NPN sensors switch the negative side of the circuit by connecting the load to ground, making them suitable for sinking current applications, while PNP sensors switch the positive side by connecting the load to the positive supply, ideal for sourcing current scenarios. Understanding the differences in wiring and signal output between NPN and PNP sensors can help you select the right sensor for your specific control system needs; read on to explore their functions and applications in detail.
Table of Comparison
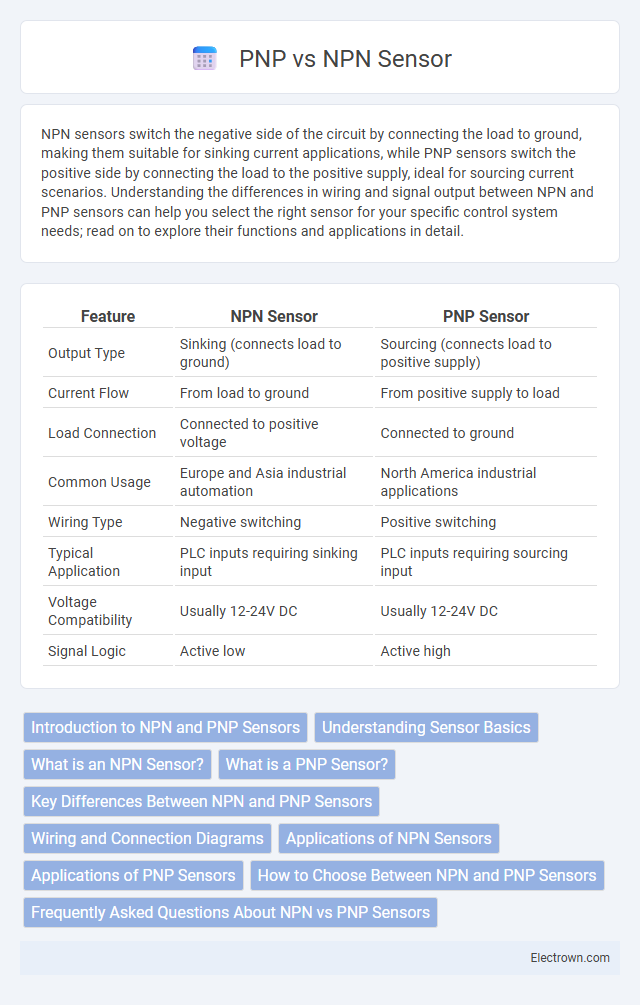
| Feature | NPN Sensor | PNP Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Output Type | Sinking (connects load to ground) | Sourcing (connects load to positive supply) |
| Current Flow | From load to ground | From positive supply to load |
| Load Connection | Connected to positive voltage | Connected to ground |
| Common Usage | Europe and Asia industrial automation | North America industrial applications |
| Wiring Type | Negative switching | Positive switching |
| Typical Application | PLC inputs requiring sinking input | PLC inputs requiring sourcing input |
| Voltage Compatibility | Usually 12-24V DC | Usually 12-24V DC |
| Signal Logic | Active low | Active high |
Introduction to NPN and PNP Sensors
NPN and PNP sensors are two common types of proximity sensors used for detecting objects in industrial automation. The primary difference lies in their output wiring: NPN sensors source current through the load to ground, while PNP sensors sink current by connecting the load to the positive supply voltage. Your choice between NPN and PNP sensors depends on the input requirements of your control system and the desired wiring configuration.
Understanding Sensor Basics
NPN and PNP sensors are types of transistor outputs that differ in how they switch current to and from the load. NPN sensors act as low-side switches, connecting the load to ground when activated, while PNP sensors function as high-side switches, providing positive voltage to the load. Understanding these basics helps you select the right sensor for your circuit's wiring configuration and ensures proper integration with your control system.
What is an NPN Sensor?
An NPN sensor is a type of proximity sensor where the output switches to ground when activated, allowing current to flow from the load to the sensor's output transistor. This sensor configuration is widely used in industrial automation for detecting the presence or absence of objects by sinking current. Understanding whether your application requires an NPN sensor helps ensure compatibility with your control system's input wiring and power requirements.
What is a PNP Sensor?
A PNP sensor is a type of proximity sensor that sources current to the load when activated, meaning it supplies positive voltage to the output. Commonly used in industrial automation, PNP sensors connect the load to the positive power supply, making them compatible with devices designed for sourcing inputs. The key advantage is their ease of integration in positive switching circuits, often preferred in European and Asian automation systems.
Key Differences Between NPN and PNP Sensors
NPN and PNP sensors differ primarily in their switching behavior and wiring configurations; NPN sensors switch the negative side (sinking current) by connecting the load to ground, while PNP sensors switch the positive side (sourcing current) by connecting the load to the positive voltage. NPN sensors are typically used in systems requiring current to flow from the load to the sensor, making them common in European industrial automation, whereas PNP sensors are favored in systems where current flows from the sensor to the load, often preferred in Asian markets. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for selecting the proper sensor to ensure compatibility with your control system and prevent wiring errors.
Wiring and Connection Diagrams
NPN and PNP sensors differ primarily in their output configurations, impacting wiring and connection diagrams. NPN sensors, also known as sinking sensors, connect the load to the positive supply, allowing current to flow from the load to the sensor's output and then to ground, while PNP sensors, or sourcing sensors, provide current from the positive supply through the sensor output to the load. Understanding these wiring distinctions is crucial for your correct sensor integration to ensure proper signal flow and avoid circuit damage in industrial automation systems.
Applications of NPN Sensors
NPN sensors are widely used in industrial automation for detecting metal objects and controlling conveyor belts due to their sinking current output, which allows easy integration with PLC inputs. Your manufacturing systems benefit from NPN sensors in applications like proximity sensing, position detection, and object counting where reliable and fast switching is critical. These sensors excel in environments requiring stable signal grounding and noise immunity, making them ideal for assembly lines and robotic automation.
Applications of PNP Sensors
PNP sensors are commonly used in automation systems where positive switching is required, such as in industrial machinery, conveyor belts, and robotic arms. They connect the load to the positive voltage, making them ideal for interfacing with PLCs and control systems that expect sourcing signals. Your choice of PNP sensors enhances system reliability in environments needing easy integration with standard DC control circuits.
How to Choose Between NPN and PNP Sensors
Choosing between NPN and PNP sensors depends on the voltage type and wiring configuration of your control system. NPN sensors source current by connecting the load to ground, making them suitable for negative switching systems, while PNP sensors source current by connecting the load to the positive supply, ideal for positive switching systems. Compatibility with existing PLC input modules and ensuring correct sensor polarity are critical factors in selection to avoid wiring errors and ensure reliable operation.
Frequently Asked Questions About NPN vs PNP Sensors
NPN and PNP sensors differ primarily in their output transistor type, affecting how they switch current to the load; NPN sensors sink current by connecting the load to ground, while PNP sensors source current by connecting the load to the positive supply. Common questions include how to determine which sensor to use with your PLC input, the wiring differences, and compatibility with load types or control systems. Understanding the voltage levels, switching behavior, and application environment helps you select the appropriate sensor type for reliable and efficient operation.
NPN vs PNP Sensor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com