A thermal fuse interrupts an electrical circuit when it detects excessive heat, providing one-time protection by permanently breaking the circuit, while a circuit breaker can be reset after tripping due to overload or short circuit conditions. Understanding the differences between these safety devices can help you choose the right protection for your electronics; continue reading to explore their functions and applications in detail.
Table of Comparison
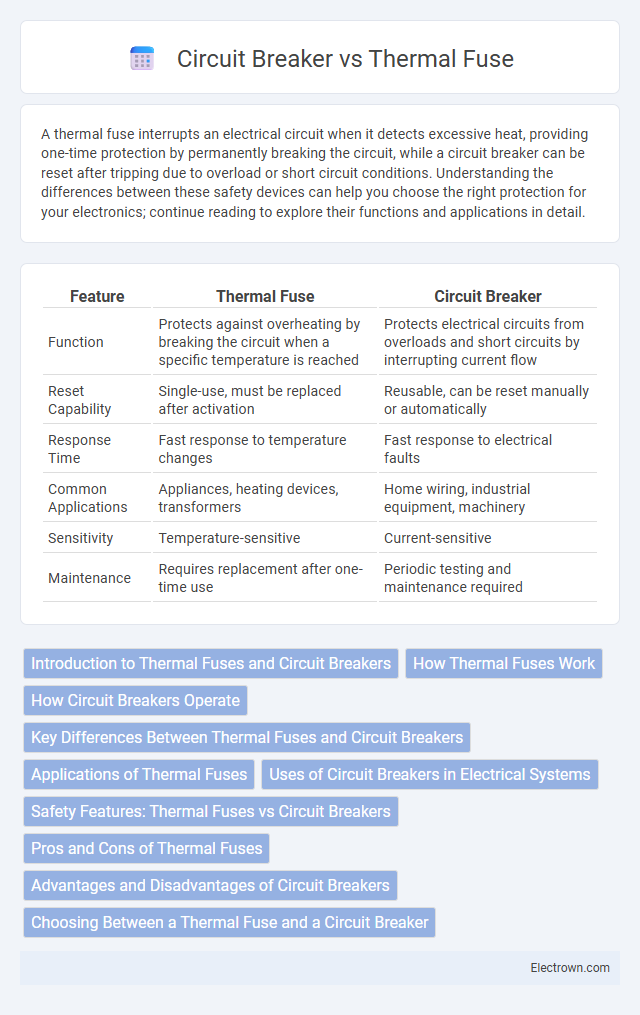
| Feature | Thermal Fuse | Circuit Breaker |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Protects against overheating by breaking the circuit when a specific temperature is reached | Protects electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits by interrupting current flow |
| Reset Capability | Single-use, must be replaced after activation | Reusable, can be reset manually or automatically |
| Response Time | Fast response to temperature changes | Fast response to electrical faults |
| Common Applications | Appliances, heating devices, transformers | Home wiring, industrial equipment, machinery |
| Sensitivity | Temperature-sensitive | Current-sensitive |
| Maintenance | Requires replacement after one-time use | Periodic testing and maintenance required |
Introduction to Thermal Fuses and Circuit Breakers
Thermal fuses and circuit breakers are essential safety devices designed to prevent electrical overloads and overheating in various electrical systems. A thermal fuse is a one-time-use component that interrupts current flow when it detects excessive temperature, providing a permanent disconnection to avoid fire hazards. Circuit breakers function as resettable switches that automatically cut off electrical circuits during overload or short-circuit events, allowing safe restoration of power once the fault is cleared.
How Thermal Fuses Work
Thermal fuses operate by using a temperature-sensitive alloy or element that melts when exposed to excessive heat, interrupting the electrical circuit to prevent overheating and potential fire hazards. Unlike circuit breakers, thermal fuses provide a one-time protection and must be replaced after activation as they do not reset automatically. Their precise temperature rating ensures reliable protection in appliances like dryers and coffee makers by cutting off current flow when specific heat thresholds are exceeded.
How Circuit Breakers Operate
Circuit breakers operate by detecting abnormal electrical currents and swiftly interrupting the flow to prevent damage or fire hazards. They use an electromagnetic coil or a bimetallic strip that trips the switch when the current exceeds safe levels. Understanding how your circuit breaker functions can help you maintain electrical safety and quickly respond to power issues in your home or business.
Key Differences Between Thermal Fuses and Circuit Breakers
Thermal fuses and circuit breakers serve as essential safety devices in electrical systems, but they operate on different mechanisms; thermal fuses rely on temperature-sensitive elements that permanently disconnect the circuit when a preset temperature is exceeded, while circuit breakers use electromagnetic or thermal-magnetic switches to trip and can be reset after fault conditions. Thermal fuses provide single-use overcurrent protection ideal for preventing overheating in appliances, whereas circuit breakers offer reusable and adjustable protection suitable for broader electrical system safety. Understanding these key differences aids in selecting appropriate protection methods for various electrical applications, optimizing both safety and functionality.
Applications of Thermal Fuses
Thermal fuses are widely used in household appliances like coffee makers, hair dryers, and microwaves to protect against overheating by permanently interrupting the circuit when a specific temperature threshold is exceeded. Unlike circuit breakers that can be reset, thermal fuses act as a one-time safety device ensuring critical components do not experience thermal damage. If your safety system relies on precise temperature control rather than overload protection, thermal fuses provide reliable, cost-effective protection for your devices.
Uses of Circuit Breakers in Electrical Systems
Circuit breakers protect electrical systems by automatically interrupting current flow during overloads or short circuits, preventing damage and fire hazards. They are essential in residential, commercial, and industrial installations for safeguarding wiring, appliances, and equipment. Your electrical system relies on circuit breakers for reliable and resettable protection, unlike thermal fuses which offer single-use protection.
Safety Features: Thermal Fuses vs Circuit Breakers
Thermal fuses provide safety by permanently cutting off electrical current when a specific temperature threshold is exceeded, preventing overheating and potential fires. Circuit breakers offer reusable protection by interrupting current flow during overloads or short circuits, allowing you to reset them after resolving the issue. Your choice between these devices depends on whether you need single-use thermal protection or resettable circuit interruption for enhanced electrical safety.
Pros and Cons of Thermal Fuses
Thermal fuses offer the advantage of precise and reliable protection against overheating by permanently breaking the circuit when a specific temperature is exceeded, ensuring safety in appliances like coffee makers and hair dryers. However, their main drawback lies in their single-use nature, requiring replacement after one activation, which can lead to inconvenience and additional maintenance costs. Your choice between thermal fuses and circuit breakers depends on whether you prioritize simple, cost-effective protection with easy replacement or reusable, resettable safety devices.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers offer rapid reset capabilities and better protection against overloads and short circuits compared to thermal fuses, enhancing circuit safety and convenience. They provide reliable fault isolation, reduce downtime, and can be manually switched off during maintenance, but they tend to be more complex and expensive than thermal fuses. However, circuit breakers are bulkier and may require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance in electrical systems.
Choosing Between a Thermal Fuse and a Circuit Breaker
Selecting between a thermal fuse and a circuit breaker depends on the specific application requirements and safety protocols. Thermal fuses provide single-use protection by interrupting current flow at predetermined temperature thresholds, ideal for preventing overheating in appliances. Circuit breakers offer reusable, resettable protection by detecting overcurrent or short circuits, making them suitable for household and industrial electrical systems.
Thermal fuse vs circuit breaker Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com