LSB (Least Significant Bit) and MSB (Most Significant Bit) represent the binary digits with the smallest and largest positional values in a binary number, respectively, playing a crucial role in data representation and manipulation. Understanding the differences between LSB and MSB is essential for effectively working with digital systems and encoding schemes, so explore the rest of the article to enhance your knowledge.
Table of Comparison
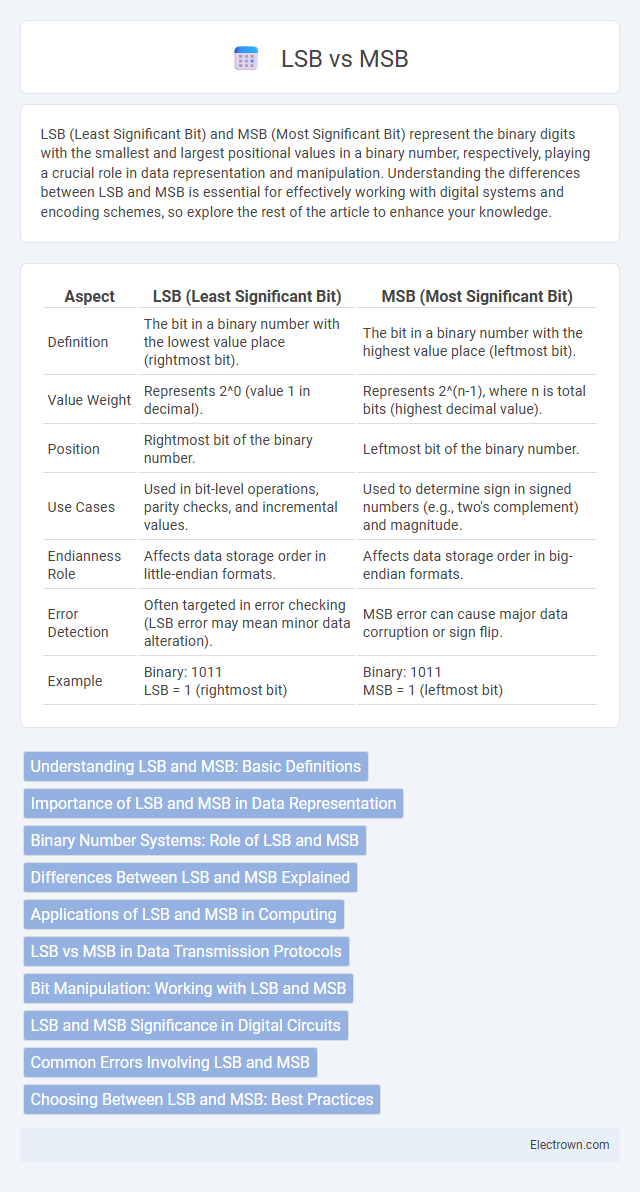
| Aspect | LSB (Least Significant Bit) | MSB (Most Significant Bit) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The bit in a binary number with the lowest value place (rightmost bit). | The bit in a binary number with the highest value place (leftmost bit). |
| Value Weight | Represents 2^0 (value 1 in decimal). | Represents 2^(n-1), where n is total bits (highest decimal value). |
| Position | Rightmost bit of the binary number. | Leftmost bit of the binary number. |
| Use Cases | Used in bit-level operations, parity checks, and incremental values. | Used to determine sign in signed numbers (e.g., two's complement) and magnitude. |
| Endianness Role | Affects data storage order in little-endian formats. | Affects data storage order in big-endian formats. |
| Error Detection | Often targeted in error checking (LSB error may mean minor data alteration). | MSB error can cause major data corruption or sign flip. |
| Example | Binary: 1011 LSB = 1 (rightmost bit) |
Binary: 1011 MSB = 1 (leftmost bit) |
Understanding LSB and MSB: Basic Definitions
LSB (Least Significant Bit) represents the lowest bit value in a binary number, holding the smallest place value, while MSB (Most Significant Bit) is the highest bit with the greatest place value. In digital systems, your data's precision or sign often depends on correctly identifying the MSB and LSB positions. Understanding these basic definitions is crucial for tasks like bitwise operations, data encoding, and error detection.
Importance of LSB and MSB in Data Representation
The Least Significant Bit (LSB) and Most Significant Bit (MSB) play crucial roles in binary data representation by determining the precision and scale of numerical values. The MSB indicates the highest value place in a binary number, essential for sign representation in signed integers, while the LSB affects granularity and is critical for applications such as error detection and digital signal processing. Understanding the significance of both LSB and MSB enhances accurate data encoding, interpretation, and manipulation in computing systems.
Binary Number Systems: Role of LSB and MSB
The Least Significant Bit (LSB) represents the smallest value place in a binary number, determining the parity and increment steps, while the Most Significant Bit (MSB) holds the highest value and often indicates the sign in signed binary representations. In binary number systems, understanding the roles of LSB and MSB is crucial for interpreting numerical data, optimizing bitwise operations, and handling data storage efficiently. Your grasp of LSB and MSB helps in debugging binary computations and designing precise digital circuits.
Differences Between LSB and MSB Explained
LSB (Least Significant Bit) and MSB (Most Significant Bit) differ primarily in their positional value within a binary number, where LSB represents the smallest value (2^0) and MSB the highest value (2^(n-1)) in an n-bit number. LSB is crucial for operations involving bitwise manipulation, error detection, and digital signal processing, while MSB determines the sign and magnitude in signed binary representations and influences numerical range and overflow conditions. Understanding the role of LSB and MSB improves your ability to optimize data encoding, memory allocation, and computational accuracy in digital systems.
Applications of LSB and MSB in Computing
Least Significant Bit (LSB) is crucial in error detection, cryptography, and steganography, where subtle data manipulation or data embedding occurs without significantly altering the original information. Most Significant Bit (MSB) plays a key role in numerical computation and floating-point representations, determining the sign and magnitude in binary encoding, which impacts arithmetic operations and data sorting. Both bits are fundamental in digital communication protocols for ensuring data integrity and proper prioritization of transmitted information.
LSB vs MSB in Data Transmission Protocols
In data transmission protocols, LSB (Least Significant Bit) and MSB (Most Significant Bit) determine the order in which bits are transmitted or interpreted within a byte or word, impacting communication accuracy and compatibility. Protocols like SPI and I2C may specify LSB-first or MSB-first transmission, influencing how devices synchronize and decode data streams. Understanding whether your system requires LSB or MSB alignment ensures reliable data integrity and proper interfacing between transmitting and receiving components.
Bit Manipulation: Working with LSB and MSB
Bit manipulation techniques often target the LSB (Least Significant Bit) and MSB (Most Significant Bit) to efficiently control data at the binary level. The LSB is used for tasks like parity checks and flags due to its position as the rightmost bit, while the MSB, positioned on the left, often indicates sign in signed integers or serves as a key control bit in protocols. Understanding the distinction between LSB and MSB allows you to precisely extract, set, or toggle bits for optimized memory and processor performance in embedded systems or low-level programming.
LSB and MSB Significance in Digital Circuits
LSB (Least Significant Bit) represents the lowest value position in a binary number, influencing fine-grained changes and precise adjustments in digital circuits. MSB (Most Significant Bit) holds the highest value position, determining the overall magnitude and sign in signed number representations like two's complement. Understanding LSB and MSB significance is essential for accurate arithmetic operations, data encoding, and error detection in digital circuit design.
Common Errors Involving LSB and MSB
Common errors involving LSB (Least Significant Bit) and MSB (Most Significant Bit) often arise from incorrect bit order interpretation, leading to data misalignment or corrupted outputs. Confusing LSB with MSB in binary manipulations can cause errors in arithmetic operations and bit-shifting processes, especially in communication protocols and embedded systems. Developers must ensure consistent endianness handling and accurate bit masking to prevent such critical mistakes.
Choosing Between LSB and MSB: Best Practices
Choosing between LSB (Least Significant Bit) and MSB (Most Significant Bit) depends on your application's data processing requirements and communication protocols. Prioritize MSB for applications requiring straightforward binary magnitude interpretation and LSB when dealing with incremental data or low-byte-first transmission formats. Ensuring consistency in your system's bit ordering can prevent data misinterpretation and improve overall data integrity.
LSB vs MSB Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com