Address decoders translate binary addresses into unique output signals that enable specific memory locations or devices, essential for efficient data routing in digital circuits. Understanding the distinct functions of address decoders and chip selectors can optimize your hardware design; explore the rest of the article to uncover detailed comparisons and applications.
Table of Comparison
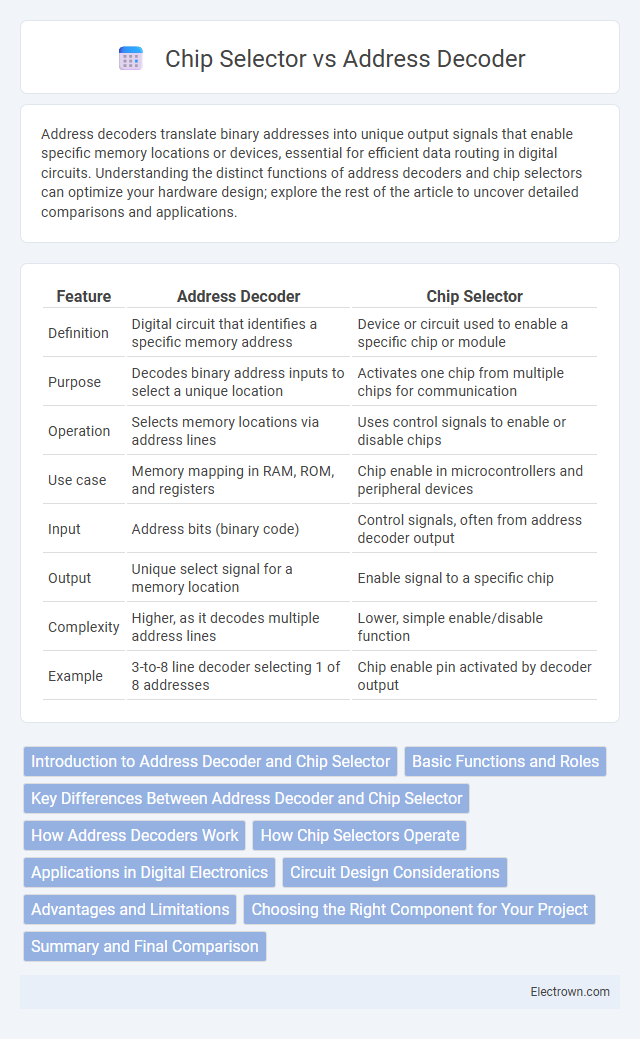
| Feature | Address Decoder | Chip Selector |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital circuit that identifies a specific memory address | Device or circuit used to enable a specific chip or module |
| Purpose | Decodes binary address inputs to select a unique location | Activates one chip from multiple chips for communication |
| Operation | Selects memory locations via address lines | Uses control signals to enable or disable chips |
| Use case | Memory mapping in RAM, ROM, and registers | Chip enable in microcontrollers and peripheral devices |
| Input | Address bits (binary code) | Control signals, often from address decoder output |
| Output | Unique select signal for a memory location | Enable signal to a specific chip |
| Complexity | Higher, as it decodes multiple address lines | Lower, simple enable/disable function |
| Example | 3-to-8 line decoder selecting 1 of 8 addresses | Chip enable pin activated by decoder output |
Introduction to Address Decoder and Chip Selector
An address decoder is a digital circuit that translates binary address inputs into unique output signals, enabling the selection of specific memory locations or peripheral devices within a microprocessor system. A chip selector operates by using these decoded signals to activate the appropriate integrated circuit or memory chip, ensuring only one chip responds at a time during data operations. Both components work together to efficiently manage memory access and peripheral communication in embedded systems and microcontrollers.
Basic Functions and Roles
Address decoders translate binary address inputs into unique output signals that enable specific memory locations or devices, ensuring accurate data access in digital systems. Chip selectors, on the other hand, use the decoded signals to activate particular memory chips or peripherals, allowing communication between the processor and the selected hardware. Both components are crucial for organizing and managing memory access, enhancing system efficiency and preventing data conflicts.
Key Differences Between Address Decoder and Chip Selector
Address decoders translate binary address inputs into a single unique output line, enabling precise selection among multiple memory locations or devices. Chip selectors activate specific integrated circuits based on decoded addresses, controlling chip-level enable signals to manage device accessibility. While address decoders focus on converting addresses into unique signals, chip selectors utilize these signals to enable or disable entire chips within a system.
How Address Decoders Work
Address decoders translate binary address inputs into unique output signals, enabling the selection of a specific memory location or device within a digital system. They function by comparing input address lines against predefined combinations, activating only the output corresponding to the selected address while keeping others inactive. This precise decoding ensures efficient memory access and minimizes conflicts on the data bus in microprocessor-based architectures.
How Chip Selectors Operate
Chip selectors manage the activation of specific integrated circuits by interpreting chip select signals, which serve as enable inputs to control communication. These selectors use logic gates or multiplexers to decode input signals and generate a unique enable signal for each chip, ensuring precise device activation. This operation minimizes bus conflicts and optimizes resource allocation in complex digital systems.
Applications in Digital Electronics
Address decoders are primarily used in memory systems to select specific memory locations based on input addresses, enhancing data retrieval efficiency. Chip selectors function in microcontroller-based projects to enable communication with individual peripheral devices, ensuring accurate control signals and data flow. Both components are essential in digital electronics for managing address spaces and controlling access to integrated circuits in complex digital systems.
Circuit Design Considerations
Address decoders and chip selectors differ in circuit design primarily by their complexity and functionality; address decoders require multi-bit input lines to generate unique output signals for memory addressing, while chip selectors typically handle simpler enable/disable functions for individual chips. Design considerations include the number of address lines, propagation delay, and power consumption, where decoders often demand optimized logic gate arrangements to minimize latency and ensure rapid data access. Selection logic arrangement and signal integrity are critical in both, but chip selectors emphasize robust enable signals to prevent bus conflicts in multi-chip systems.
Advantages and Limitations
Address decoders provide precise memory mapping by selectively enabling one memory location out of many, enhancing efficient data retrieval and reducing hardware complexity. Chip selectors simplify control signals by activating entire integrated circuits, which streamlines system design but may lead to wasted resources when partial memory access is needed. While address decoders ensure fine-grained access and scalability, chip selectors offer straightforward implementation at the cost of reduced flexibility and potential increased power consumption.
Choosing the Right Component for Your Project
Selecting between an address decoder and a chip selector depends on your project's complexity and memory requirements. Address decoders efficiently handle multiple memory locations by converting binary inputs into unique outputs, ideal for expanding memory address space. Chip selectors are perfect for enabling or disabling specific integrated circuits, ensuring your design activates only the necessary chips, streamlining control in simpler or segmented systems.
Summary and Final Comparison
Address decoders and chip selectors both play crucial roles in memory and peripheral device management by enabling specific components based on input addresses. Address decoders translate binary address signals into unique outputs to activate particular memory locations, while chip selectors use control signals to enable or disable entire integrated circuits. Understanding the distinctions in functionality helps you optimize digital circuit design for targeted component activation and efficient data retrieval.
Address Decoder vs Chip Selector Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com