Aluminum electrolytic capacitors offer high capacitance and cost-effectiveness but suffer from limited lifespan and higher Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR), while solid polymer capacitors provide enhanced reliability, lower ESR, and better temperature stability for demanding applications. Discover how choosing the right capacitor can optimize Your electronic designs by reading the rest of this article.
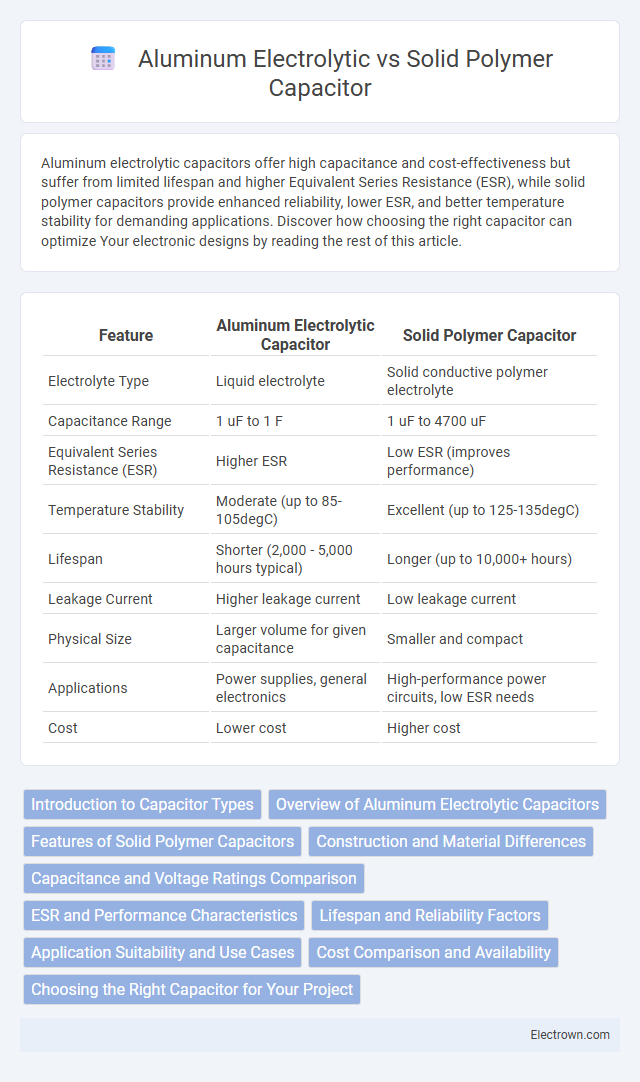
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitor | Solid Polymer Capacitor |
|---|---|---|
| Electrolyte Type | Liquid electrolyte | Solid conductive polymer electrolyte |
| Capacitance Range | 1 uF to 1 F | 1 uF to 4700 uF |
| Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) | Higher ESR | Low ESR (improves performance) |
| Temperature Stability | Moderate (up to 85-105degC) | Excellent (up to 125-135degC) |
| Lifespan | Shorter (2,000 - 5,000 hours typical) | Longer (up to 10,000+ hours) |
| Leakage Current | Higher leakage current | Low leakage current |
| Physical Size | Larger volume for given capacitance | Smaller and compact |
| Applications | Power supplies, general electronics | High-performance power circuits, low ESR needs |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Capacitor Types
Aluminum electrolytic capacitors offer high capacitance values and cost efficiency, making them ideal for power supply filtering and bulk energy storage applications. Solid polymer capacitors provide lower equivalent series resistance (ESR), better temperature stability, and longer lifespan, enhancing performance in high-frequency and precision circuits. Choosing the right capacitor type depends on your circuit requirements for durability, size, and electrical characteristics.
Overview of Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors
Aluminum electrolytic capacitors consist of an aluminum foil anode, a liquid electrolyte, and a paper separator, offering high capacitance values and cost-effective performance in power supply smoothing and filtering applications. These capacitors typically provide capacitance ranges from 1 uF to several thousand microfarads with voltage ratings up to 450V or higher. You benefit from their excellent energy storage capacity and relatively low equivalent series resistance (ESR) compared to solid polymer capacitors, but they exhibit shorter lifespans and higher leakage currents due to the liquid electrolyte.
Features of Solid Polymer Capacitors
Solid polymer capacitors use conductive polymers as electrolytes, offering lower Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) compared to aluminum electrolytic capacitors, resulting in better performance at high frequencies. They provide improved stability and longer lifespan, especially under thermal stress and high ripple currents, making them ideal for demanding electronic applications. Your devices benefit from enhanced reliability and reduced risk of leakage or failure when using solid polymer capacitors.
Construction and Material Differences
Aluminum electrolytic capacitors feature an aluminum foil anode, a liquid electrolyte, and a paper separator, enabling high capacitance but with higher ESR and limited lifespan. Solid polymer capacitors use conductive polymer as the electrolyte, offering lower ESR, improved stability, and longer durability due to their solid-state construction. Your choice depends on application requirements regarding capacitance, reliability, and performance under varying temperatures.
Capacitance and Voltage Ratings Comparison
Aluminum electrolytic capacitors typically offer higher capacitance values ranging from 1 uF to several thousand microfarads, making them suitable for applications requiring bulk energy storage. Solid polymer capacitors, while generally available in lower capacitance ranges (0.1 uF to a few hundred microfarads), provide superior voltage ratings with stable performance up to 35V or higher. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize higher capacitance for filtering or robust voltage stability for high-performance electronics.
ESR and Performance Characteristics
Aluminum electrolytic capacitors typically exhibit higher Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR), resulting in increased heat generation and limited high-frequency performance compared to solid polymer capacitors. Solid polymer capacitors, with their low ESR and stable capacitance, provide superior performance in applications requiring high ripple current handling and extended lifespan. The enhanced electrical conductivity of solid polymer electrolytes ensures better efficiency and reliability in power supply filtering and decoupling circuits.
Lifespan and Reliability Factors
Aluminum electrolytic capacitors typically have a shorter lifespan, ranging from 1,000 to 10,000 hours at 85degC, due to electrolyte evaporation and drying, which affects reliability over time. Solid polymer capacitors offer enhanced lifespan and stability, often exceeding 10,000 to 20,000 hours at higher temperatures, thanks to their non-liquid conductive polymer electrolyte that resists leakage and degradation. Reliability factors for aluminum electrolytic capacitors include temperature sensitivity and voltage derating, while solid polymer capacitors provide better performance under thermal stress and reduced equivalent series resistance (ESR), improving overall circuit robustness.
Application Suitability and Use Cases
Aluminum electrolytic capacitors are ideal for high-capacitance, low-frequency applications such as power supplies and audio equipment due to their cost-effectiveness and large capacitance range. Solid polymer capacitors excel in high-frequency circuits and automotive electronics where low ESR, long life, and thermal stability are critical. Your choice between these capacitors should consider the specific performance demands of your application environment to ensure reliability and efficiency.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Aluminum electrolytic capacitors are generally more cost-effective and widely available due to their simpler manufacturing process and extensive use in various electronics. Solid polymer capacitors tend to be more expensive as they offer improved performance, such as lower equivalent series resistance (ESR) and higher reliability, making them ideal for high-end or specialized applications. The market availability of aluminum electrolytic capacitors is broader, while solid polymer capacitors are predominantly found in premium devices and niche industrial sectors.
Choosing the Right Capacitor for Your Project
Selecting the right capacitor involves analyzing key performance factors such as equivalent series resistance (ESR), lifespan, and operating temperature. Aluminum electrolytic capacitors offer high capacitance and cost-effectiveness for power supply filtering, but solid polymer capacitors provide lower ESR, enhanced stability, and longer life, making them ideal for high-frequency and precision applications. Evaluate project-specific requirements like ripple current tolerance and durability to determine the optimal capacitor type.
Aluminum electrolytic vs Solid polymer capacitor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com