Shadow registers store backup copies of data from primary registers, enabling faster context switching and improved fault tolerance in processors, while mirror registers maintain identical data simultaneously for reliability and error detection in memory systems. Explore the article to understand how these registers impact your system's performance and reliability.
Table of Comparison
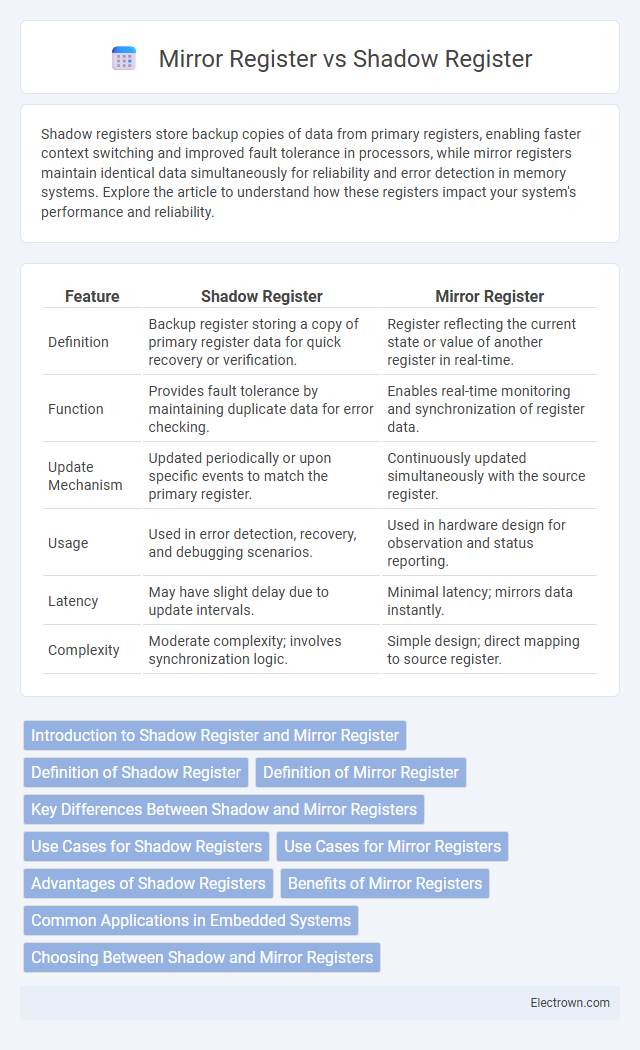
| Feature | Shadow Register | Mirror Register |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Backup register storing a copy of primary register data for quick recovery or verification. | Register reflecting the current state or value of another register in real-time. |
| Function | Provides fault tolerance by maintaining duplicate data for error checking. | Enables real-time monitoring and synchronization of register data. |
| Update Mechanism | Updated periodically or upon specific events to match the primary register. | Continuously updated simultaneously with the source register. |
| Usage | Used in error detection, recovery, and debugging scenarios. | Used in hardware design for observation and status reporting. |
| Latency | May have slight delay due to update intervals. | Minimal latency; mirrors data instantly. |
| Complexity | Moderate complexity; involves synchronization logic. | Simple design; direct mapping to source register. |
Introduction to Shadow Register and Mirror Register
Shadow registers and mirror registers both serve as vital components in digital circuit design for data storage and synchronization. Shadow registers temporarily hold data during clock transitions to prevent glitches, enhancing signal stability in sequential circuits. Mirror registers provide a replica of the primary register's contents, enabling comparison and error detection in your digital system.
Definition of Shadow Register
Shadow registers are specialized storage units that duplicate the contents of primary registers, enabling faster access to critical data during processing tasks. Mirror registers, in contrast, serve as exact replicas of registers used primarily for redundancy and fault tolerance in computer systems. Your understanding of shadow registers enhances optimization of memory management and data retrieval in embedded systems and microcontrollers.
Definition of Mirror Register
Mirror registers are specialized hardware registers used to maintain a synchronized copy of another register's data, ensuring data consistency and fault tolerance within microprocessor systems. They enhance reliability by providing a backup of critical register contents, enabling quick recovery in case of errors or system malfunctions. This concept contrasts with shadow registers, which serve as temporary storage for saving and restoring data during context switches or interrupt handling.
Key Differences Between Shadow and Mirror Registers
Shadow registers store a copy of a hardware register's content to facilitate read-modify-write operations without affecting the original register during processing. Mirror registers, on the other hand, provide a continuous synchronized backup of the original register to detect and correct errors in real time. Key differences include shadow registers being primarily used for temporary buffering in sequential logic, while mirror registers serve error detection and fault tolerance purposes through constant mirroring.
Use Cases for Shadow Registers
Shadow registers are primarily used in embedded systems for fault tolerance and error detection, ensuring critical data is preserved during power failures or system resets. These registers store a duplicate copy of essential system states, allowing quick recovery and minimizing downtime in real-time applications such as automotive control units and industrial automation. Mirror registers, by contrast, are mainly employed for debugging and monitoring, providing a real-time reflection of register contents without impacting system performance.
Use Cases for Mirror Registers
Mirror registers provide reliable data backup and synchronization in digital systems, making them ideal for error detection and fault tolerance applications. You can use mirror registers to maintain an exact copy of critical data during real-time processing, enhancing system stability and enabling quick recovery from hardware faults. Their use is essential in safety-critical environments such as aerospace, automotive control systems, and industrial automation where data integrity is paramount.
Advantages of Shadow Registers
Shadow registers enhance system performance by providing faster read access compared to mirror registers, which require synchronization with the actual register. They improve data integrity during critical operations by storing temporary values separately, reducing the risk of corrupting the main register contents. Shadow registers also enable efficient debugging and error tracking by preserving previous states without affecting the active registers.
Benefits of Mirror Registers
Mirror registers provide enhanced data redundancy by creating real-time copies of the original data, ensuring high reliability and fault tolerance in systems. Their ability to maintain synchronized data minimizes the risk of information loss during system failures, making them ideal for critical applications requiring continuous uptime. You benefit from faster recovery times and improved data integrity when using mirror registers over shadow registers.
Common Applications in Embedded Systems
Shadow registers and mirror registers are essential in embedded systems for enhancing data integrity and real-time processing efficiency. Shadow registers frequently store critical configuration parameters to prevent data loss during power fluctuations, while mirror registers are used for synchronizing data between different clock domains to ensure consistent sensor readings or communication signals. Their integration is common in microcontroller-based applications like automotive control units, industrial automation, and real-time monitoring systems, where reliability and fast access to accurate data are crucial.
Choosing Between Shadow and Mirror Registers
Choosing between shadow and mirror registers depends on the specific application needs for data integrity and synchronization. Shadow registers are ideal for temporarily holding data during processing to prevent inadvertent overwrites, while mirror registers provide real-time duplication to ensure consistent data states across multiple system components. Understanding system timing and fault tolerance requirements guides the optimal selection for accurate and reliable data management.
Shadow Register vs Mirror Register Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com