Step-up transformers increase voltage from the primary to the secondary coil, making them essential for power transmission over long distances, while step-down transformers reduce voltage to safer levels for consumer use and electronic devices. Understanding the differences can help you choose the right transformer for your electrical needs; explore the rest of the article to learn more.
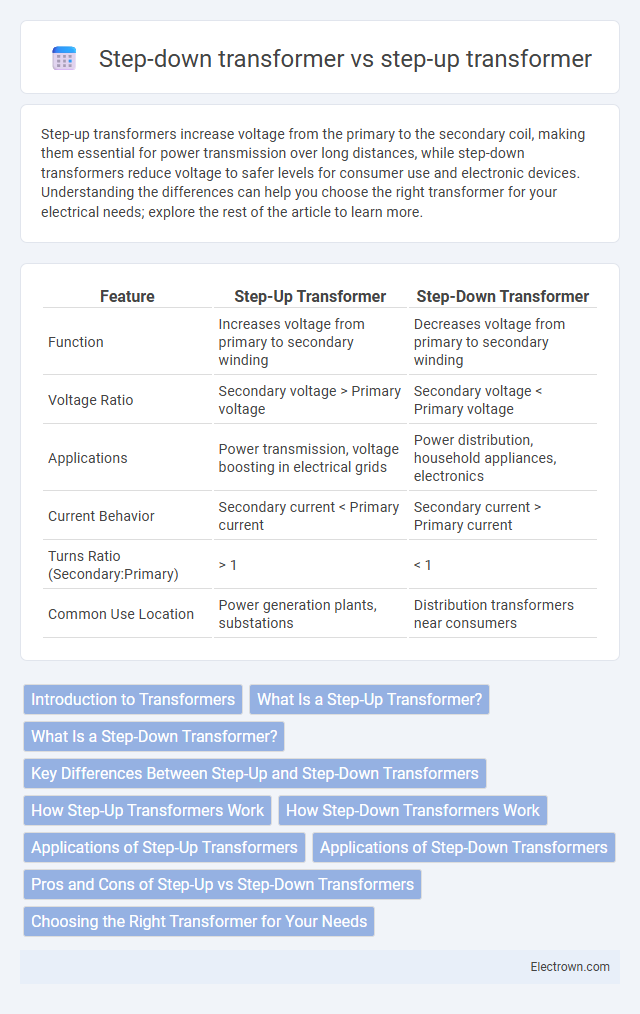
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Step-Up Transformer | Step-Down Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Increases voltage from primary to secondary winding | Decreases voltage from primary to secondary winding |
| Voltage Ratio | Secondary voltage > Primary voltage | Secondary voltage < Primary voltage |
| Applications | Power transmission, voltage boosting in electrical grids | Power distribution, household appliances, electronics |
| Current Behavior | Secondary current < Primary current | Secondary current > Primary current |
| Turns Ratio (Secondary:Primary) | > 1 | < 1 |
| Common Use Location | Power generation plants, substations | Distribution transformers near consumers |
Introduction to Transformers
Transformers are electrical devices used to change voltage levels in power systems, operating on electromagnetic induction principles. Step-up transformers increase voltage from primary to secondary windings, essential for long-distance power transmission to reduce energy loss. Step-down transformers decrease voltage, making electricity safe for residential and commercial use, ensuring compatibility with various electrical appliances.
What Is a Step-Up Transformer?
A step-up transformer increases voltage from a lower primary voltage to a higher secondary voltage, making it essential for efficient power transmission over long distances. Your electrical systems benefit from step-up transformers by reducing current and minimizing energy loss during transmission. These transformers consist of more turns in the secondary coil than in the primary coil, enabling voltage elevation while maintaining power balance.
What Is a Step-Down Transformer?
A step-down transformer reduces voltage from a higher primary voltage to a lower secondary voltage, making it essential for safely powering electronic devices that require lower voltage than supplied by the main electrical grid. It works by having fewer turns in the secondary coil than in the primary coil, which decreases the voltage while increasing the current. Common applications include power adapters, household appliances, and electrical devices needing stable, lower voltage inputs.
Key Differences Between Step-Up and Step-Down Transformers
Step-up transformers increase voltage from primary to secondary coil, while step-down transformers reduce voltage. Step-up transformers are commonly used in power generation to transmit electricity over long distances efficiently, whereas step-down transformers are used in distribution to provide safe, usable voltage levels for homes and businesses. Your choice between the two depends on whether you need to raise or lower voltage for a specific electrical application.
How Step-Up Transformers Work
Step-up transformers increase voltage from the primary to the secondary coil by having more turns in the secondary winding than in the primary. This voltage transformation occurs through electromagnetic induction, where alternating current in the primary coil generates a magnetic field that induces a higher voltage in the secondary coil. You can use step-up transformers in applications requiring voltage boosts, such as power transmission over long distances to reduce energy loss.
How Step-Down Transformers Work
Step-down transformers reduce high voltage from the primary coil to a lower voltage in the secondary coil by having more turns of wire in the primary winding than the secondary winding. This voltage transformation occurs through electromagnetic induction, where alternating current in the primary coil creates a changing magnetic field that induces a lower voltage in the secondary coil. Step-down transformers are essential in electrical grids, allowing safe voltage levels for household appliances and electronic devices.
Applications of Step-Up Transformers
Step-up transformers are essential in power transmission systems, increasing voltage levels from power plants to reduce energy loss over long distances. These transformers are used in industries requiring high voltage equipment, such as electric arc furnaces and large-scale industrial processes. Understanding the role of a step-up transformer helps you optimize energy efficiency in applications where voltage elevation is critical.
Applications of Step-Down Transformers
Step-down transformers are commonly used in electrical power distribution to reduce high transmission voltages to lower, safer levels suitable for residential and commercial use. They are essential in devices like chargers, power adapters, and household appliances, converting voltage from the mains supply to the operating voltage required by electronic equipment. Industrial applications also rely on step-down transformers to safely power machinery and control circuits with reduced voltage inputs.
Pros and Cons of Step-Up vs Step-Down Transformers
Step-up transformers increase voltage while decreasing current, making them ideal for long-distance power transmission with reduced energy loss but require robust insulation and pose higher safety risks. Step-down transformers lower voltage and increase current, ensuring safe and usable power levels for homes and businesses, though they can result in increased transmission losses if used improperly. Your choice depends on whether the priority is efficient voltage transmission or safe, practical voltage levels at the point of use.
Choosing the Right Transformer for Your Needs
Selecting the right transformer depends on whether you need to increase or decrease voltage levels; step-up transformers raise voltage for efficient power transmission, while step-down transformers reduce voltage for safe consumption in homes and businesses. Consider the required input and output voltages, load capacity, and application type to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency. Proper transformer selection enhances electrical system reliability and prevents equipment damage by matching voltage requirements precisely.
Step-up transformer vs step-down transformer Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com