Low drop-out (LDO) regulators maintain a stable output voltage with minimal input-to-output voltage difference, resulting in higher efficiency and reduced heat generation compared to ordinary regulators. Discover how choosing the right regulator can enhance your device's performance by continuing to explore the full article.
Table of Comparison
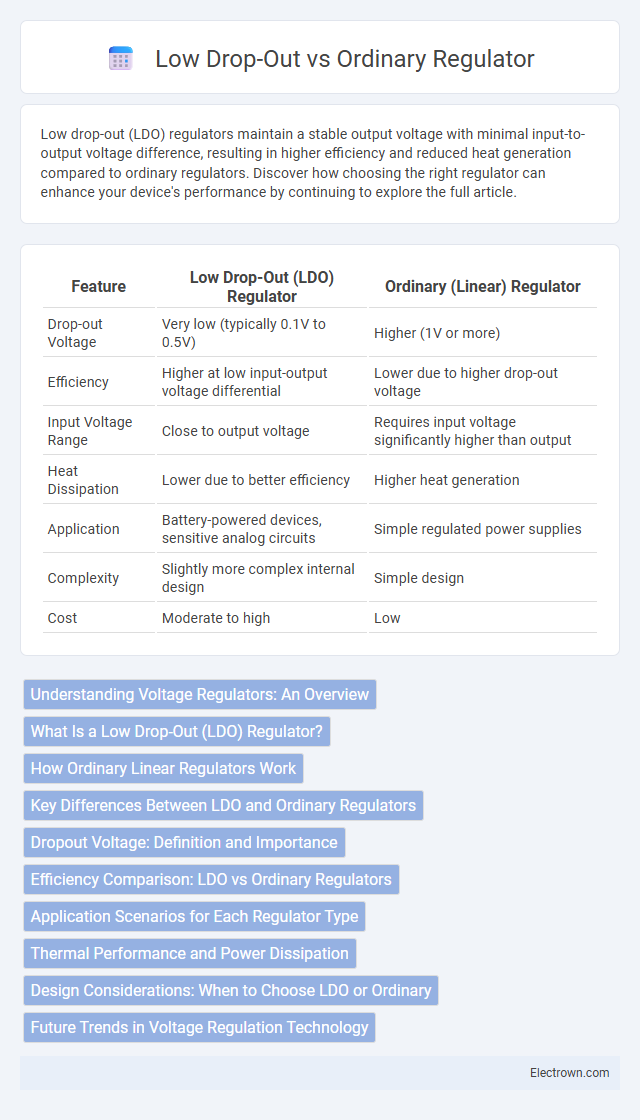
| Feature | Low Drop-Out (LDO) Regulator | Ordinary (Linear) Regulator |
|---|---|---|
| Drop-out Voltage | Very low (typically 0.1V to 0.5V) | Higher (1V or more) |
| Efficiency | Higher at low input-output voltage differential | Lower due to higher drop-out voltage |
| Input Voltage Range | Close to output voltage | Requires input voltage significantly higher than output |
| Heat Dissipation | Lower due to better efficiency | Higher heat generation |
| Application | Battery-powered devices, sensitive analog circuits | Simple regulated power supplies |
| Complexity | Slightly more complex internal design | Simple design |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low |
Understanding Voltage Regulators: An Overview
Low drop-out (LDO) regulators maintain a stable output voltage even when the input voltage is close to the desired output, enhancing efficiency in battery-powered devices. Ordinary voltage regulators typically require a higher input voltage than the output, resulting in greater power dissipation and heat generation. Understanding the differences helps you select the right regulator for your application, optimizing performance and conserving energy.
What Is a Low Drop-Out (LDO) Regulator?
A Low Drop-Out (LDO) regulator is a voltage regulator designed to maintain a steady output voltage with a very small difference between the input and output voltages, known as the dropout voltage. Unlike ordinary regulators that require a larger input-output voltage gap to operate efficiently, LDOs offer improved performance in applications where power efficiency and minimal voltage loss are critical. You can optimize your power management system by selecting an LDO regulator when your circuit demands low noise, compact size, and enhanced regulation at low voltage differentials.
How Ordinary Linear Regulators Work
Ordinary linear regulators function by maintaining a constant output voltage through a variable resistance that dissipates excess input voltage as heat, ensuring a stable power supply despite fluctuations. They rely on a reference voltage and an error amplifier to control the pass transistor's conduction level, adjusting the voltage drop to regulate output. This simplicity results in lower efficiency, especially when the input voltage significantly exceeds the output voltage.
Key Differences Between LDO and Ordinary Regulators
Low Drop-Out (LDO) regulators differ from ordinary linear regulators primarily in their ability to maintain a stable output voltage with a very low input-to-output voltage differential, often less than 0.3 volts, which enhances efficiency in battery-powered devices. Ordinary regulators typically require a higher voltage drop, around 2 volts or more, resulting in increased power dissipation and reduced battery life. LDOs also feature faster transient response and lower noise, making them suitable for sensitive analog and RF applications compared to traditional linear regulators.
Dropout Voltage: Definition and Importance
Dropout voltage is the minimum voltage difference between the input and output required for a regulator to maintain a stable output voltage. Low drop-out (LDO) regulators have significantly lower dropout voltages, often below 0.3 volts, compared to ordinary linear regulators that may require 1-2 volts. This lower dropout voltage is crucial in battery-powered and low-voltage applications to maximize efficiency and extend battery life.
Efficiency Comparison: LDO vs Ordinary Regulators
Low drop-out (LDO) regulators maintain higher efficiency than ordinary linear regulators, especially when the input voltage is close to the output voltage, minimizing power loss. Ordinary regulators typically exhibit lower efficiency due to larger voltage drops, resulting in higher heat dissipation and energy waste. Your choice of an LDO can improve overall system performance by reducing power consumption and thermal management challenges.
Application Scenarios for Each Regulator Type
Low drop-out (LDO) regulators excel in battery-powered and portable devices where maintaining efficiency and minimizing voltage loss are critical, especially in smartphones, wearables, and precision analog circuits. Ordinary regulators find their best application in systems with stable input voltages or where higher dropout voltage is acceptable, such as in powering microcontrollers in desktops or industrial equipment with robust power supplies. Choosing between LDO and ordinary regulators depends on the input-output voltage differential and efficiency requirements in the specific application scenario.
Thermal Performance and Power Dissipation
Low drop-out (LDO) regulators excel in thermal performance due to their ability to maintain low voltage drops, which reduces power dissipation compared to ordinary linear regulators that typically have higher dropout voltages. This efficiency minimizes heat generation, allowing LDOs to operate cooler under similar load conditions, improving reliability and longevity. If your application demands efficient power conversion with reduced thermal stress, choosing an LDO regulator can optimize your system's thermal management.
Design Considerations: When to Choose LDO or Ordinary
Low drop-out (LDO) regulators are ideal when your design requires a voltage regulator to operate efficiently with a very small difference between input and output voltage, ensuring minimal power loss and heat dissipation in battery-powered or portable devices. Ordinary linear regulators work well when the input voltage significantly exceeds the output voltage, allowing for simpler design and typically lower cost without the stringent low voltage dropout constraint. Choosing between an LDO and an ordinary regulator depends on factors such as input-output voltage difference, thermal management needs, efficiency requirements, and the overall application environment.
Future Trends in Voltage Regulation Technology
Low drop-out (LDO) regulators offer higher efficiency and lower voltage differential compared to ordinary linear regulators, making them essential as electronic devices demand more power efficiency and reduced heat dissipation. Future trends in voltage regulation technology emphasize integrating advanced semiconductor materials like GaN and SiC to further reduce power losses and improve thermal performance. You can expect more intelligent, adaptive voltage regulation systems that dynamically adjust output to optimize power consumption in real-time applications such as IoT and wearable devices.
Low drop-out vs ordinary regulator Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com