Debug Wire offers simpler hardware requirements by using a single data line for debugging, while Serial Wire Debug (SWD) provides faster and more efficient communication through a two-wire interface, enhancing your embedded system development. Explore the rest of the article to understand which debugging protocol best fits your project's needs.
Table of Comparison
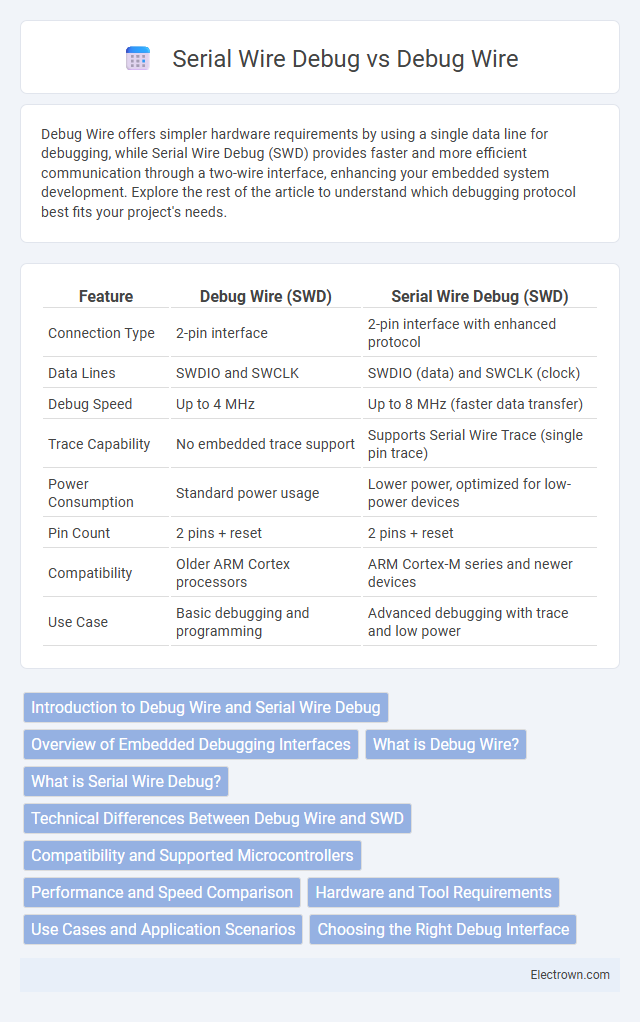
| Feature | Debug Wire (SWD) | Serial Wire Debug (SWD) |
|---|---|---|
| Connection Type | 2-pin interface | 2-pin interface with enhanced protocol |
| Data Lines | SWDIO and SWCLK | SWDIO (data) and SWCLK (clock) |
| Debug Speed | Up to 4 MHz | Up to 8 MHz (faster data transfer) |
| Trace Capability | No embedded trace support | Supports Serial Wire Trace (single pin trace) |
| Power Consumption | Standard power usage | Lower power, optimized for low-power devices |
| Pin Count | 2 pins + reset | 2 pins + reset |
| Compatibility | Older ARM Cortex processors | ARM Cortex-M series and newer devices |
| Use Case | Basic debugging and programming | Advanced debugging with trace and low power |
Introduction to Debug Wire and Serial Wire Debug
Debug Wire (DW) is a single-wire debug protocol primarily used in low-pin-count microcontrollers to facilitate in-circuit debugging without sacrificing multiple pins. Serial Wire Debug (SWD) is a two-wire protocol developed by ARM, offering a more efficient and higher-speed debugging interface with both data and clock lines, ideal for complex embedded systems. Your choice between DW and SWD depends on your microcontroller's architecture and the required debugging capabilities.
Overview of Embedded Debugging Interfaces
Debug Wire and Serial Wire Debug are crucial embedded debugging interfaces used to test and troubleshoot microcontrollers efficiently. Debug Wire operates through a single dedicated pin, primarily for Atmel AVR devices, enabling basic debugging with minimal pin usage. Your choice between Debug Wire and Serial Wire Debug depends on device compatibility and debugging complexity, with Serial Wire Debug offering faster data throughput and more advanced features via a two-pin interface.
What is Debug Wire?
Debug Wire (DW) is a one-pin interface used primarily for low-pin-count microcontrollers, providing a simple means to perform on-chip debugging and programming. It operates by repurposing the reset pin to transmit debugging data, allowing breakpoint setting, memory inspection, and control without additional pins. DW is less complex than Serial Wire Debug (SWD), making it suitable for constrained hardware environments where minimal pin usage is critical.
What is Serial Wire Debug?
Serial Wire Debug (SWD) is a two-pin interface developed by ARM as a streamlined alternative to the traditional Debug Wire interface. It enables efficient communication between a debugger and an embedded system, offering faster data transfer rates and reduced pin usage compared to Debug Wire. Your development process benefits from SWD's enhanced debugging capabilities, including real-time control and monitoring of ARM Cortex microcontrollers.
Technical Differences Between Debug Wire and SWD
Debug Wire (DW) uses a single bidirectional pin for communication, limiting data transfer rates and requiring higher latency in triggering debug operations. Serial Wire Debug (SWD) employs a two-wire interface consisting of SWDIO (data input/output) and SWCLK (clock), enabling faster, more reliable data transfer with lower pin count compared to traditional JTAG. SWD supports higher speeds, enhanced power efficiency, and improved debugging features such as breakpoint management and real-time trace compared to the simpler, slower Debug Wire protocol.
Compatibility and Supported Microcontrollers
Debug Wire (DW) is mainly compatible with older AVR microcontrollers from Atmel, providing a simple, low-pin interface for on-chip debugging, whereas Serial Wire Debug (SWD) supports a wider range of ARM Cortex-M microcontrollers, including STM32 and NXP devices, enabling more advanced debugging features with fewer pins. SWD offers broader industry support due to its inclusion in the ARM Debug Interface Specification, making it the preferred choice for modern embedded development. Your selection should consider the specific microcontroller architecture to ensure compatibility with the appropriate debug protocol.
Performance and Speed Comparison
Debug Wire offers slower data transfer rates compared to Serial Wire Debug (SWD), as it typically supports lower clock frequencies, limiting performance in complex microcontroller debugging scenarios. Serial Wire Debug provides higher throughput with a two-pin interface, enabling faster memory access and real-time data capture, which enhances debugging efficiency. When optimizing your development process, using SWD over Debug Wire significantly improves speed and responsiveness during firmware analysis.
Hardware and Tool Requirements
Debug Wire utilizes a single-wire interface that simplifies hardware connections by requiring fewer pins and is often supported by basic microcontroller systems. Serial Wire Debug (SWD) demands a two-wire interface and compatible debugging tools like advanced programmers or debuggers, enabling higher data throughput and real-time debugging capabilities. Both interfaces necessitate dedicated debug support on the microcontroller, but SWD generally offers broader toolchain compatibility and enhanced performance for complex debugging tasks.
Use Cases and Application Scenarios
Debug Wire (DW) is primarily used in low-pin-count microcontrollers where minimal I/O usage is crucial, making it ideal for simple embedded systems with limited resources. Serial Wire Debug (SWD) supports higher data throughput and advanced debugging features, suited for complex applications requiring real-time debugging and multi-threaded environments like ARM Cortex-M processors. SWD's compatibility with industry-standard tools also makes it preferable for development and production testing in automotive, IoT, and consumer electronics sectors.
Choosing the Right Debug Interface
Choosing the right debug interface depends on your application's complexity and pin availability, where Serial Wire Debug (SWD) offers a streamlined two-pin solution ideal for compact ARM Cortex-M microcontrollers. Debug Wire (DW), primarily used in older AVR devices, provides single-wire debugging with limited features but requires fewer pins compared to traditional JTAG. Your decision should balance the need for advanced debugging capabilities in SWD against the simplicity and legacy support of Debug Wire.
Debug Wire vs Serial Wire Debug Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com