Core Balance CT measures the overall stability of the spine by assessing load distribution across the core muscles, while Residual CT evaluates the residual strength and fatigue levels after physical exertion to determine functional endurance. Explore the rest of this article to understand how these assessments impact your spinal health and performance optimization.
Table of Comparison
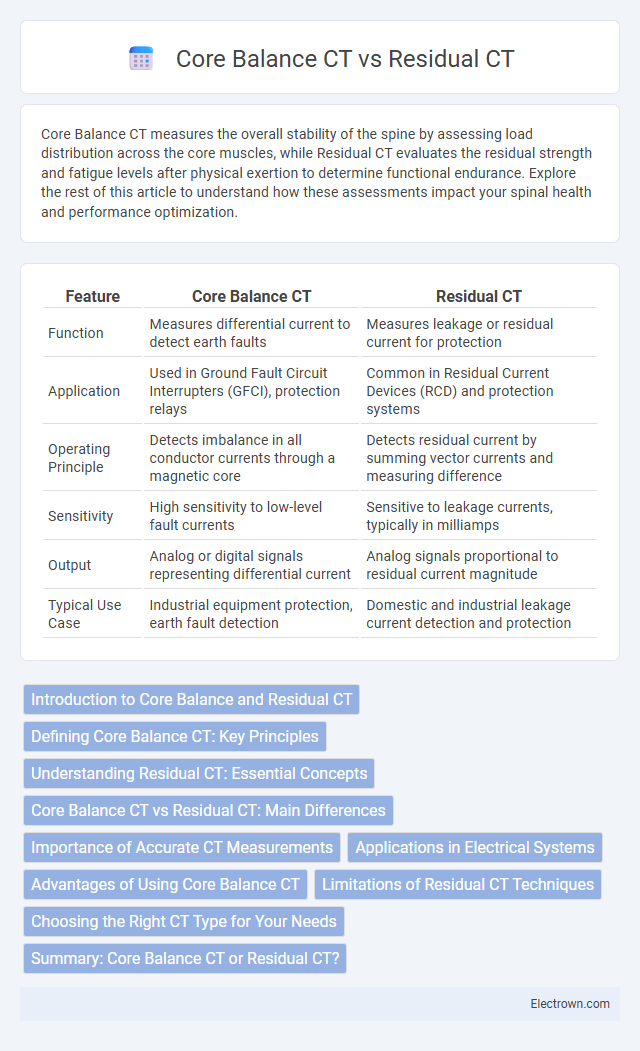
| Feature | Core Balance CT | Residual CT |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Measures differential current to detect earth faults | Measures leakage or residual current for protection |
| Application | Used in Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCI), protection relays | Common in Residual Current Devices (RCD) and protection systems |
| Operating Principle | Detects imbalance in all conductor currents through a magnetic core | Detects residual current by summing vector currents and measuring difference |
| Sensitivity | High sensitivity to low-level fault currents | Sensitive to leakage currents, typically in milliamps |
| Output | Analog or digital signals representing differential current | Analog signals proportional to residual current magnitude |
| Typical Use Case | Industrial equipment protection, earth fault detection | Domestic and industrial leakage current detection and protection |
Introduction to Core Balance and Residual CT
Core Balance CT measures the essential forward power in your electrical system, reflecting the total current minus any neutral or leakage currents. Residual CT detects imbalances caused by leakage currents returning through the ground, crucial for identifying fault conditions and ensuring safety. Understanding these two types helps optimize energy management and protect equipment by accurately monitoring current flow and fault detection.
Defining Core Balance CT: Key Principles
Core Balance CT optimizes radiation dose by dynamically adjusting the current during a CT scan based on the patient's anatomy and tissue density. This technique enhances image quality while minimizing exposure, focusing on the central region to maintain diagnostic accuracy. Your imaging outcomes benefit from precise modulation of X-ray intensity, unlike Residual CT, which typically manages dose adjustments in post-processing rather than during acquisition.
Understanding Residual CT: Essential Concepts
Residual CT refers to the current that remains unmeasured due to imperfect balance in the Core Balance CT system, causing leakage currents to go undetected. It is crucial to understand that Residual CT measures the differential current between live conductors, identifying ground faults and enhancing safety. Accurate detection of Residual CT helps prevent electrical hazards by triggering protective devices when leakage currents exceed predefined thresholds.
Core Balance CT vs Residual CT: Main Differences
Core Balance CT measures the actual cash available by adjusting the account balance for outstanding transactions, providing a real-time snapshot of your liquidity. Residual CT, on the other hand, represents the remaining credit limit after accounting for authorized but not yet processed transactions, highlighting your available credit capacity. Understanding these differences helps you manage your finances more accurately by distinguishing between immediate cash flow and future spending power.
Importance of Accurate CT Measurements
Accurate Core Balance CT measurements are crucial for optimizing load distribution and preventing equipment overheating, while Residual CT readings help detect insulation faults and potential current leakage. Both measurement types ensure the safety and efficiency of electrical systems, minimizing downtime and costly repairs. Your maintenance strategy benefits significantly from precise CT data, enhancing overall system reliability and performance.
Applications in Electrical Systems
Core Balance CTs (Current Transformers) are primarily used for earth fault detection in electrical systems by measuring the vector sum of currents in all live conductors to identify leakage currents. Residual CTs, often configured as a summation type, serve in differential protection schemes by detecting imbalances between incoming and outgoing currents, critical for fault localization and system protection. Both devices enhance system safety and reliability by providing accurate ground fault and differential current monitoring in power distribution networks.
Advantages of Using Core Balance CT
Core Balance CT provides accurate and stable current measurements across a wide frequency range, enhancing protection and control in electrical systems. Its compact design and inherent immunity to external magnetic interference improve reliability in harsh environments. This reduces maintenance costs and increases the lifespan of connected equipment compared to traditional Residual CTs.
Limitations of Residual CT Techniques
Residual CT techniques often struggle with accuracy due to their reliance on subtracting measured currents, leading to cumulative errors and reduced sensitivity in detecting low-level ground faults. Core Balance CTs provide more reliable performance by directly measuring the net magnetic flux, minimizing error margins and improving fault detection in complex grounding systems. Limitations of Residual CT include susceptibility to external magnetic interference and difficulty in compensating for asymmetrical load conditions, which can result in false tripping or missed faults.
Choosing the Right CT Type for Your Needs
Core Balance CT provides precise measurement of the total current flowing through all conductors, ideal for applications requiring accurate energy monitoring and power quality analysis. Residual CT, on the other hand, detects imbalance currents by measuring the difference between incoming and outgoing currents, making it essential for ground fault detection and safety protection. Understanding your specific requirements for accuracy, fault detection, and energy monitoring will help you choose the right CT type tailored to your system's needs.
Summary: Core Balance CT or Residual CT?
Core Balance CT provides a precise measurement of a building's thermal balance by accounting for all energy inputs and outputs, ensuring accurate assessment of energy efficiency. Residual CT estimates the remaining energy consumption after subtracting known contributions, offering a practical way to identify unexplained energy losses. Your choice depends on whether you require comprehensive energy accounting (Core Balance CT) or a simplified analysis highlighting discrepancies (Residual CT).
Core Balance CT vs Residual CT Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com