Hall effect sensors provide precise, non-contact magnetic field detection with higher durability and faster response times compared to reed switches, which rely on mechanical contacts prone to wear and slower operation. Discover which option best suits Your application by exploring the detailed comparison in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
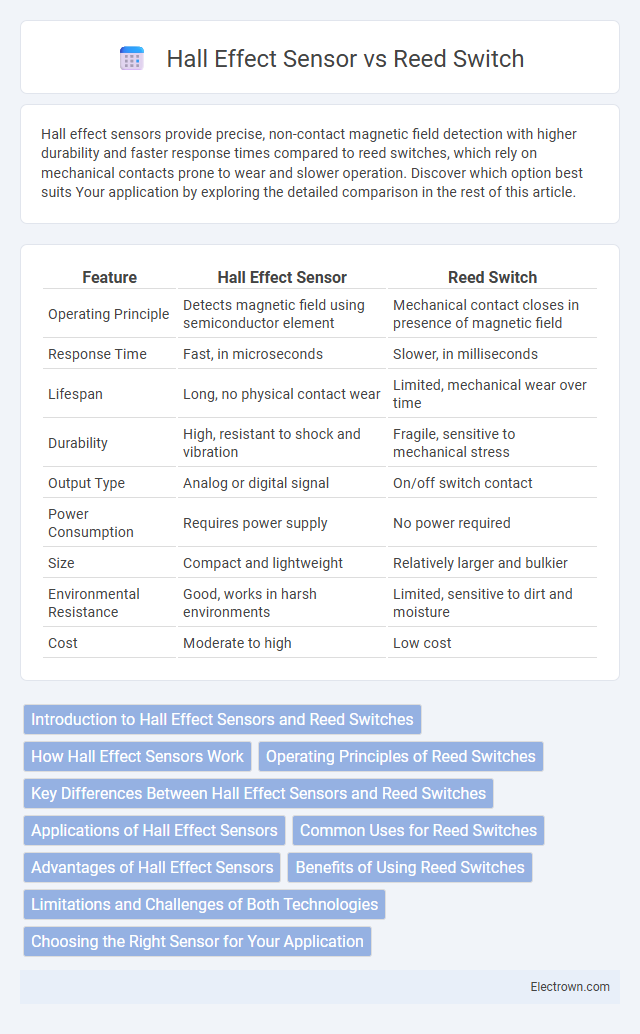
| Feature | Hall Effect Sensor | Reed Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Principle | Detects magnetic field using semiconductor element | Mechanical contact closes in presence of magnetic field |
| Response Time | Fast, in microseconds | Slower, in milliseconds |
| Lifespan | Long, no physical contact wear | Limited, mechanical wear over time |
| Durability | High, resistant to shock and vibration | Fragile, sensitive to mechanical stress |
| Output Type | Analog or digital signal | On/off switch contact |
| Power Consumption | Requires power supply | No power required |
| Size | Compact and lightweight | Relatively larger and bulkier |
| Environmental Resistance | Good, works in harsh environments | Limited, sensitive to dirt and moisture |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low cost |
Introduction to Hall Effect Sensors and Reed Switches
Hall Effect sensors detect magnetic fields through the voltage generated perpendicular to the current flow in a conductor, offering precise, non-contact magnetic sensing with fast response times. Reed switches operate by mechanically closing or opening contacts when exposed to a magnetic field, providing simple, low-power on-off switching. Understanding the differences in technology and application helps you select the right sensor for your magnetic detection needs.
How Hall Effect Sensors Work
Hall Effect sensors detect magnetic fields by measuring the voltage generated across a conductor through which current flows when exposed to a perpendicular magnetic field, allowing precise and contactless sensing. These sensors convert magnetic flux into electrical signals, enabling accurate measurement of position, speed, and current without mechanical wear. Unlike reed switches that rely on physical contact closing within a magnetic field, Hall Effect sensors provide faster response times, higher durability, and enhanced sensitivity in industrial and automotive applications.
Operating Principles of Reed Switches
Reed switches operate using two ferromagnetic blades sealed within a glass capsule that close or open an electrical circuit when exposed to a magnetic field. The magnetic field causes the reeds to magnetize, attracting and making contact to complete the circuit, enabling switch activation without physical contact. This simple operating principle provides high sensitivity and reliability in detecting magnetic presence or motion in various applications.
Key Differences Between Hall Effect Sensors and Reed Switches
Hall Effect sensors detect magnetic fields through semiconductor-based sensing elements, offering contactless operation and high sensitivity, while Reed switches rely on physical contact between ferromagnetic reeds within a sealed glass tube to open or close circuits. Hall Effect sensors provide faster response times, better durability under mechanical stress, and can measure variable magnetic field strengths, whereas Reed switches are simpler, cost-effective, and operate solely as binary on/off devices. The choice between the two depends on application requirements such as longevity, precision, switching speed, and environmental conditions.
Applications of Hall Effect Sensors
Hall Effect sensors are widely used in automotive systems for precise position sensing, such as detecting crankshaft and camshaft positions, and in industrial automation to monitor conveyor belts and robotic arms. They offer reliable, contactless sensing in harsh environments, making them ideal for speed detection, current sensing in smart meters, and proximity detection in consumer electronics. Your choice of a Hall Effect sensor enables accurate, durable performance where non-contact and high-frequency response is critical.
Common Uses for Reed Switches
Reed switches are commonly used in applications requiring reliable, low-power contact sensing, such as security systems for door and window sensors, position sensing in industrial machinery, and proximity detection in consumer electronics. Their mechanical operation makes them suitable for detecting the open or closed state without power consumption, ideal for battery-operated devices. You can rely on reed switches for durable performance in environments where magnetic actuation is needed without complex electronic circuitry.
Advantages of Hall Effect Sensors
Hall Effect sensors offer precise, non-contact sensing with high durability and faster response times compared to Reed switches, making them ideal for applications requiring reliability and longevity. They operate effectively in harsh environments due to their solid-state design, which resists wear and mechanical failure. Your projects benefit from enhanced accuracy and maintenance-free performance when choosing Hall Effect sensors over Reed switches.
Benefits of Using Reed Switches
Reed switches offer exceptional durability and reliability in harsh environments due to their hermetically sealed contacts, which prevent corrosion and contamination. They are highly sensitive to magnetic fields, enabling precise detection with low power consumption ideal for battery-operated devices. Your choice of a reed switch can ensure a cost-effective and maintenance-free solution for position sensing and proximity applications.
Limitations and Challenges of Both Technologies
Hall Effect sensors face limitations such as sensitivity to electromagnetic interference and temperature variations, which can impact accuracy in harsh environments. Reed switches are prone to mechanical wear and contact bounce, leading to reduced lifespan and slower response times under frequent switching conditions. Both technologies encounter challenges in balancing durability, response speed, and environmental resilience for optimal performance in industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Sensor for Your Application
When selecting between a Hall Effect sensor and a reed switch, consider factors such as response time, durability, and environmental conditions. Hall Effect sensors offer faster response, greater reliability, and are ideal for applications involving high-speed or continuous contact detection in harsh environments. Reed switches are cost-effective, suitable for simple on/off applications with low current, but they may wear out faster due to mechanical contacts.
Hall Effect Sensor vs Reed Switch Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com