Polyimide offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to PET, making it ideal for high-performance electronic and aerospace applications. Explore the rest of the article to understand which material best suits Your specific needs.
Table of Comparison
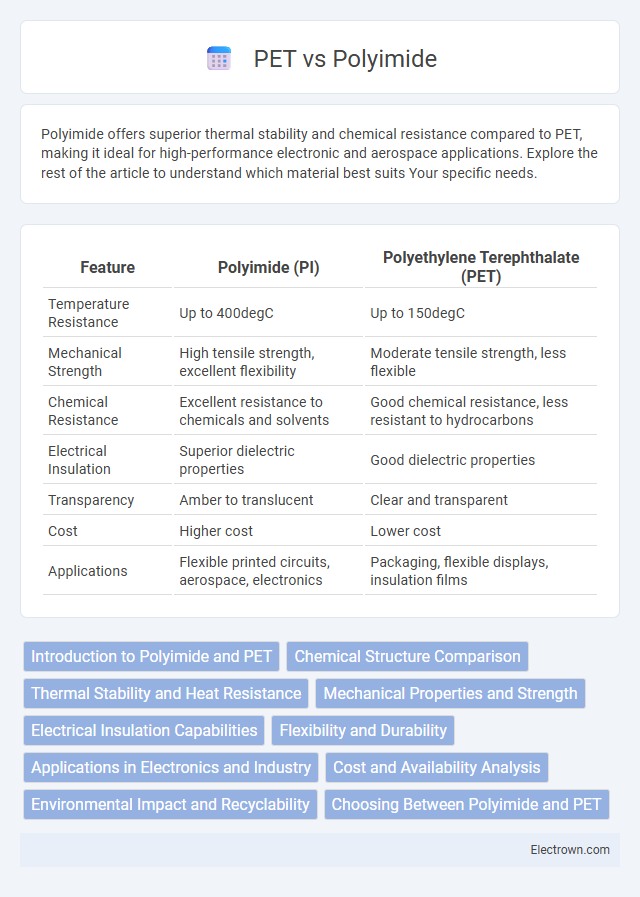
| Feature | Polyimide (PI) | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 400degC | Up to 150degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength, excellent flexibility | Moderate tensile strength, less flexible |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to chemicals and solvents | Good chemical resistance, less resistant to hydrocarbons |
| Electrical Insulation | Superior dielectric properties | Good dielectric properties |
| Transparency | Amber to translucent | Clear and transparent |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Applications | Flexible printed circuits, aerospace, electronics | Packaging, flexible displays, insulation films |
Introduction to Polyimide and PET
Polyimide is a high-performance polymer known for its exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for aerospace and electronics applications. PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) is a widely used thermoplastic polyester valued for its clarity, durability, and recyclability, commonly found in packaging and textile industries. Understanding the distinct properties of polyimide and PET helps you choose the right material for your project's thermal endurance and flexibility requirements.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Polyimide features aromatic rings connected by imide linkages, creating a rigid and thermally stable polymer chain, whereas PET consists of repeating units formed by terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol with ester linkages. The imide groups in polyimide contribute to its superior chemical resistance and high-temperature performance compared to the ester linkages in PET, which are more prone to hydrolysis. This fundamental chemical structure difference results in polyimide's exceptional durability in harsh environments, while PET offers enhanced flexibility and clarity for packaging applications.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Polyimide exhibits superior thermal stability and heat resistance compared to PET, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 400degC, whereas PET typically withstands up to 150degC. This makes polyimide ideal for applications requiring long-term exposure to extreme heat, such as aerospace and electronics. Your choice of material should align with the thermal demands of your specific project to ensure optimal performance.
Mechanical Properties and Strength
Polyimide exhibits superior mechanical properties and strength compared to PET, offering exceptional tensile strength, flexibility, and high-temperature resistance. This makes polyimide ideal for demanding applications requiring durability under stress, such as flexible electronics and aerospace components. Your choice between these materials should consider polyimide's enhanced toughness and thermal stability versus PET's cost-effectiveness and ease of processing.
Electrical Insulation Capabilities
Polyimide offers superior electrical insulation capabilities compared to PET, featuring high dielectric strength and stability under extreme temperatures and harsh chemical environments. PET provides good insulation but tends to degrade faster when exposed to high heat or prolonged electrical stress. You should choose polyimide for applications requiring reliable, long-term electrical insulation in demanding conditions.
Flexibility and Durability
Polyimide films exhibit superior flexibility and durability compared to PET, making them ideal for high-temperature and chemically harsh environments. Their molecular structure allows them to maintain mechanical stability and resist thermal degradation up to 400degC, whereas PET typically withstands temperatures only up to 150degC. PET offers good flexibility for everyday applications but lacks the long-term durability and heat resistance found in polyimide materials.
Applications in Electronics and Industry
Polyimide offers superior thermal stability and electrical insulation, making it ideal for flexible printed circuit boards, wire coatings, and high-performance electronic devices, while PET is commonly used in less demanding applications such as packaging films and insulation layers due to its cost-effectiveness and mechanical strength. In industrial settings, polyimide's resistance to chemicals and temperature extremes supports use in aerospace components, insulation tapes, and gaskets, whereas PET is favored for lightweight, durable containers and labels. Your choice depends on whether advanced thermal and chemical resistance or economical mechanical durability is the priority in your application.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Polyimide offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance but comes at a significantly higher cost compared to PET, which is more budget-friendly and widely available in various forms. The production complexity of polyimide limits its availability, primarily catering to high-performance industrial applications, whereas PET's mass production ensures easy accessibility for everyday use. Your choice hinges on balancing budget constraints with performance requirements, as PET dominates in cost efficiency and supply chain presence.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyimide exhibits superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to PET, but its complex molecular structure makes recycling challenging and less environmentally friendly. PET, widely used in packaging, benefits from well-established recycling processes that reduce waste and lower environmental impact significantly. Your choice between Polyimide and PET should consider PET's recyclability advantages for eco-conscious applications.
Choosing Between Polyimide and PET
Choosing between polyimide and PET depends on your application's thermal and chemical resistance requirements. Polyimide offers superior heat resistance up to 400degC and excellent chemical stability, making it ideal for demanding industrial uses. PET provides good mechanical strength and flexibility at a lower cost, suitable for less extreme environments like packaging and electrical insulation.
Polyimide vs PET Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com