VFDs control motor speed by adjusting frequency and voltage, making them ideal for simple variable speed applications and energy savings, while servo drives provide precise position, velocity, and torque control essential for high-performance industrial automation. Discover which drive suits your specific needs by exploring the detailed comparisons ahead.
Table of Comparison
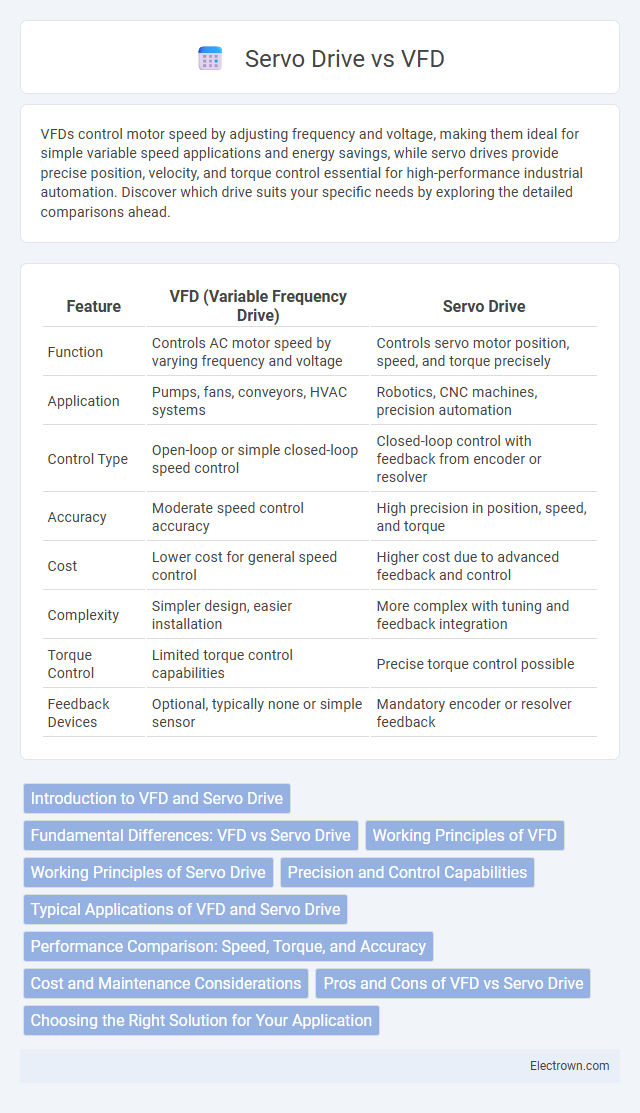
| Feature | VFD (Variable Frequency Drive) | Servo Drive |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Controls AC motor speed by varying frequency and voltage | Controls servo motor position, speed, and torque precisely |
| Application | Pumps, fans, conveyors, HVAC systems | Robotics, CNC machines, precision automation |
| Control Type | Open-loop or simple closed-loop speed control | Closed-loop control with feedback from encoder or resolver |
| Accuracy | Moderate speed control accuracy | High precision in position, speed, and torque |
| Cost | Lower cost for general speed control | Higher cost due to advanced feedback and control |
| Complexity | Simpler design, easier installation | More complex with tuning and feedback integration |
| Torque Control | Limited torque control capabilities | Precise torque control possible |
| Feedback Devices | Optional, typically none or simple sensor | Mandatory encoder or resolver feedback |
Introduction to VFD and Servo Drive
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) control the speed of AC motors by adjusting the frequency and voltage supplied, optimizing energy consumption and performance in applications such as pumps, fans, and conveyors. Servo Drives provide precise control of position, speed, and torque in servo motors, making them essential for robotics, CNC machines, and automated manufacturing systems. Both technologies enhance efficiency and accuracy but serve distinct roles based on system requirements and complexity.
Fundamental Differences: VFD vs Servo Drive
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) regulate AC motor speed by adjusting frequency and voltage, primarily used for constant torque applications in pumps, fans, and conveyors. Servo drives provide precise position, speed, and torque control through feedback mechanisms, ideal for robotics, CNC machines, and automated manufacturing. The fundamental difference lies in control accuracy and application specificity: VFDs offer broad speed control for standard motors, whereas servo drives deliver high-performance motion control with closed-loop feedback systems.
Working Principles of VFD
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) regulate motor speed by adjusting the frequency and voltage of the power supplied to an AC motor, utilizing pulse width modulation (PWM) to synthesize a variable voltage waveform. This control method allows precise speed adjustment by changing the input power frequency, directly influencing the motor's synchronous speed. VFDs optimize energy efficiency and process control in applications requiring variable motor speeds, such as conveyors, pumps, and HVAC systems.
Working Principles of Servo Drive
Servo drives operate by receiving input signals from a controller and regulating the position, velocity, and torque of servo motors through continuous feedback using encoders or resolvers. They employ closed-loop control systems to adjust motor output precisely, ensuring accurate motion control in real-time applications. This contrasts with VFDs, which mainly vary motor speed by adjusting voltage and frequency without direct feedback for positioning.
Precision and Control Capabilities
Servo drives offer superior precision and control capabilities compared to VFDs, as they use feedback systems like encoders to achieve accurate position, speed, and torque control. VFDs primarily control motor speed by varying frequency and voltage, which limits their ability to maintain exact positioning and fine-tuned motion. Your application will benefit from servo drives when high-precision movements and dynamic response are essential.
Typical Applications of VFD and Servo Drive
VFDs (Variable Frequency Drives) are commonly used in applications requiring adjustable speed control of AC motors, such as pumps, fans, conveyors, and HVAC systems, where energy efficiency and simple speed regulation are essential. Servo drives excel in precision motion control applications like robotics, CNC machinery, printing presses, and automated assembly lines, where accurate positioning and rapid response are critical. Your choice between VFD and servo drive depends on the required performance, with VFDs suited for general-purpose speed control and servo drives designed for high-precision, dynamic movements.
Performance Comparison: Speed, Torque, and Accuracy
VFDs provide variable speed control with good torque performance but lack the precise accuracy of servo drives, which deliver superior speed control, high torque at low speeds, and exceptional positional accuracy through closed-loop feedback. Servo drives maintain consistent torque across a wide speed range and excel in applications requiring rapid acceleration, deceleration, and precise motion control. Your choice depends on the need for high-precision motion versus general variable speed control in industrial automation.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
VFDs (Variable Frequency Drives) typically have lower upfront costs and simpler maintenance requirements compared to servo drives, making them cost-effective for applications with basic speed control needs. Servo drives, while more expensive initially, offer precise control and higher efficiency, which can reduce long-term operational costs in high-performance or complex systems. Your choice should consider the total cost of ownership, including maintenance complexity, frequency of repairs, and the level of accuracy required for your specific application.
Pros and Cons of VFD vs Servo Drive
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) offer cost-effective speed control, energy efficiency, and simple installation but lack precise positioning and high dynamic response, making them ideal for pumps and fans. Servo drives provide superior accuracy, fast acceleration, and precise torque control, suitable for robotics and CNC machines, but come with higher costs and complexity. Choosing between VFD and servo drive depends on the application's requirement for precision, speed control, and budget constraints.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Application
Selecting between a Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) and a Servo Drive depends on application precision, speed control, and load dynamics. VFDs excel in controlling standard AC motors for energy-efficient variable speed applications with moderate accuracy, while Servo Drives provide high-precision torque, position, and speed control essential for robotics and CNC machines. Assessing factors such as required feedback systems, response time, and cost-efficiency ensures the optimal drive choice for your specific industrial or automation needs.
VFD vs Servo Drive Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com