective PPG?
Reflective photoplethysmography (PPG) is a non-invasive optical technique that measures blood volume changes by emitting light into the skin and detecting the amount of light reflected back from underlying blood vessels. This method places both the light source and photodetector on the same side of the tissue, making it ideal for wearable devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers. Reflective PPG provides continuous cardiovascular monitoring by capturing pulse rate, blood oxygen saturation, and other hemodynamic parameters.
What is Transmissive PPG?
Transmissive photoplethysmography (PPG) measures blood volume changes by passing light through a part of the body, typically a fingertip or earlobe, where the detector is located opposite the light source. This method captures the amount of light transmitted through the tissue, which varies based on blood flow and oxygen saturation. Commonly used in pulse oximeters, transmissive PPG provides accurate heart rate and oxygen level readings by analyzing the light absorption characteristics of pulsatile blood flow.
Core Differences: Reflective vs Transmissive PPG
Reflective PPG measures blood volume changes by emitting light and detecting reflections from tissue, typically used on the wrist or forehead, while transmissive PPG requires light to pass through a body part like a fingertip or earlobe to measure blood flow. The core difference lies in sensor placement and light path; reflective sensors emit and capture light on the same side of the tissue, whereas transmissive sensors detect light transmitted through the tissue. Understanding these distinctions helps optimize your choice of PPG technology for wearable health monitoring or clinical applications.
Sensor Placement and Application Areas
Reflective PPG sensors are typically placed on areas with ample soft tissue, such as the wrist or forehead, enabling continuous monitoring in wearable devices and fitness trackers. Transmissive PPG sensors require placement on thin tissue sites like the fingertip or earlobe, ensuring accurate light transmission for clinical settings and pulse oximetry. The choice between reflective and transmissive PPG depends on the application's need for comfort, accuracy, and measurement location.
Signal Quality and Measurement Accuracy
Reflective PPG sensors capture light reflected from tissue, offering versatility in monitoring peripheral sites but often facing challenges with signal quality due to ambient light interference and motion artifacts. Transmissive PPG sensors measure light passing through tissue, such as a fingertip or earlobe, providing higher measurement accuracy and stronger signal quality due to consistent light path and reduced external noise. Studies demonstrate transmissive PPG typically yields more reliable heart rate and oxygen saturation readings, especially in clinical settings requiring precise physiological monitoring.
Advantages of Reflective PPG
Reflective PPG offers enhanced versatility by measuring blood flow using a single sensor placed on various body parts such as the wrist or forehead, unlike transmissive PPG which requires light to pass through tissue. This method provides greater convenience and comfort for continuous monitoring, especially during daily activities or sleep. Reflective PPG's ability to capture signals in diverse environments makes it ideal for wearable health devices tracking heart rate and oxygen saturation.
Advantages of Transmissive PPG
Transmissive photoplethysmography (PPG) offers superior signal quality due to direct light transmission through tissue, resulting in higher accuracy for heart rate and oxygen saturation measurements. Its ability to capture deeper vascular signals makes it ideal for clinical applications requiring precise cardiovascular monitoring. You benefit from reduced motion artifacts and enhanced reliability, especially in wearable devices placed on thin body sites like fingers or earlobes.
Common Use Cases in Healthcare and Wearables
Reflective PPG sensors are commonly used in wearable devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers to monitor heart rate and oxygen saturation by detecting blood volume changes from the skin's surface. Transmissive PPG, found primarily in clinical settings, offers higher accuracy by measuring light passed through thinner body parts such as fingertips or earlobes, making it ideal for patient monitoring and medical diagnostics. Your choice between reflective and transmissive PPG depends on the balance between convenience and precision required for specific healthcare applications.
Future Trends and Developments in PPG Technology
Reflective PPG sensors are expected to benefit from advancements in flexible materials and miniaturized optics, enabling more accurate and comfortable wearable devices. Transmissive PPG technology will likely see improvements in penetration depth and signal quality through integration with novel wavelengths and multimodal sensor fusion. Emerging trends point to AI-enhanced signal processing and real-time health analytics, driving personalized and continuous cardiovascular monitoring in both clinical and consumer applications.
Reflective vs Transmissive PPG Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com