Open-loop control systems operate without feedback, relying solely on input commands to perform actions, which may lead to inaccuracies if disturbances occur. Closed-loop control systems use feedback to continuously adjust and correct system output, ensuring higher precision and stability; discover how these mechanisms affect your system's performance in the detailed comparison ahead.
Table of Comparison
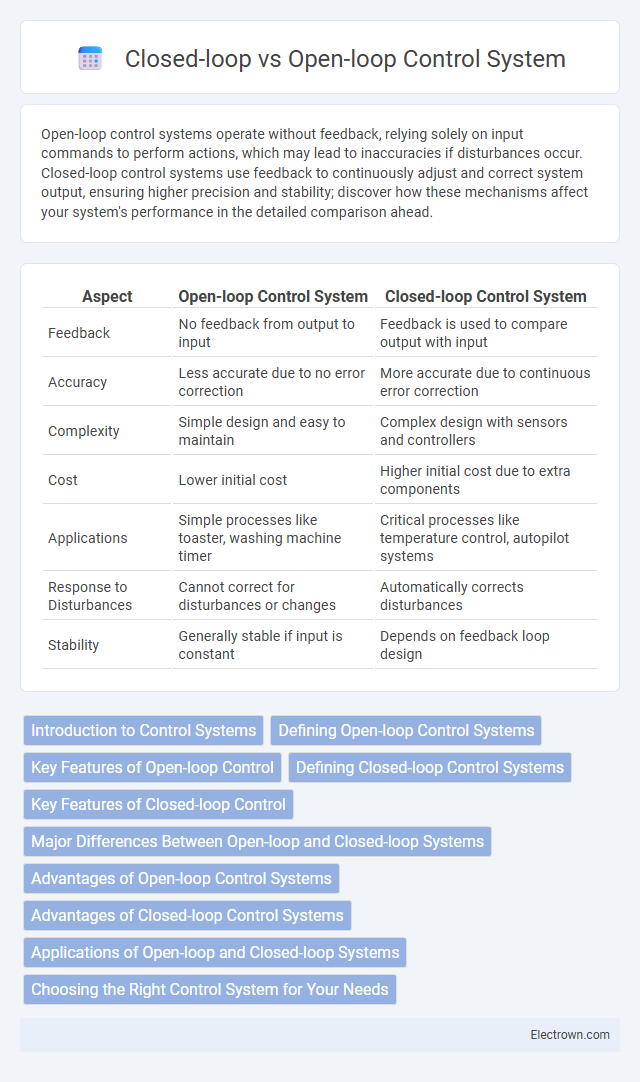
| Aspect | Open-loop Control System | Closed-loop Control System |
|---|---|---|
| Feedback | No feedback from output to input | Feedback is used to compare output with input |
| Accuracy | Less accurate due to no error correction | More accurate due to continuous error correction |
| Complexity | Simple design and easy to maintain | Complex design with sensors and controllers |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost due to extra components |
| Applications | Simple processes like toaster, washing machine timer | Critical processes like temperature control, autopilot systems |
| Response to Disturbances | Cannot correct for disturbances or changes | Automatically corrects disturbances |
| Stability | Generally stable if input is constant | Depends on feedback loop design |
Introduction to Control Systems
Control systems regulate the behavior of other devices or systems using control loops, categorized into open-loop and closed-loop systems. An open-loop control system operates without feedback, executing commands based solely on predefined inputs, resulting in potential inaccuracies when disturbances occur. In contrast, a closed-loop control system continuously monitors output through feedback, adjusting inputs dynamically to maintain desired performance and improve stability in applications such as temperature regulation, robotics, and industrial automation.
Defining Open-loop Control Systems
Open-loop control systems operate without feedback, executing predetermined commands regardless of output results, making them simpler and less costly. They rely on input signals and a control algorithm to drive the process, but cannot correct errors or adapt to disturbances. Common examples include basic household appliances like washing machines and microwave ovens, where the control action is independent of the actual output performance.
Key Features of Open-loop Control
An open-loop control system operates without feedback, relying solely on preset instructions to execute tasks, which allows for simpler design and lower cost. It is characterized by a fixed control action that does not adjust based on output variations, making it suitable for processes where the output is predictable and disturbances are minimal. Typical examples include household appliances like washing machines and microwave ovens, where timing and sequence control suffice without feedback.
Defining Closed-loop Control Systems
Closed-loop control systems continuously monitor output through feedback to automatically adjust inputs and maintain desired performance despite disturbances. These systems rely on sensors and controllers to compare actual output against reference values, ensuring accuracy and stability. Closed-loop control enhances precision in applications such as temperature regulation, motor speed control, and robotic positioning.
Key Features of Closed-loop Control
Closed-loop control systems are characterized by the continuous monitoring of output through feedback mechanisms to automatically correct deviations from desired performance. These systems enhance accuracy and stability by adjusting input signals based on real-time data, effectively minimizing errors caused by disturbances or system uncertainties. Key features include feedback loops, error detection, self-correction, and improved robustness compared to open-loop control systems.
Major Differences Between Open-loop and Closed-loop Systems
Open-loop control systems operate without feedback, relying solely on predefined inputs to produce outputs, which can lead to errors if external disturbances occur. Closed-loop control systems utilize feedback to continuously monitor output and adjust inputs accordingly, enhancing accuracy and stability. Key differences include the presence of feedback, error correction capability, and response adaptability to changing conditions.
Advantages of Open-loop Control Systems
Open-loop control systems offer advantages such as simplicity in design and cost-effectiveness since they do not require feedback components or sensors. These systems provide faster response times and are less prone to instability or oscillations because there is no feedback loop to cause potential delays or errors. Open-loop control is ideal for applications with predictable and stable environments where precise control adjustments are unnecessary.
Advantages of Closed-loop Control Systems
Closed-loop control systems offer superior accuracy and stability by continuously monitoring output and adjusting inputs to minimize errors. Your processes benefit from increased adaptability to disturbances and variations, ensuring consistent performance in dynamic environments. These systems improve reliability, reduce the impact of external noise, and enhance overall efficiency compared to open-loop configurations.
Applications of Open-loop and Closed-loop Systems
Open-loop control systems find applications in simple processes where precise feedback is unnecessary, such as washing machines and microwave ovens, where preset instructions execute without adjustment during operation. Closed-loop control systems are widely used in industrial automation, robotics, and HVAC systems, where continuous monitoring and feedback ensure accuracy and stability by adjusting the output based on sensor data. In automotive cruise control and temperature regulation, closed-loop systems maintain desired performance by compensating for external disturbances and system variations.
Choosing the Right Control System for Your Needs
Selecting the right control system depends on the level of accuracy and feedback required for your application. Open-loop control systems operate without feedback, offering simplicity and cost-effectiveness for processes with predictable, stable conditions. Closed-loop control systems use real-time feedback to adjust performance, making them ideal for applications where precision and adaptability are crucial.
Open-loop vs Closed-loop Control System Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com