Bit-banging enables direct software control of communication protocols by manually toggling I/O pins, offering flexibility at the expense of increased CPU usage and slower speeds compared to hardware interfaces. Discover how understanding the trade-offs between bit-banging and hardware interfaces can optimize your project's performance by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
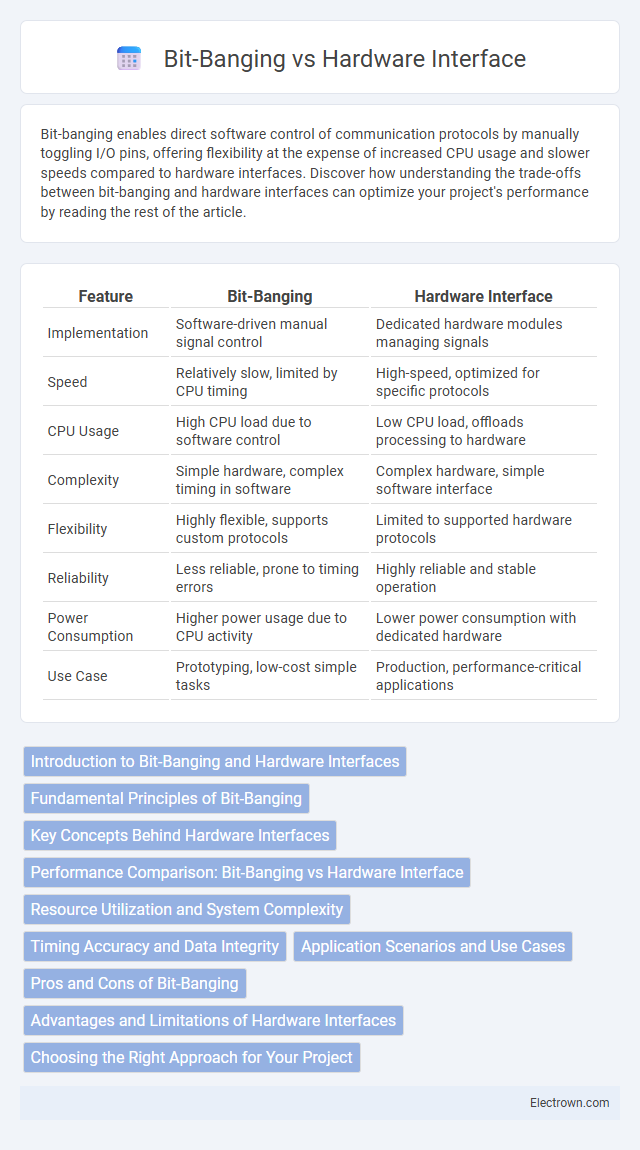
| Feature | Bit-Banging | Hardware Interface |
|---|---|---|
| Implementation | Software-driven manual signal control | Dedicated hardware modules managing signals |
| Speed | Relatively slow, limited by CPU timing | High-speed, optimized for specific protocols |
| CPU Usage | High CPU load due to software control | Low CPU load, offloads processing to hardware |
| Complexity | Simple hardware, complex timing in software | Complex hardware, simple software interface |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, supports custom protocols | Limited to supported hardware protocols |
| Reliability | Less reliable, prone to timing errors | Highly reliable and stable operation |
| Power Consumption | Higher power usage due to CPU activity | Lower power consumption with dedicated hardware |
| Use Case | Prototyping, low-cost simple tasks | Production, performance-critical applications |
Introduction to Bit-Banging and Hardware Interfaces
Bit-banging is a software-driven technique where microcontrollers manually control communication protocols by toggling I/O pins, enabling flexible data transfer without dedicated hardware. In contrast, hardware interfaces use specialized integrated circuits or peripherals designed for specific communication standards, providing faster and more reliable data exchange. Understanding the differences between bit-banging and hardware interfaces is crucial for optimizing microcontroller performance and resource allocation in embedded systems.
Fundamental Principles of Bit-Banging
Bit-banging is a technique where software directly controls the timing and logic levels of communication protocols by manipulating GPIO pins, bypassing dedicated hardware interfaces. It relies on precise timing loops and CPU instruction execution to simulate protocol behavior, allowing flexibility but demanding high processor resources. Your choice between bit-banging and hardware interfaces depends on the trade-off between control granularity and efficient resource usage.
Key Concepts Behind Hardware Interfaces
Hardware interfaces leverage dedicated peripherals such as SPI, I2C, or UART controllers to manage data transmission efficiently through specialized registers and timing control. These interfaces ensure precise synchronization, higher data rates, and reduced CPU overhead compared to bit-banging, which relies on software-driven manipulation of GPIO pins. Key concepts behind hardware interfaces include interrupt handling, direct memory access (DMA), and clock generation that facilitate reliable and consistent communication with external devices.
Performance Comparison: Bit-Banging vs Hardware Interface
Bit-banging relies on software-driven signal generation, resulting in slower data transmission and higher CPU usage compared to hardware interfaces, which utilize dedicated peripherals for efficient and consistent communication. Hardware interfaces offer superior timing accuracy and higher throughput, making them suitable for applications demanding real-time performance. Your choice impacts device responsiveness, with hardware interfaces generally preferred for performance-critical tasks.
Resource Utilization and System Complexity
Bit-banging consumes more CPU resources as the microcontroller manually controls each signal transition, reducing processing power for other tasks and increasing code size. Hardware interfaces, such as dedicated UART or SPI peripherals, offload signal timing and control from the CPU, significantly lowering system complexity and enhancing real-time performance. Utilizing hardware modules minimizes interrupt overhead and enables efficient multitasking in embedded systems.
Timing Accuracy and Data Integrity
Bit-banging relies on software-driven signal generation, leading to variable timing accuracy due to processor load and interrupt latency, which can compromise data integrity in high-speed communications. Hardware interfaces use dedicated timing circuits, such as UART or SPI controllers, ensuring precise clock signals and stable data transfer, thus enhancing timing accuracy and minimizing errors. Reliable data integrity is maintained in hardware interfaces because of consistent timing and built-in error detection mechanisms, critical in applications demanding robust communication.
Application Scenarios and Use Cases
Bit-banging is ideal for low-speed, low-complexity applications such as simple sensors, hobbyist projects, and prototyping where hardware resources are limited or absent. Hardware interfaces excel in high-speed communication, real-time data transfer, and industrial automation systems demanding precise timing and high reliability. Automotive electronics, consumer devices, and embedded systems commonly utilize hardware interfaces to optimize performance and reduce CPU load.
Pros and Cons of Bit-Banging
Bit-banging offers flexibility by allowing you to implement communication protocols without dedicated hardware, making it ideal for low-cost or prototype designs. However, it consumes more CPU resources and is less reliable for high-speed or time-critical data transfers compared to hardware interfaces. The simplicity and cost-effectiveness of bit-banging come at the expense of increased latency and potential timing inaccuracies.
Advantages and Limitations of Hardware Interfaces
Hardware interfaces provide faster data transfer rates and increased reliability compared to bit-banging methods by utilizing dedicated circuitry for communication protocols such as SPI, I2C, or UART. They reduce CPU overhead, allowing the processor to handle other tasks while the hardware manages signal timing and protocol details. However, hardware interfaces may lack flexibility in customization and can be limited by fixed pin assignments or support for fewer protocol variations.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Project
Bit-banging offers a flexible and cost-effective method for controlling communication protocols via software, ideal for projects with limited hardware resources or prototyping needs. Hardware interfaces provide faster, more reliable data transfer and lower CPU usage, making them suitable for high-speed or complex applications requiring precise timing. Selecting between bit-banging and hardware interfaces depends on project requirements, including speed, complexity, power consumption, and available hardware support.
Bit-Banging vs Hardware Interface Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com