Isolation transformers provide electrical isolation between circuits by having separate primary and secondary windings, enhancing safety and reducing noise interference. Autotransformers, on the other hand, use a single winding with taps for voltage adjustment, offering a more compact and cost-effective solution but without electrical isolation; explore the detailed comparison to determine which transformer suits your needs best.
Table of Comparison
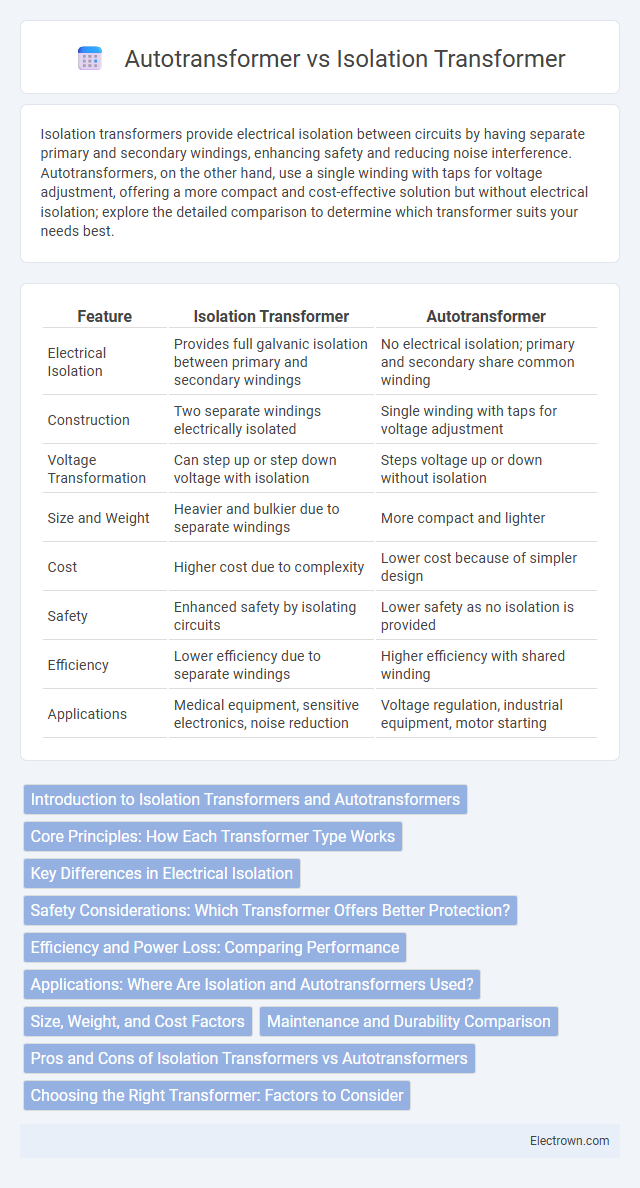
| Feature | Isolation Transformer | Autotransformer |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Isolation | Provides full galvanic isolation between primary and secondary windings | No electrical isolation; primary and secondary share common winding |
| Construction | Two separate windings electrically isolated | Single winding with taps for voltage adjustment |
| Voltage Transformation | Can step up or step down voltage with isolation | Steps voltage up or down without isolation |
| Size and Weight | Heavier and bulkier due to separate windings | More compact and lighter |
| Cost | Higher cost due to complexity | Lower cost because of simpler design |
| Safety | Enhanced safety by isolating circuits | Lower safety as no isolation is provided |
| Efficiency | Lower efficiency due to separate windings | Higher efficiency with shared winding |
| Applications | Medical equipment, sensitive electronics, noise reduction | Voltage regulation, industrial equipment, motor starting |
Introduction to Isolation Transformers and Autotransformers
Isolation transformers provide galvanic isolation between their input and output windings, enhancing safety and reducing electrical noise in sensitive equipment. Autotransformers share a single winding with electrically connected input and output sections, offering efficient voltage transformation with smaller size and reduced copper usage. Understanding your power requirements will help determine whether the isolation and noise reduction of an isolation transformer or the compact efficiency of an autotransformer is best suited for your application.
Core Principles: How Each Transformer Type Works
Isolation transformers operate using two separate windings--primary and secondary--that magnetically couple but electrically isolate the input from the output, ensuring safety by preventing direct electrical connection. Autotransformers utilize a single winding with a shared portion acting as both primary and secondary, allowing voltage transformation through tapping but lacking electrical isolation. Understanding these core principles helps you choose the right transformer for applications requiring either isolation or efficient voltage regulation.
Key Differences in Electrical Isolation
Isolation transformers provide complete electrical isolation between the input and output windings, ensuring no direct electrical connection and significantly reducing the risk of electric shock and noise interference. Autotransformers share a common winding for both input and output, offering voltage transformation without true isolation, which can lead to potential safety hazards in sensitive applications. The key difference lies in isolation transformers' ability to maintain galvanic isolation, whereas autotransformers do not, impacting safety and noise reduction capabilities.
Safety Considerations: Which Transformer Offers Better Protection?
Isolation transformers provide superior safety by physically separating the primary and secondary windings, reducing the risk of electric shock and minimizing the chance of ground faults. Autotransformers share a common winding between input and output, which can expose users to higher shock hazards and offer less protection against electrical noise and surges. For better protection of Your equipment and personal safety, isolation transformers are the preferred choice in sensitive or hazardous environments.
Efficiency and Power Loss: Comparing Performance
Isolation transformers generally exhibit lower efficiency than autotransformers due to their separate windings, which cause higher copper and core losses. Autotransformers offer improved efficiency and reduced power loss by sharing a common winding for primary and secondary circuits, minimizing material use and resistance. However, isolation transformers provide enhanced electrical isolation and safety at the expense of slightly increased losses and reduced efficiency.
Applications: Where Are Isolation and Autotransformers Used?
Isolation transformers are primarily used in medical equipment, sensitive electronic devices, and industrial machinery to provide electrical isolation and reduce noise interference. Autotransformers find applications in voltage regulation, motor starting, and power distribution systems due to their compact size and efficiency in stepping voltage up or down. Both transformer types are integral in ensuring stable and safe power delivery across various sectors.
Size, Weight, and Cost Factors
Isolation transformers are typically larger, heavier, and more expensive due to their separate primary and secondary windings, which provide galvanic isolation and enhanced safety. Autotransformers have a smaller size and lighter weight because they share common windings, resulting in reduced material usage and lower manufacturing costs. Your choice depends on the balance between safety requirements and budget constraints, with autotransformers offering cost efficiency but less electrical isolation.
Maintenance and Durability Comparison
Isolation transformers require more frequent maintenance due to their complex windings and insulation systems, ensuring safety and performance over time. Autotransformers, with fewer windings and simpler construction, generally offer greater durability and lower upkeep costs but lack the isolation benefits. Your choice should consider the balance between the need for electrical isolation and long-term maintenance investment.
Pros and Cons of Isolation Transformers vs Autotransformers
Isolation transformers provide galvanic isolation, enhancing safety by preventing direct electrical connection between circuits and reducing noise and interference, but they are typically larger, heavier, and more expensive than autotransformers. Autotransformers offer higher efficiency, smaller size, and cost-effectiveness by sharing winding sections but lack isolation, posing a higher risk of electrical shock and noise transmission. Choosing between the two depends on prioritizing safety and noise reduction with isolation transformers or efficiency and cost savings with autotransformers.
Choosing the Right Transformer: Factors to Consider
When choosing between an isolation transformer and an autotransformer, consider factors such as electrical isolation requirements, voltage regulation, and safety needs. Isolation transformers provide galvanic isolation, enhancing safety by preventing direct electrical contact and reducing noise, ideal for sensitive equipment. Autotransformers are more compact and efficient for voltage adjustment but lack isolation, making them suitable when isolation is not critical for your application.
isolation transformer vs autotransformer Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com