Shielded cables reduce electromagnetic interference by surrounding the conductors with a protective layer, making them ideal for environments with high electrical noise, while unshielded cables are more flexible, cost-effective, and suitable for low-interference settings. Understanding the differences between shielded and unshielded cables will help you choose the best option for your specific wiring needs; continue reading to learn more about their applications and benefits.
Table of Comparison
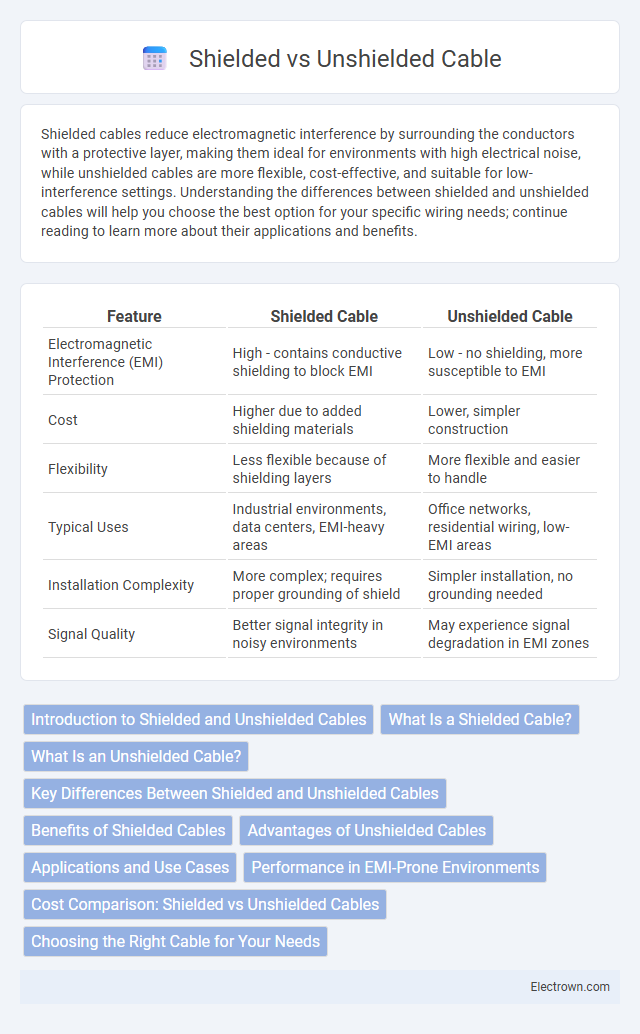
| Feature | Shielded Cable | Unshielded Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Protection | High - contains conductive shielding to block EMI | Low - no shielding, more susceptible to EMI |
| Cost | Higher due to added shielding materials | Lower, simpler construction |
| Flexibility | Less flexible because of shielding layers | More flexible and easier to handle |
| Typical Uses | Industrial environments, data centers, EMI-heavy areas | Office networks, residential wiring, low-EMI areas |
| Installation Complexity | More complex; requires proper grounding of shield | Simpler installation, no grounding needed |
| Signal Quality | Better signal integrity in noisy environments | May experience signal degradation in EMI zones |
Introduction to Shielded and Unshielded Cables
Shielded cables feature a protective layer made of metal foil or braided mesh that minimizes electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk, making them ideal for environments with high electrical noise. Unshielded cables lack this protective layer, relying on twisted pairs of wires to reduce interference, which makes them suitable for low-interference settings and shorter cable runs. Choosing between shielded and unshielded cables depends on factors such as the installation environment, signal integrity requirements, and budget constraints.
What Is a Shielded Cable?
A shielded cable features a protective layer made of metal foil or braided mesh that surrounds the internal conductors, designed to block electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). This shielding enhances signal integrity and reduces noise in environments with high electrical interference, making it ideal for industrial settings and audio-video applications. Shielded cables are commonly used in Ethernet networks, audio equipment, and control systems where maintaining data quality and preventing cross-talk is critical.
What Is an Unshielded Cable?
An unshielded cable consists of twisted pairs of wires without any additional shielding material, making it more flexible and cost-effective for general networking applications. It relies on the twisting of pairs to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk, which is sufficient for most residential and office environments. Unshielded cables are commonly used in Ethernet networks, such as Cat5e and Cat6 UTP cables, where minimal external noise is present.
Key Differences Between Shielded and Unshielded Cables
Shielded cables feature a protective layer of conductive material that reduces electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk, making them ideal for environments with high electrical noise. Unshielded cables lack this protection, offering more flexibility and lower cost but are more susceptible to signal degradation over long distances or in noisy settings. Understanding these differences helps you select the right cable to ensure optimal signal quality and network performance.
Benefits of Shielded Cables
Shielded cables provide superior protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI), ensuring stable and high-quality signal transmission in environments with heavy electronic noise. Their design minimizes signal degradation and crosstalk, making them ideal for industrial settings, data centers, and audio/video applications. Enhanced durability and reduced data errors contribute to longer cable lifespan and improved overall system performance.
Advantages of Unshielded Cables
Unshielded cables offer superior flexibility and are generally easier to install in tight or complex environments, making them ideal for residential and office networking. These cables are cost-effective, providing a budget-friendly solution without sacrificing performance in low-interference areas. By choosing unshielded cables, you benefit from straightforward handling and reliable data transmission where electromagnetic interference is minimal.
Applications and Use Cases
Shielded cables are ideal for environments with high electromagnetic interference (EMI), such as industrial automation, audio equipment, and medical devices, where signal integrity and reduced noise are critical. Unshielded cables are commonly used in residential wiring, office networking, and general-purpose data transmission where EMI levels are low and cost efficiency is important. Your choice depends on the specific environmental conditions and the need for noise reduction to ensure reliable performance and data quality.
Performance in EMI-Prone Environments
Shielded cables provide superior performance in electromagnetic interference (EMI)-prone environments by incorporating a protective layer that blocks external noise, ensuring a stable and clear signal transmission. Unshielded cables lack this protective barrier, making them more susceptible to signal degradation and data loss when exposed to high levels of EMI. Choosing shielded cable for your setup maximizes reliability and minimizes disruptions caused by interference in sensitive electronic applications.
Cost Comparison: Shielded vs Unshielded Cables
Shielded cables generally cost more than unshielded cables due to the additional materials and manufacturing processes required to incorporate the shielding layer. The shielding provides enhanced protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI), making them ideal for environments with high noise, but this added benefit comes with higher upfront expenses. Your choice between shielded and unshielded cables should balance budget constraints with the need for signal integrity in your specific application.
Choosing the Right Cable for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate cable depends on the environmental interference and application requirements, where shielded cables provide superior protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI) in industrial settings. Unshielded cables are suitable for environments with minimal electrical noise, offering flexibility and cost savings in residential or office installations. Prioritizing signal integrity and installation context ensures optimal performance and longevity for network or communication systems.
Shielded vs Unshielded Cable Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com