Fieldbus and Profibus are industrial communication protocols designed to connect field devices, with Fieldbus providing a standardized, digital two-way communication system for automation, while Profibus offers high-speed data exchange, particularly in manufacturing processes. Explore the following article to understand their key differences and choose the best fit for your automation needs.
Table of Comparison
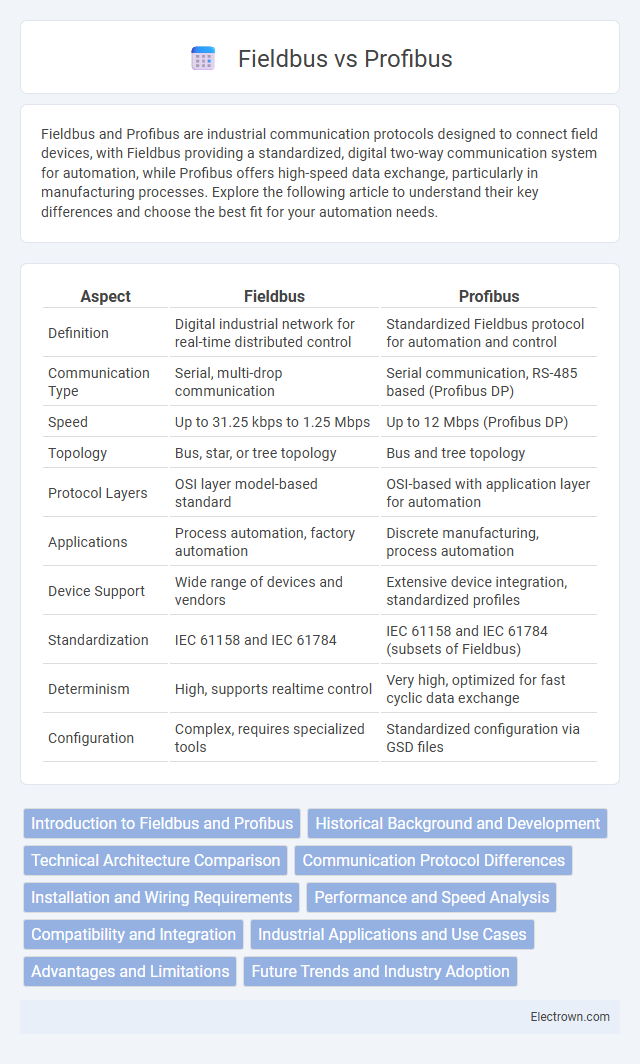
| Aspect | Fieldbus | Profibus |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital industrial network for real-time distributed control | Standardized Fieldbus protocol for automation and control |
| Communication Type | Serial, multi-drop communication | Serial communication, RS-485 based (Profibus DP) |
| Speed | Up to 31.25 kbps to 1.25 Mbps | Up to 12 Mbps (Profibus DP) |
| Topology | Bus, star, or tree topology | Bus and tree topology |
| Protocol Layers | OSI layer model-based standard | OSI-based with application layer for automation |
| Applications | Process automation, factory automation | Discrete manufacturing, process automation |
| Device Support | Wide range of devices and vendors | Extensive device integration, standardized profiles |
| Standardization | IEC 61158 and IEC 61784 | IEC 61158 and IEC 61784 (subsets of Fieldbus) |
| Determinism | High, supports realtime control | Very high, optimized for fast cyclic data exchange |
| Configuration | Complex, requires specialized tools | Standardized configuration via GSD files |
Introduction to Fieldbus and Profibus
Fieldbus and Profibus are advanced industrial communication protocols designed to enhance automation systems by enabling real-time data exchange between controllers and field devices. Fieldbus serves as a broad category of digital, two-way communication networks, integrating sensors and actuators within a single cable, while Profibus is a specific type of Fieldbus widely adopted in manufacturing and process automation for its reliable and standardized data transmission. Understanding these technologies can optimize your control system's efficiency and interoperability in complex industrial environments.
Historical Background and Development
Fieldbus technology emerged in the 1980s as a digital communication system designed to replace traditional analog wiring in industrial automation, facilitating more efficient data exchange between devices. Profibus, developed in 1989 by a consortium including Siemens and other industry leaders, quickly became one of the most widely adopted Fieldbus standards due to its robust performance and compatibility with various automation equipment. Your choice between Fieldbus and Profibus should consider the historical evolution, as Profibus benefits from extensive industry support and continuous advancements in protocols.
Technical Architecture Comparison
Fieldbus and Profibus differ significantly in their technical architecture; Fieldbus uses a decentralized communication protocol allowing multiple devices to communicate over a single network segment with a master-slave relationship or peer-to-peer communication. Profibus, a type of Fieldbus, operates with a master-slave polling mechanism, specifically designed for real-time automation with deterministic data transfer and higher data rates up to 12 Mbps. Your choice depends on the required network topology, device compatibility, and communication speed for industrial control systems.
Communication Protocol Differences
Fieldbus and Profibus differ primarily in their communication protocols, with Fieldbus offering a range of open, standardized protocols designed for real-time distributed control in industrial environments. Profibus, a specific type of Fieldbus, utilizes a master-slave communication model optimized for high-speed, deterministic data exchange in automation systems. Understanding these protocol differences helps you select the appropriate network for efficient and reliable industrial communication.
Installation and Wiring Requirements
Fieldbus installation requires a daisy-chain topology with trunk and spur wiring, supporting multidrop connections that reduce cable usage and simplify network layout. Profibus demands a linear bus topology with terminating resistors at both ends, using shielded twisted-pair cables to minimize electromagnetic interference and ensure signal integrity. Both systems necessitate careful grounding and adherence to specific cable length limits to maintain reliable communication and network performance.
Performance and Speed Analysis
Fieldbus and Profibus differ significantly in performance and speed, with Profibus offering data transmission rates up to 12 Mbps, suitable for high-speed industrial automation applications. Fieldbus typically operates at lower speeds, around 31.25 kbps to 1.5 Mbps, optimized for reliability and deterministic communication in process control environments. Understanding these speed capabilities helps you select the appropriate protocol for time-sensitive and high-throughput industrial networks.
Compatibility and Integration
Fieldbus systems offer broad compatibility with various industrial devices through standardized protocols, enabling seamless integration across multiple manufacturers. Profibus, a specific type of Fieldbus, provides enhanced compatibility within Siemens-based environments and supports complex automation networks with integrated diagnostics. Both systems facilitate reliable communication and interoperability, but Profibus excels in environments requiring tight integration with Siemens automation equipment.
Industrial Applications and Use Cases
Fieldbus and Profibus are widely used industrial communication protocols tailored for automation and process control systems. Fieldbus supports various topologies and is preferred in integrating complex devices like sensors and actuators in process industries such as oil and gas or chemical plants, whereas Profibus excels in fast, deterministic communication ideal for factory automation, robotics, and discrete manufacturing. The robustness of Profibus DP (Decentralized Peripherals) and the versatility of Fieldbus Foundation protocols highlight their critical roles in enhancing production efficiency and real-time data exchange in industrial environments.
Advantages and Limitations
Fieldbus offers enhanced device-level communication with simplified wiring and reduced installation costs, making it ideal for complex automation systems. Profibus excels in high-speed, real-time data exchange and robust network diagnostics but requires specialized hardware and can be less flexible in mixed vendor environments. Your choice depends on system requirements for scalability, interoperability, and performance priorities.
Future Trends and Industry Adoption
Fieldbus technologies are evolving with increased integration of Ethernet-based solutions, enhancing real-time communication and interoperability across industrial automation systems. Profibus maintains strong industry adoption due to its reliability and extensive device compatibility, but the shift toward PROFINET reflects future trends favoring faster, scalable network architectures. Your choice should consider the growing demand for high-speed data transfer and seamless integration within Industry 4.0 environments.
Fieldbus vs Profibus Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com