Low-side switches control the load by connecting the ground side, offering simpler wiring and cost-effectiveness, while high-side switches connect the power side, providing better protection and safety for your circuit. Discover which type best suits your electronic project by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
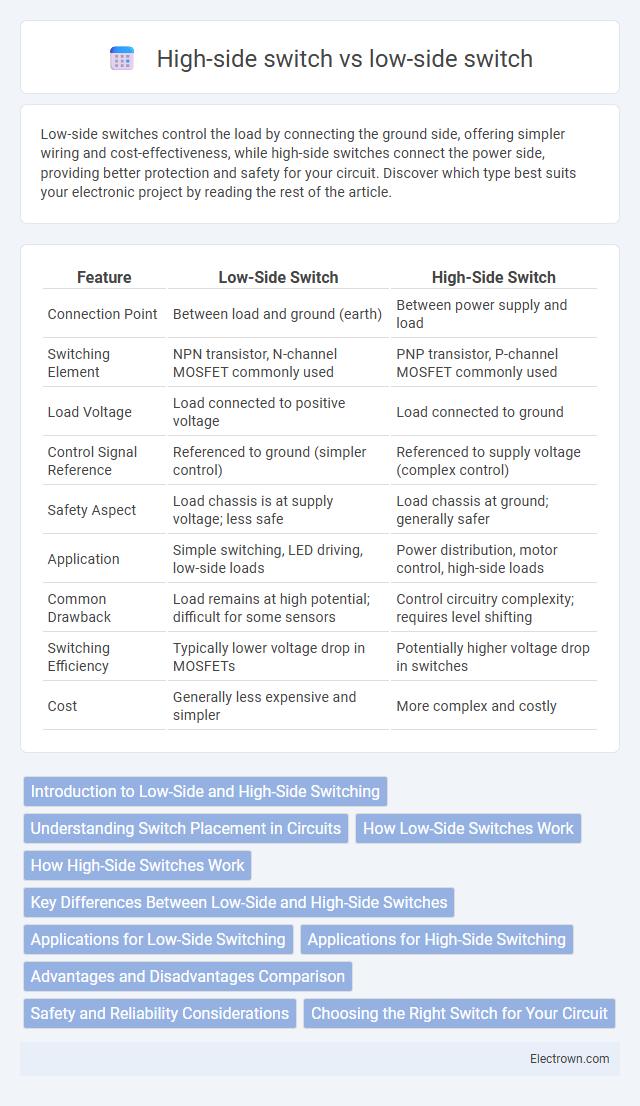
| Feature | Low-Side Switch | High-Side Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Connection Point | Between load and ground (earth) | Between power supply and load |
| Switching Element | NPN transistor, N-channel MOSFET commonly used | PNP transistor, P-channel MOSFET commonly used |
| Load Voltage | Load connected to positive voltage | Load connected to ground |
| Control Signal Reference | Referenced to ground (simpler control) | Referenced to supply voltage (complex control) |
| Safety Aspect | Load chassis is at supply voltage; less safe | Load chassis at ground; generally safer |
| Application | Simple switching, LED driving, low-side loads | Power distribution, motor control, high-side loads |
| Common Drawback | Load remains at high potential; difficult for some sensors | Control circuitry complexity; requires level shifting |
| Switching Efficiency | Typically lower voltage drop in MOSFETs | Potentially higher voltage drop in switches |
| Cost | Generally less expensive and simpler | More complex and costly |
Introduction to Low-Side and High-Side Switching
Low-side switches control the connection to ground, allowing current to flow through the load when activated. High-side switches connect the load to the positive voltage supply, enabling current flow from the power source to the device. Your choice between low-side and high-side switching depends on factors such as load type, safety requirements, and control logic.
Understanding Switch Placement in Circuits
Low-side switches connect the load to ground, allowing control by switching the negative side of the circuit, which simplifies wiring and is commonly used in digital circuits with NPN transistors or N-channel MOSFETs. High-side switches connect the load to the positive supply voltage, requiring PNP transistors or P-channel MOSFETs for controlling current flow on the positive voltage line, offering safer operation in some applications by preventing the load from being energized when off. Selecting switch placement depends on factors like load type, voltage levels, switching speed, and safety considerations to optimize circuit performance and reliability.
How Low-Side Switches Work
Low-side switches control the connection to ground in a circuit, allowing current to flow through the load when the switch is closed. By placing the switch between the load and ground, they simplify control and reduce complexity in switching devices like transistors or MOSFETs. These switches effectively pull the load terminal to zero volts, enabling efficient current flow and easy integration with microcontrollers and digital logic circuits.
How High-Side Switches Work
High-side switches connect the load to the positive supply voltage, allowing control by switching the supply line rather than the ground. They operate by using a P-channel MOSFET or a PNP transistor that, when activated, completes the circuit to the positive voltage, enabling current flow through the load. This configuration provides better protection against ground faults and is ideal for controlling devices in automotive and industrial applications.
Key Differences Between Low-Side and High-Side Switches
Low-side switches connect the load to ground, allowing the control device to switch the negative side, whereas high-side switches connect the load to the positive voltage supply, switching the positive side. Low-side switches are simpler to implement and are commonly used in applications where the control circuit shares a common ground with the load, but they can cause issues with signal referencing. High-side switches provide better load protection and safety by isolating the load from the power supply when off, making them preferable for switching loads in automotive and industrial systems.
Applications for Low-Side Switching
Low-side switches are widely used in applications such as LED control, motor drivers, and relay activation where the load is connected to the positive supply voltage, and the switch connects the load to ground. These switches offer advantages in simplicity and cost-effectiveness for circuits requiring a common positive rail and easier fault detection when grounding issues occur. Low-side switching is ideal for driving resistive loads, low-current devices, and scenarios where controlling the ground path simplifies the overall circuit design.
Applications for High-Side Switching
High-side switches are commonly used in applications where controlling the power supply to a load is critical, such as in automotive systems, industrial automation, and LED lighting control. These switches connect the load to the positive voltage rail, providing safer and more efficient switching by protecting against short circuits and ground faults. Your circuits benefit from improved noise immunity and easier load grounding when using high-side switching configurations.
Advantages and Disadvantages Comparison
Low-side switches offer simple wiring and cost-effectiveness by connecting the load to the positive supply and switching the ground, but they can cause ground reference issues and are less suitable for high-voltage applications. High-side switches provide safer control by switching the positive voltage, preventing ground disturbances and enabling load disconnection from the power source, yet they are more complex and often require specialized driver circuits. Choosing between low-side and high-side switching depends on factors such as voltage level, load type, safety requirements, and circuit complexity.
Safety and Reliability Considerations
Low-side switches, positioned between the load and ground, offer simpler control but can pose safety risks due to potential grounding faults and stray currents. High-side switches, placed between the power supply and load, enhance safety by isolating the load from the power source during off states, reducing the risk of short circuits and electromagnetic interference. Evaluating your circuit's safety requirements and reliability needs is crucial when choosing between low-side and high-side switching configurations.
Choosing the Right Switch for Your Circuit
Low-side switches connect the load to ground, making it easier to control circuits with NPN transistors or N-channel MOSFETs, while high-side switches connect the load to the positive supply, ideal for PNP transistors or P-channel MOSFETs needing to provide full voltage to the load. When choosing the right switch for your circuit, consider factors like load type, supply voltage, and control signal availability to ensure proper operation and safety. Your design will benefit from selecting a switch type that matches the control logic and minimizes voltage drops or thermal stress.
Low-side switch vs high-side switch Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com