Back EMF and armature reaction both affect the performance of electric motors by influencing voltage and magnetic fields within the machine. Understanding how these phenomena interact is crucial for optimizing your motor's efficiency and stability--explore the details further in the article.
Table of Comparison
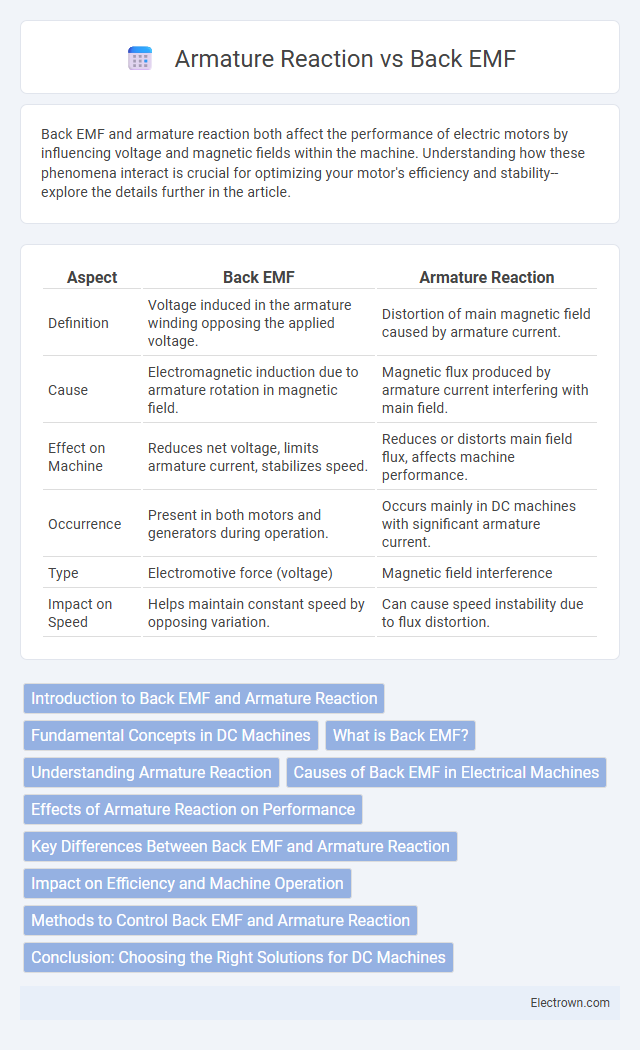
| Aspect | Back EMF | Armature Reaction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voltage induced in the armature winding opposing the applied voltage. | Distortion of main magnetic field caused by armature current. |
| Cause | Electromagnetic induction due to armature rotation in magnetic field. | Magnetic flux produced by armature current interfering with main field. |
| Effect on Machine | Reduces net voltage, limits armature current, stabilizes speed. | Reduces or distorts main field flux, affects machine performance. |
| Occurrence | Present in both motors and generators during operation. | Occurs mainly in DC machines with significant armature current. |
| Type | Electromotive force (voltage) | Magnetic field interference |
| Impact on Speed | Helps maintain constant speed by opposing variation. | Can cause speed instability due to flux distortion. |
Introduction to Back EMF and Armature Reaction
Back EMF is the voltage generated within a motor's armature winding opposing the applied input voltage, critical in regulating motor speed and current. Armature Reaction refers to the distortion and weakening of the main magnetic field caused by the armature current in a DC machine, influencing the machine's performance and efficiency. Understanding both phenomena is essential for optimizing motor design and operation, ensuring efficient energy conversion and stability under varying loads.
Fundamental Concepts in DC Machines
Back EMF in DC machines is the voltage generated opposing the applied voltage, caused by the armature conductors cutting magnetic flux, crucial for regulating current and speed. Armature reaction refers to the distortion and weakening of the main magnetic field due to the magnetic field created by current flowing in the armature winding, affecting the machine's efficiency and commutation. Understanding these phenomena is essential for optimizing your DC machine's performance and maintaining stable operation.
What is Back EMF?
Back EMF, or Electromotive Force, is the voltage generated in a motor's armature winding that opposes the applied input voltage as the rotor spins. This counteracting voltage arises due to the motor's rotation within the magnetic field, directly influencing the current flow and preventing excessive current draw. Understanding Back EMF is crucial for efficiently controlling your motor's speed and preventing overheating or damage.
Understanding Armature Reaction
Armature reaction refers to the impact of the magnetic field generated by the armature current on the main field flux in a DC machine, causing distortion or weakening of the original flux. This phenomenon affects the commutation process and can lead to sparking at the brushes, reducing efficiency and performance. Understanding armature reaction helps you optimize machine design and improve operational stability in generators and motors.
Causes of Back EMF in Electrical Machines
Back EMF in electrical machines is primarily caused by the relative motion between the armature conductors and the magnetic field, inducing a voltage that opposes the applied voltage according to Lenz's law. This phenomenon arises due to the machine's rotating armature cutting through magnetic flux lines, generating an electromotive force that restricts the current flow. Understanding the causes of Back EMF is crucial for optimizing motor performance and preventing excessive current draw during startup.
Effects of Armature Reaction on Performance
Armature reaction primarily causes distortion and weakening of the main magnetic field during motor or generator operation, leading to reduced torque and efficiency. This distortion results in increased sparking at the brushes and voltage fluctuations, negatively impacting your machine's performance and lifespan. Managing armature reaction through compensating windings or interpoles helps maintain stable output and protects the system from severe operational issues.
Key Differences Between Back EMF and Armature Reaction
Back EMF is the voltage generated in the armature winding of a motor or generator that opposes the applied voltage, directly influencing the machine's speed and efficiency. Armature reaction refers to the distortion and weakening of the main magnetic field caused by the armature current, affecting the machine's flux distribution and commutation. Understanding these key differences helps you optimize motor performance by managing voltage opposition and magnetic field interactions effectively.
Impact on Efficiency and Machine Operation
Back EMF generates a counter voltage opposing the input voltage, which regulates armature current and enhances motor efficiency by reducing power loss under load conditions. Armature reaction distorts the main magnetic field, causing flux weakening and reducing torque production, leading to decreased machine performance and operational stability. Minimizing armature reaction through design improvements such as compensating windings helps maintain consistent flux and improves overall efficiency in electric machines.
Methods to Control Back EMF and Armature Reaction
Controlling Back EMF involves using methods such as adjusting the supply voltage, employing field weakening techniques, or incorporating electronic controllers like pulse-width modulation (PWM) drives to maintain motor speed and torque. Armature Reaction can be managed by using compensating windings, interpoles, or by improving the magnetic circuit design to reduce distortion of the main field flux. Understanding these control methods helps optimize Your motor's performance and efficiency in various operating conditions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solutions for DC Machines
Back EMF and armature reaction each significantly impact the performance of DC machines, with Back EMF regulating speed and voltage, while armature reaction affects flux distribution and commutation. Proper design and control strategies, such as selecting suitable compensating windings and using external resistors or electronic controllers, effectively mitigate these effects to enhance efficiency and reliability. Choosing the right solution depends on the specific application requirements, operating conditions, and machine design parameters.
Back EMF vs Armature Reaction Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com