Busbars provide a compact, efficient way to distribute high amperage electricity with less heat generation compared to traditional cables, which are more flexible but occupy more space and require careful routing. Explore the rest of the article to understand which option best suits your electrical setup and efficiency needs.
Table of Comparison
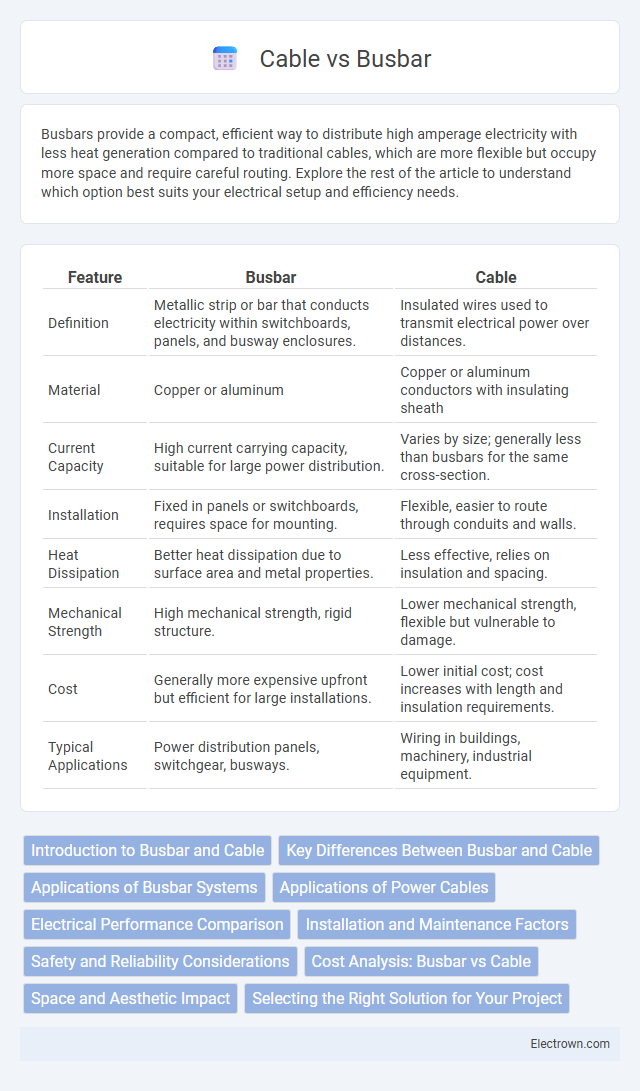
| Feature | Busbar | Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Metallic strip or bar that conducts electricity within switchboards, panels, and busway enclosures. | Insulated wires used to transmit electrical power over distances. |
| Material | Copper or aluminum | Copper or aluminum conductors with insulating sheath |
| Current Capacity | High current carrying capacity, suitable for large power distribution. | Varies by size; generally less than busbars for the same cross-section. |
| Installation | Fixed in panels or switchboards, requires space for mounting. | Flexible, easier to route through conduits and walls. |
| Heat Dissipation | Better heat dissipation due to surface area and metal properties. | Less effective, relies on insulation and spacing. |
| Mechanical Strength | High mechanical strength, rigid structure. | Lower mechanical strength, flexible but vulnerable to damage. |
| Cost | Generally more expensive upfront but efficient for large installations. | Lower initial cost; cost increases with length and insulation requirements. |
| Typical Applications | Power distribution panels, switchgear, busways. | Wiring in buildings, machinery, industrial equipment. |
Introduction to Busbar and Cable
Busbars are metallic strips or bars that conduct electricity within switchboards, distribution boards, and electrical panels, offering high current carrying capacity and low resistance connections. Cables consist of insulated conductors designed for flexible power transmission across distances, typically used in wiring buildings and machinery. Busbars provide efficient power distribution with enhanced durability, while cables offer versatility in routing electrical currents where flexibility and insulation are required.
Key Differences Between Busbar and Cable
Busbars are rigid metal strips or bars used for high current power distribution in switchgear and panel boards, offering better heat dissipation and easier fault management compared to cables. Cables consist of insulated conductors designed for flexible routing of electrical power over longer distances, with higher installation complexity and potential voltage drop. Busbars provide a compact, low impedance solution ideal for centralized electrical systems, whereas cables are preferred in applications requiring flexibility and extended reach.
Applications of Busbar Systems
Busbar systems are extensively used in industrial and commercial electrical distribution due to their ability to handle high current loads efficiently and provide compact, scalable solutions for power distribution. Your facility can benefit from busbars in applications such as switchgear, panel boards, and large electrical switchboards where space-saving and ease of maintenance are crucial. Busbars offer superior heat dissipation and reduced electrical losses compared to traditional cable systems, making them ideal for high-capacity and high-reliability installations.
Applications of Power Cables
Power cables are widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial applications to transmit electrical power over various distances, offering flexibility in installation and routing compared to busbars. They are essential in underground and overhead power distribution, connecting transformers, switchgear, and electrical panels where complex layouts or long distances make busbars impractical. Power cables provide reliable insulation, protection against environmental factors, and adaptability in projects requiring dynamic configurations or remote power delivery.
Electrical Performance Comparison
Busbars offer superior electrical performance compared to cables due to lower resistance and inductance, resulting in reduced energy loss and improved current-carrying capacity. Their solid metal construction ensures consistent conductivity and efficient heat dissipation, minimizing voltage drops and enhancing system reliability. Cables, while flexible and easier to install, exhibit higher impedance which can limit their performance in high-current applications and cause greater power dissipation.
Installation and Maintenance Factors
Busbars offer streamlined installation with simplified mounting and fewer connection points, reducing labor time and the potential for wiring errors. Cables require extensive routing and securing, which can increase installation complexity and maintenance challenges such as inspection and fault isolation. Your choice influences long-term upkeep costs, as busbars generally provide easier access and quicker troubleshooting compared to traditional cable systems.
Safety and Reliability Considerations
Busbars offer superior safety and reliability due to their robust design that minimizes electrical resistance and heat generation, reducing fire hazards and mechanical failures. Cables, while flexible and easier to install, are more prone to insulation degradation, damage, and faults caused by environmental factors or mechanical stress. Industrial settings prioritize busbars for high-current applications to ensure consistent performance and enhanced operator protection under demanding electrical loads.
Cost Analysis: Busbar vs Cable
Busbars generally offer lower installation and maintenance costs compared to cables, especially in large-scale electrical distribution systems where they reduce labor and material expenses. Cables may incur higher costs due to insulation, trenching, and longer installation times, making busbars a more cost-effective choice for high current applications. Your project's scale and electrical requirements will ultimately determine the most economical option between busbars and cables.
Space and Aesthetic Impact
Busbars occupy significantly less space than traditional cables due to their flat, compact design, allowing for more efficient electrical panel layouts and reducing clutter. Their sleek, modular appearance enhances aesthetic appeal in both industrial and commercial installations, offering a cleaner and more organized look. This streamlined form factor also simplifies maintenance and improves airflow, contributing to better thermal management compared to bulky cable bundles.
Selecting the Right Solution for Your Project
Choosing between busbars and cables depends on factors like current capacity, installation space, and maintenance requirements. Busbars offer higher current ratings, better heat dissipation, and easier scalability for large power distribution systems, while cables provide flexibility and simpler installation in confined or complex routing scenarios. Evaluating your project's load demands, physical constraints, and future expansion plans ensures the optimal balance between efficiency, safety, and cost.
Busbar vs Cable Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com