CVD diamond offers exceptional purity and optical clarity ideal for high-precision applications, while PCD diamond combines synthetic diamond with a carbide binder for superior wear resistance in cutting and machining tools. Explore the differences in performance, cost, and applications to determine which diamond type best suits your needs in the full article.
Table of Comparison
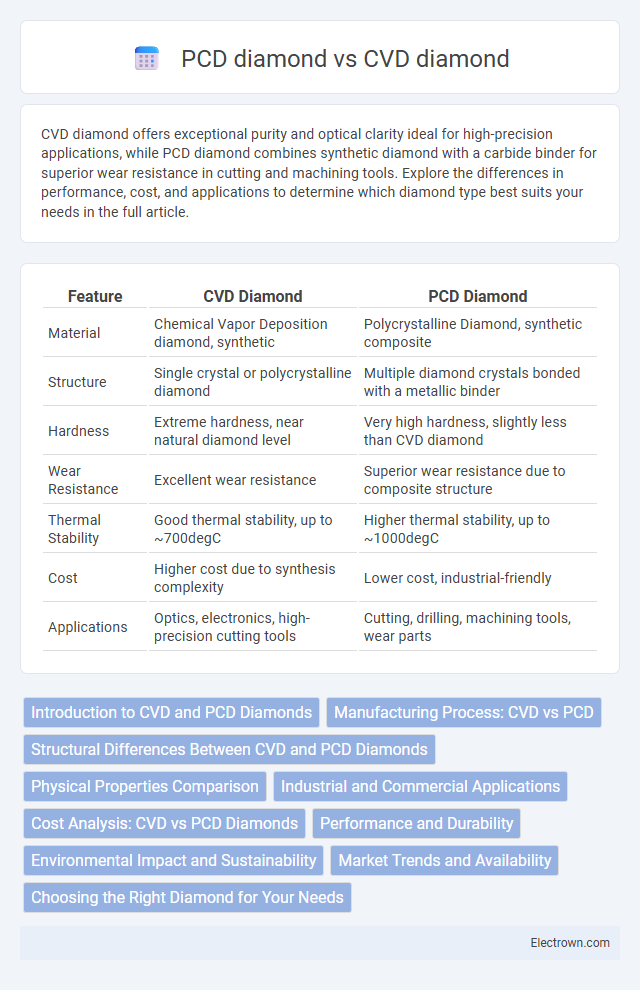
| Feature | CVD Diamond | PCD Diamond |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Chemical Vapor Deposition diamond, synthetic | Polycrystalline Diamond, synthetic composite |
| Structure | Single crystal or polycrystalline diamond | Multiple diamond crystals bonded with a metallic binder |
| Hardness | Extreme hardness, near natural diamond level | Very high hardness, slightly less than CVD diamond |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent wear resistance | Superior wear resistance due to composite structure |
| Thermal Stability | Good thermal stability, up to ~700degC | Higher thermal stability, up to ~1000degC |
| Cost | Higher cost due to synthesis complexity | Lower cost, industrial-friendly |
| Applications | Optics, electronics, high-precision cutting tools | Cutting, drilling, machining tools, wear parts |
Introduction to CVD and PCD Diamonds
CVD diamonds are produced using Chemical Vapor Deposition, a process that grows diamond layers atom by atom on a substrate, resulting in high-purity synthetic diamonds with excellent optical and thermal properties. PCD diamonds, or Polycrystalline Diamond, consist of sintered diamond particles bonded under high pressure and temperature, offering exceptional hardness and wear resistance for cutting tools and industrial applications. Both CVD and PCD diamonds exhibit unique structural characteristics that influence their performance in electronics, cutting, and abrasive technologies.
Manufacturing Process: CVD vs PCD
CVD diamonds are synthesized through a chemical vapor deposition process, where a carbon-containing gas is activated to crystallize diamond layers atom by atom on a substrate. PCD diamonds, or polycrystalline diamond, are created by sintering diamond particles under high pressure and temperature conditions, often using a metal catalyst to bond grains together. The CVD method allows precise control over purity and thickness, while PCD offers enhanced toughness due to its composite grain structure.
Structural Differences Between CVD and PCD Diamonds
CVD diamonds are synthetically grown through chemical vapor deposition, resulting in a single-crystal structure with uniform atomic arrangement, whereas PCD diamonds consist of polycrystalline layers bonded together, creating a composite material with grain boundaries. The uniform lattice of CVD diamonds offers higher purity and fewer defects, enhancing optical clarity and fracture resistance compared to the multi-grain structure of PCD. Your choice between these diamonds depends on the required performance, as CVD excels in precision applications while PCD provides exceptional abrasion resistance.
Physical Properties Comparison
CVD diamonds exhibit superior thermal conductivity and greater purity with fewer inclusions compared to PCD diamonds, enhancing their performance in high-precision cutting applications. PCD diamonds, however, possess higher toughness and wear resistance due to their polycrystalline structure, making them ideal for abrasive conditions. Your choice between CVD and PCD diamonds should consider the balance between thermal management and mechanical durability based on specific industrial requirements.
Industrial and Commercial Applications
CVD diamond offers exceptional purity and uniformity, making it ideal for high-precision optical components, electronics, and cutting tools requiring sharp edges and thermal stability. PCD diamond excels in industrial applications like drilling, machining, and grinding due to its superior hardness, wear resistance, and ability to cut abrasive materials such as metals and composites. Both materials serve critical roles in manufacturing, with CVD diamonds preferred for electronics and optics, while PCD diamonds dominate heavy-duty cutting and abrasive environments.
Cost Analysis: CVD vs PCD Diamonds
CVD diamonds typically cost less than PCD diamonds due to their synthetic origin and more controlled production process, resulting in lower manufacturing expenses. PCD diamonds, made with polycrystalline diamond layers, are more expensive because of their enhanced toughness and wear resistance suited for industrial cutting tools. Cost analysis reveals that while CVD diamonds offer affordability for jewelry and electronic applications, PCD diamonds command higher prices justified by superior performance in demanding industrial environments.
Performance and Durability
CVD diamonds exhibit exceptional hardness and thermal stability, making them ideal for precision cutting and high-performance industrial applications, while PCD diamonds offer superior wear resistance due to their polycrystalline structure, enhancing durability in abrasive environments. Performance-wise, CVD diamonds provide higher purity and consistent quality, enabling sharper cutting edges and extended tool life. Durability in PCD diamonds is boosted by the random orientation of grains, which prevents crack propagation and ensures longer service life under extreme mechanical stress.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
CVD diamond production typically has a lower environmental impact than PCD diamond manufacturing because it uses less energy-intensive processes and avoids extensive mining operations. PCD diamonds, synthesized by combining natural diamond grit with a binder under high pressure and temperature, involve more resource-heavy techniques that contribute to higher carbon emissions and waste. Sustainable practices in CVD technology are enhancing its appeal by reducing raw material consumption and enabling recycling, making CVD diamonds more eco-friendly compared to conventional PCD options.
Market Trends and Availability
CVD diamond technology is rapidly gaining traction in industrial markets due to its customizable properties and lower production costs compared to PCD diamonds, which remain highly sought after for extreme wear resistance in cutting tools and machining components. The global demand for PCD diamonds is steady, driven primarily by automotive and aerospace industries, while CVD diamonds see expanding applications in electronics and optics, reflecting broader versatility. Availability of CVD diamonds is improving with advancements in deposition techniques, offering more uniform quality and larger sizes, whereas PCD diamonds rely heavily on natural diamond substrates, limiting scalability and increasing prices.
Choosing the Right Diamond for Your Needs
CVD diamond offers exceptional purity and optical quality, making it ideal for precision optics and high-tech applications, while PCD diamond excels in hardness and thermal conductivity, perfect for cutting and grinding tools. Your choice depends on whether optical performance or mechanical strength is more critical for your specific use. Selecting the right diamond ensures optimal performance and durability tailored to your project's requirements.
CVD diamond vs PCD diamond Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com