A process transmitter converts physical process variables into standardized output signals, enabling accurate monitoring and control in industrial systems, while a signal isolator protects equipment by electrically isolating input and output signals to prevent ground loops and interference. Explore the rest of the article to understand which device suits Your application needs best.
Table of Comparison
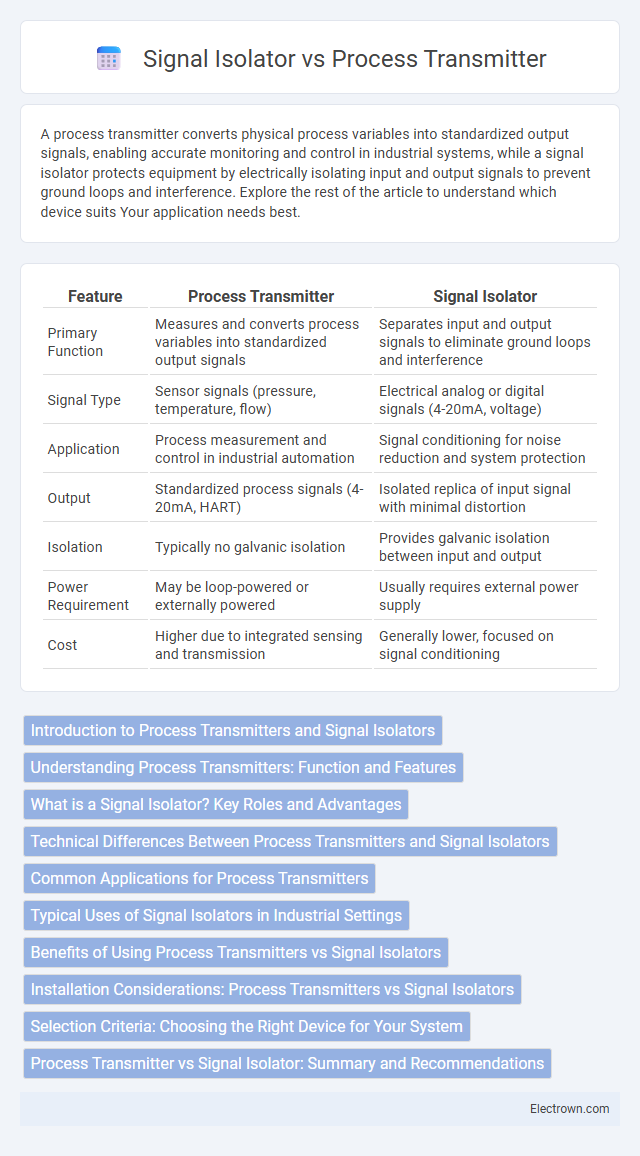
| Feature | Process Transmitter | Signal Isolator |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Measures and converts process variables into standardized output signals | Separates input and output signals to eliminate ground loops and interference |
| Signal Type | Sensor signals (pressure, temperature, flow) | Electrical analog or digital signals (4-20mA, voltage) |
| Application | Process measurement and control in industrial automation | Signal conditioning for noise reduction and system protection |
| Output | Standardized process signals (4-20mA, HART) | Isolated replica of input signal with minimal distortion |
| Isolation | Typically no galvanic isolation | Provides galvanic isolation between input and output |
| Power Requirement | May be loop-powered or externally powered | Usually requires external power supply |
| Cost | Higher due to integrated sensing and transmission | Generally lower, focused on signal conditioning |
Introduction to Process Transmitters and Signal Isolators
Process transmitters convert physical parameters such as pressure, temperature, or flow into standardized electrical signals for monitoring and control systems. Signal isolators prevent ground loops and electrical noise by electrically separating input and output signals, ensuring signal integrity and system safety. Both devices play crucial roles in industrial automation by enhancing measurement accuracy and protecting instrumentation networks.
Understanding Process Transmitters: Function and Features
Process transmitters convert physical process parameters such as temperature, pressure, and flow into standardized electrical signals for accurate monitoring and control. Their features include high precision, robust housings for industrial environments, and compatibility with various sensor inputs to ensure reliable data transmission. You can optimize system performance by selecting a transmitter that matches your specific measurement requirements and electrical output standards.
What is a Signal Isolator? Key Roles and Advantages
A signal isolator is a critical device used in industrial automation to electrically separate input and output signals, preventing ground loops and reducing noise interference that can compromise measurement accuracy. Key roles include protecting sensitive equipment, ensuring signal integrity, and enhancing system safety by isolating different process segments. Your process control system benefits from improved reliability, reduced downtime, and more accurate data transmission when integrating a high-quality signal isolator.
Technical Differences Between Process Transmitters and Signal Isolators
Process transmitters convert physical process variables such as pressure, temperature, or flow into standardized electrical signals for control systems, offering accurate measurement and output functionality. Signal isolators primarily serve to electrically isolate input and output signals, preventing ground loops and reducing noise without altering the measurement value. Key technical differences include the transmitter's active sensing and signal generation capabilities contrasted with the isolator's passive signal conditioning and protection features.
Common Applications for Process Transmitters
Process transmitters are commonly used in industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and water treatment to accurately measure parameters like pressure, temperature, and flow. These devices convert physical measurements into standardized signals for monitoring and control systems, ensuring reliable process automation and safety. Your choice of a process transmitter can optimize data communication while minimizing interference, which is critical in complex industrial environments.
Typical Uses of Signal Isolators in Industrial Settings
Signal isolators are commonly used in industrial settings to eliminate ground loops and prevent electrical noise interference, ensuring accurate and stable signal transmission. They protect sensitive measurement instruments by electrically isolating input and output signals, which is critical in environments with high-voltage equipment or varying ground potentials. Your control systems benefit from increased reliability and safety when signal isolators are deployed between process transmitters and receiving devices.
Benefits of Using Process Transmitters vs Signal Isolators
Process transmitters provide precise measurement and real-time data transmission, enhancing process control and operational efficiency in industrial automation. Signal isolators prevent ground loops and electrical noise, ensuring signal integrity and equipment protection by electrically separating input and output signals. Using process transmitters offers the benefit of integrated measurement and communication, reducing wiring complexity compared to signal isolators, which are primarily focused on signal protection rather than measurement.
Installation Considerations: Process Transmitters vs Signal Isolators
Process transmitters require direct connection to sensing elements, often demanding precise mounting and calibration near process points to ensure accurate data transmission. Signal isolators are typically installed inline within control loops or between field devices and control systems, emphasizing electrical isolation and noise reduction while maintaining signal integrity. Proper grounding and wiring practices are critical for both devices, but signal isolators often necessitate additional space and compliance with electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards.
Selection Criteria: Choosing the Right Device for Your System
Selecting between a process transmitter and a signal isolator depends on factors such as the need for accurate measurement, signal conditioning, and protection against ground loops or electrical noise. Process transmitters are ideal for applications requiring direct measurement and conversion of process variables into standardized signals, while signal isolators are essential for electrical isolation and ensuring signal integrity in complex or noisy environments. Consider process parameters, installation environment, and required signal accuracy to choose the most suitable device for optimal system performance.
Process Transmitter vs Signal Isolator: Summary and Recommendations
Process transmitters convert physical measurements such as pressure, temperature, or flow into standardized electrical signals for monitoring and control, ensuring accurate data transmission in industrial systems. Signal isolators provide electrical isolation between measurement devices and control systems, preventing ground loops, reducing noise, and protecting sensitive instrumentation. For applications requiring signal integrity and protection in noisy environments, use signal isolators; for direct measurement conversion and transmission, process transmitters are recommended.
Process Transmitter vs Signal Isolator Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com