Dual converters offer precise speed control by converting AC to DC and back to AC, enabling smooth bidirectional motor operation. Understanding the differences between dual converters and cycloconverters can help you choose the best solution for your power conversion needs--continue reading to explore their unique features and applications.
Table of Comparison
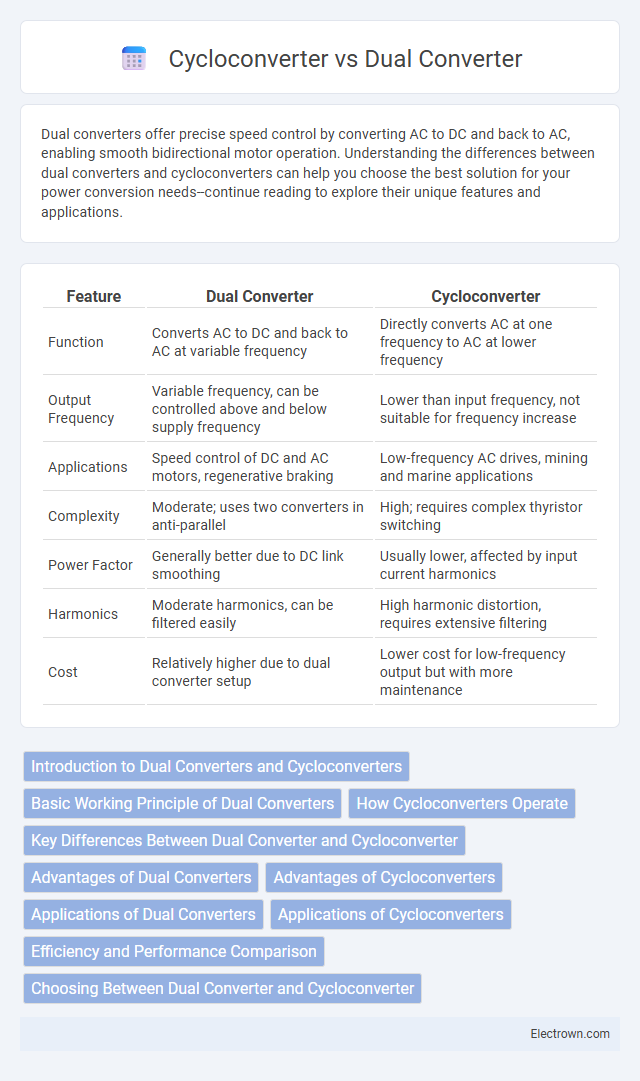
| Feature | Dual Converter | Cycloconverter |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Converts AC to DC and back to AC at variable frequency | Directly converts AC at one frequency to AC at lower frequency |
| Output Frequency | Variable frequency, can be controlled above and below supply frequency | Lower than input frequency, not suitable for frequency increase |
| Applications | Speed control of DC and AC motors, regenerative braking | Low-frequency AC drives, mining and marine applications |
| Complexity | Moderate; uses two converters in anti-parallel | High; requires complex thyristor switching |
| Power Factor | Generally better due to DC link smoothing | Usually lower, affected by input current harmonics |
| Harmonics | Moderate harmonics, can be filtered easily | High harmonic distortion, requires extensive filtering |
| Cost | Relatively higher due to dual converter setup | Lower cost for low-frequency output but with more maintenance |
Introduction to Dual Converters and Cycloconverters
Dual converters consist of two controlled rectifiers connected in antiparallel, enabling bidirectional power flow and precise speed control in DC motors by converting AC to variable DC voltage. Cycloconverters directly convert AC power from one frequency to another lower frequency without an intermediate DC link, making them ideal for low-speed, high-power applications such as large synchronous motors. Your choice between a dual converter and cycloconverter depends on the specific requirements for frequency control and power conversion efficiency in your application.
Basic Working Principle of Dual Converters
Dual converters operate by using two rectifiers connected in anti-parallel to provide both positive and negative voltage outputs, enabling seamless reversible DC power conversion. They achieve controlled bidirectional current flow by alternately switching between the rectifiers, facilitating smooth regulation of output voltage and current. This principle is widely employed in applications requiring precise speed control and regenerative braking in DC motor drives.
How Cycloconverters Operate
Cycloconverters operate by directly converting fixed-frequency AC power to variable-frequency AC power without an intermediate DC stage, using an array of thyristors or semiconductor switches to control output voltage and frequency. These devices synthesize the output waveform by segmenting and phase-shifting portions of the input AC waveform, enabling smooth frequency modulation typically in the low-frequency range. Cycloconverters are commonly employed in applications requiring adjustable speed control of large AC motors, such as in rolling mills and ship propulsion systems, due to their ability to provide continuous and stepless frequency variation.
Key Differences Between Dual Converter and Cycloconverter
Dual converters enable bidirectional power flow by combining two converters in antiparallel, allowing smooth and continuous control of DC motors at variable speeds. Cycloconverters directly convert AC input frequency to a lower output frequency without an intermediate DC link, mainly used for large synchronous or induction motors with low-speed, high-torque requirements. Key differences include operational frequency range, power flow directionality, complexity, and typical applications, where dual converters excel in precise DC motor control, and cycloconverters dominate in variable frequency AC drive systems.
Advantages of Dual Converters
Dual converters provide precise control of output voltage and enable bidirectional power flow, making them ideal for applications requiring smooth speed reversal and regenerative braking. They offer better efficiency and reduced harmonic distortion compared to cycloconverters, enhancing overall system performance. Dual converters also support continuous operation under varying load conditions due to their ability to quickly reverse the current direction without mechanical switching.
Advantages of Cycloconverters
Cycloconverters offer the advantage of directly converting fixed AC frequency to a variable AC frequency without an intermediate DC link, enhancing efficiency in low-frequency applications. They provide precise control over output frequency and voltage, making them ideal for large industrial motors requiring smooth speed variations. Your system benefits from reduced harmonic distortion and improved power factor compared to dual converters in specific use cases.
Applications of Dual Converters
Dual converters are widely used in applications requiring reversible DC power control, such as in electroplating, DC motor drives, and traction systems where precise speed and torque control is essential. They enable smooth and continuous variation of output voltage by combining two fully controlled converters operating in opposite directions, making them ideal for industrial processes demanding bidirectional power flow. Unlike cycloconverters, dual converters offer better control in DC applications and are preferred in situations where adjustable output voltage and current are critical.
Applications of Cycloconverters
Cycloconverters are primarily used in applications requiring variable frequency output at low frequencies, such as in large industrial motor drives, rolling mills, and ship propulsion systems. They efficiently convert fixed AC frequencies to a lower variable frequency without intermediate DC conversion, making them ideal for controlling heavy-duty motors with precise speed and torque. Your industrial processes benefit from cycloconverters when variable frequency control is needed for high-power, low-speed operations.
Efficiency and Performance Comparison
Dual converters offer higher efficiency and better performance in applications requiring smooth control of motor speed and direction due to their capability to provide continuous power flow with minimal harmonics. Cycloconverters typically exhibit lower efficiency because of their complex switching and limited output frequency range, leading to increased harmonic distortion and reduced power quality. Your choice depends on the specific application requirements, with dual converters favored for precise speed regulation and cycloconverters suitable for low-frequency large power drives.
Choosing Between Dual Converter and Cycloconverter
Choosing between a dual converter and a cycloconverter depends on your specific application requirements such as desired output frequency, control complexity, and power handling. Dual converters offer bidirectional power flow with precise speed control ideal for DC motor drives, while cycloconverters directly convert AC frequency, making them suitable for low-frequency applications like large synchronous motors. Your decision should consider factors like efficiency, harmonic distortion, and system cost to optimize performance and reliability.
Dual Converter vs Cycloconverter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com