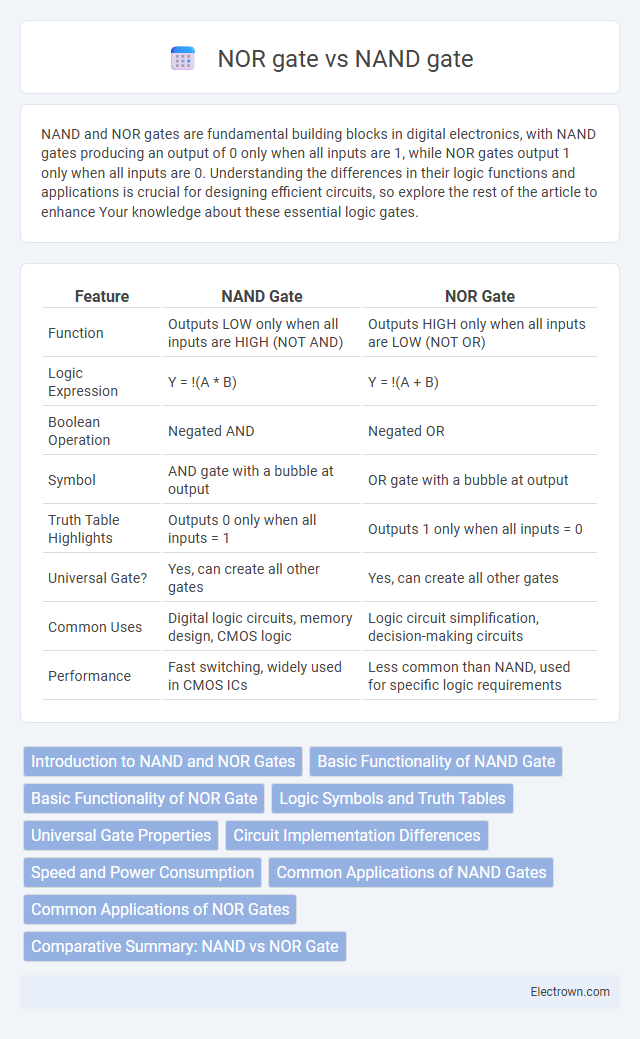
NAND and NOR gates are fundamental building blocks in digital electronics, with NAND gates producing an output of 0 only when all inputs are 1, while NOR gates output 1 only when all inputs are 0. Understanding the differences in their logic functions and applications is crucial for designing efficient circuits, so explore the rest of the article to enhance Your knowledge about these essential logic gates.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | NAND Gate | NOR Gate |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Outputs LOW only when all inputs are HIGH (NOT AND) | Outputs HIGH only when all inputs are LOW (NOT OR) |
| Logic Expression | Y = !(A * B) | Y = !(A + B) |
| Boolean Operation | Negated AND | Negated OR |
| Symbol | AND gate with a bubble at output | OR gate with a bubble at output |
| Truth Table Highlights | Outputs 0 only when all inputs = 1 | Outputs 1 only when all inputs = 0 |
| Universal Gate? | Yes, can create all other gates | Yes, can create all other gates |
| Common Uses | Digital logic circuits, memory design, CMOS logic | Logic circuit simplification, decision-making circuits |
| Performance | Fast switching, widely used in CMOS ICs | Less common than NAND, used for specific logic requirements |
Introduction to NAND and NOR Gates
NAND and NOR gates are fundamental digital logic gates used in electronic circuits, performing basic NAND (NOT AND) and NOR (NOT OR) operations respectively. The NAND gate outputs a low signal only when all inputs are high, while the NOR gate outputs a high signal only when all inputs are low. Understanding the behavior of these gates is crucial for designing complex digital systems and optimizing logic circuits in your electronic projects.
Basic Functionality of NAND Gate
A NAND gate performs a logical operation that outputs false only when all its inputs are true, making it an essential building block in digital circuits. Its functionality combines the AND gate followed by a NOT operation, ensuring the result is inverted. Understanding the basic functionality of a NAND gate is crucial for designing efficient digital systems and optimizing your logic circuits.
Basic Functionality of NOR Gate
A NOR gate outputs a logic HIGH only when all its inputs are LOW, making it a universal gate capable of performing any logical operation. It combines the functions of OR and NOT gates, producing an inverted OR output. Understanding the basic functionality of a NOR gate helps you design efficient digital circuits with simpler logic structures.
Logic Symbols and Truth Tables
The NAND gate symbol is a standard AND gate with a small circle (inversion bubble) at the output, while the NOR gate symbol is an OR gate with an inversion bubble at the output. In the NAND gate truth table, the output is 0 only when all inputs are 1, whereas the NOR gate outputs 1 only when all inputs are 0. Both gates perform universal logic functions but differ in output conditions and symbol representation.
Universal Gate Properties
NAND and NOR gates are both universal gates, meaning they can be used to implement any Boolean function without needing other gate types. NAND gates are often preferred in digital circuits due to their faster switching speed and ease of fabrication in CMOS technology, whereas NOR gates are advantageous in applications requiring active-low logic. Their universality enables flexible circuit design and optimization for performance, power consumption, and complexity in digital electronics.
Circuit Implementation Differences
NAND gate circuits are implemented using transistors arranged to output low only when all inputs are high, enabling faster switching and simpler fabrication in CMOS technology. NOR gate circuits are designed to output high only when all inputs are low, often requiring more complex transistor arrangements that increase propagation delay. Your choice between NAND and NOR gates impacts circuit speed, power consumption, and layout complexity based on these fundamental implementation differences.
Speed and Power Consumption
NAND gates generally exhibit faster switching speeds compared to NOR gates due to their simpler transistor structure, resulting in lower propagation delay. In terms of power consumption, NAND gates are more energy-efficient as they require fewer transistors and have less parasitic capacitance affecting dynamic power usage. Consequently, NAND gates are preferred in high-speed, low-power digital circuit designs over NOR gates.
Common Applications of NAND Gates
NAND gates are widely used in digital electronics for implementing basic logic functions, memory storage elements like flip-flops, and arithmetic circuits such as adders and counters. Their ability to form any other logic gate makes them essential in constructing programmable logic devices and integrated circuits. Understanding how NAND gates function can optimize your design of robust, cost-effective digital systems.
Common Applications of NOR Gates
NOR gates are widely used in digital circuits for implementing logic functions such as OR and NOT simultaneously, enabling efficient circuit designs in multiplexers, demultiplexers, and simple memory storage elements like SR flip-flops. They play a crucial role in creating combinational and sequential logic where minimal gate usage is essential, especially in programmable logic arrays (PLAs) and hardware optimization. Your electronics projects can benefit from NOR gates due to their ability to simplify logic designs and reduce power consumption in integrated circuits.
Comparative Summary: NAND vs NOR Gate
NAND gates output a LOW signal only when all inputs are HIGH, making them fundamental in digital circuits for implementing universal logic functions with faster switching speeds and lower power consumption compared to NOR gates. NOR gates output a HIGH signal only when all inputs are LOW, often used in applications requiring active-low logic and simpler implementation of certain logic expressions. Your choice between NAND vs NOR gates depends on the desired logic function, timing requirements, and circuit design complexity.
NAND gate vs NOR gate Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com