Multi-layer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) provide higher capacitance and better voltage stability by stacking multiple ceramic dielectric layers, whereas single-layer ceramic capacitors offer lower capacitance and are typically used for high-frequency applications. Discover how understanding the differences between these capacitors can optimize Your electronic designs in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
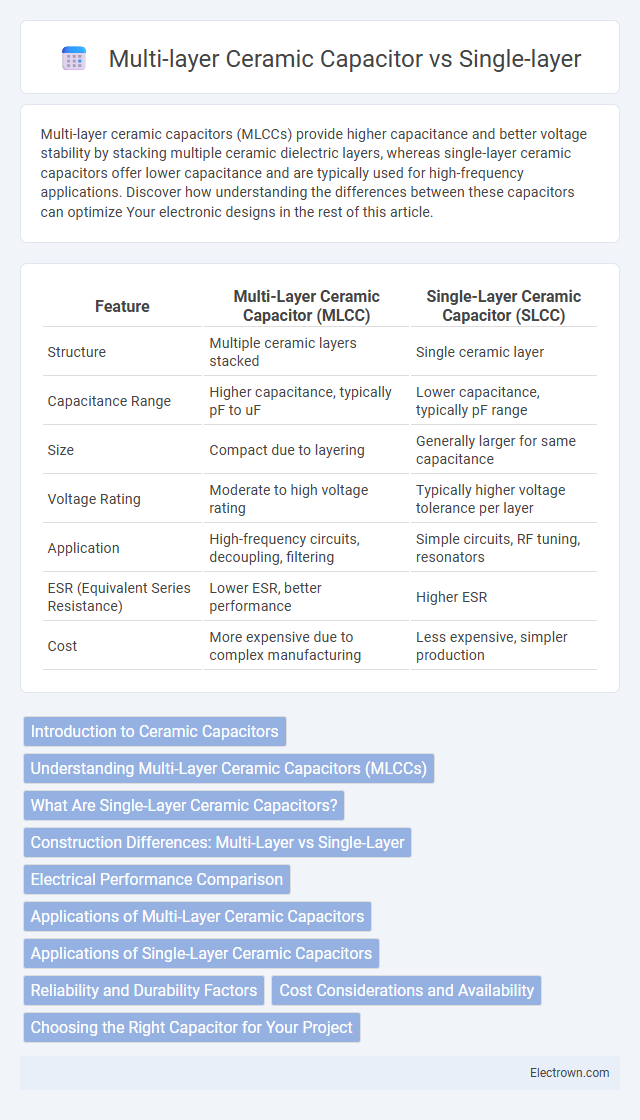
| Feature | Multi-Layer Ceramic Capacitor (MLCC) | Single-Layer Ceramic Capacitor (SLCC) |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Multiple ceramic layers stacked | Single ceramic layer |
| Capacitance Range | Higher capacitance, typically pF to uF | Lower capacitance, typically pF range |
| Size | Compact due to layering | Generally larger for same capacitance |
| Voltage Rating | Moderate to high voltage rating | Typically higher voltage tolerance per layer |
| Application | High-frequency circuits, decoupling, filtering | Simple circuits, RF tuning, resonators |
| ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance) | Lower ESR, better performance | Higher ESR |
| Cost | More expensive due to complex manufacturing | Less expensive, simpler production |
Introduction to Ceramic Capacitors
Multi-layer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) consist of multiple ceramic and metal layers stacked to achieve higher capacitance in a compact form, whereas single-layer ceramic capacitors have just one ceramic dielectric layer. The multi-layer design enhances capacitance density and reliability, making MLCCs ideal for modern electronic circuits requiring small size and high performance. When selecting capacitors for your project, understanding the structural differences helps optimize circuit functionality and stability.
Understanding Multi-Layer Ceramic Capacitors (MLCCs)
Multi-Layer Ceramic Capacitors (MLCCs) consist of multiple alternating layers of ceramic dielectric and metal electrodes, providing higher capacitance in a compact size compared to single-layer ceramic capacitors. MLCCs offer superior reliability, better temperature stability, and enhanced voltage ratings, making them essential in modern electronic circuits. Your choice of MLCCs can significantly improve circuit performance due to their lower Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) and enhanced energy storage capabilities.
What Are Single-Layer Ceramic Capacitors?
Single-layer ceramic capacitors (SLCCs) consist of a single dielectric ceramic layer sandwiched between two metal electrodes, offering simplicity and compact size. They provide lower capacitance values compared to multi-layer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) due to the single dielectric layer but excel in high-frequency applications by minimizing parasitic inductance. SLCCs are ideal for circuits requiring precise capacitance with reduced mechanical stress and are commonly used in filtering and tuning applications.
Construction Differences: Multi-Layer vs Single-Layer
Multi-layer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) consist of multiple alternating layers of ceramic dielectric and metal electrodes stacked together, enabling higher capacitance in a compact form. Single-layer ceramic capacitors feature a single ceramic dielectric layer with metal electrodes on either side, resulting in lower capacitance and larger physical sizes for comparable values. The multi-layer construction enhances volumetric efficiency and electrical performance by increasing the effective surface area within a small footprint.
Electrical Performance Comparison
Multi-layer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) offer superior electrical performance compared to single-layer ceramic capacitors due to their higher capacitance values and lower equivalent series resistance (ESR), which enhances signal stability and reduces power loss. MLCCs provide improved insulation resistance and better high-frequency characteristics, making them ideal for demanding electronic applications requiring precise filtering and decoupling. Your circuit benefits from the greater reliability and efficiency of MLCCs, especially in environments with high-frequency signals and rapid transient response needs.
Applications of Multi-Layer Ceramic Capacitors
Multi-layer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) are widely used in high-frequency and high-reliability applications such as smartphones, automotive electronics, and industrial machinery due to their superior capacitance density and stability compared to single-layer ceramic capacitors. Their multi-layer structure allows for smaller package sizes while providing higher capacitance values, making them ideal for decoupling, filtering, and energy storage in compact electronic circuits. MLCCs are preferred in applications requiring enhanced electrical performance and durability under varying temperature and voltage conditions.
Applications of Single-Layer Ceramic Capacitors
Single-layer ceramic capacitors excel in applications requiring high-frequency performance and precise capacitance values, such as in RF circuits, impedance matching, and filtering applications. Their simple structure offers low equivalent series resistance (ESR) and inductance, making them ideal for signal coupling and decoupling in communication devices and precision instruments. Industries like aerospace, telecommunications, and consumer electronics frequently utilize single-layer capacitors for their stability and reliability in critical signal processing tasks.
Reliability and Durability Factors
Multi-layer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) exhibit superior reliability and durability compared to single-layer ceramic capacitors due to their multiple dielectric layers that distribute voltage stress and reduce the risk of dielectric breakdown. MLCCs also maintain stable capacitance over a wide temperature range and endure higher mechanical and thermal cycling, making them ideal for high-reliability applications such as automotive and aerospace electronics. Conversely, single-layer capacitors are more prone to cracking and performance degradation under repeated stress, limiting their use in demanding environments.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Multi-layer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) generally offer lower cost per capacitance value due to their compact design and mass production, while single-layer ceramic capacitors tend to be more expensive for equivalent ratings because of less efficient manufacturing processes. MLCCs are widely available in a variety of capacitance values and voltage ratings, making them more accessible for diverse applications compared to single-layer capacitors, which are typically limited in range and supply. Supply chain constraints can impact both types, but MLCCs benefit from established production lines and economies of scale, ensuring better overall availability in the market.
Choosing the Right Capacitor for Your Project
Selecting the right capacitor involves evaluating multi-layer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) versus single-layer ceramic capacitors based on capacitance value, voltage rating, and stability requirements. MLCCs offer higher capacitance and better reliability due to their stacked dielectric layers, making them ideal for high-frequency applications and compact circuit designs. Single-layer capacitors, with simpler construction, provide cost-effective solutions for low-frequency or less demanding circuits where space and performance constraints are minimal.
multi-layer ceramic capacitor vs single-layer Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com