Float switches detect liquid levels through physical contact with the fluid surface, making them ideal for controlling pumps and alarms in tanks. Proximity switches sense the presence of objects without contact using electromagnetic fields, suited for detecting solid items or metal parts; discover the key differences and applications to choose the right switch for your needs in the full article.
Table of Comparison
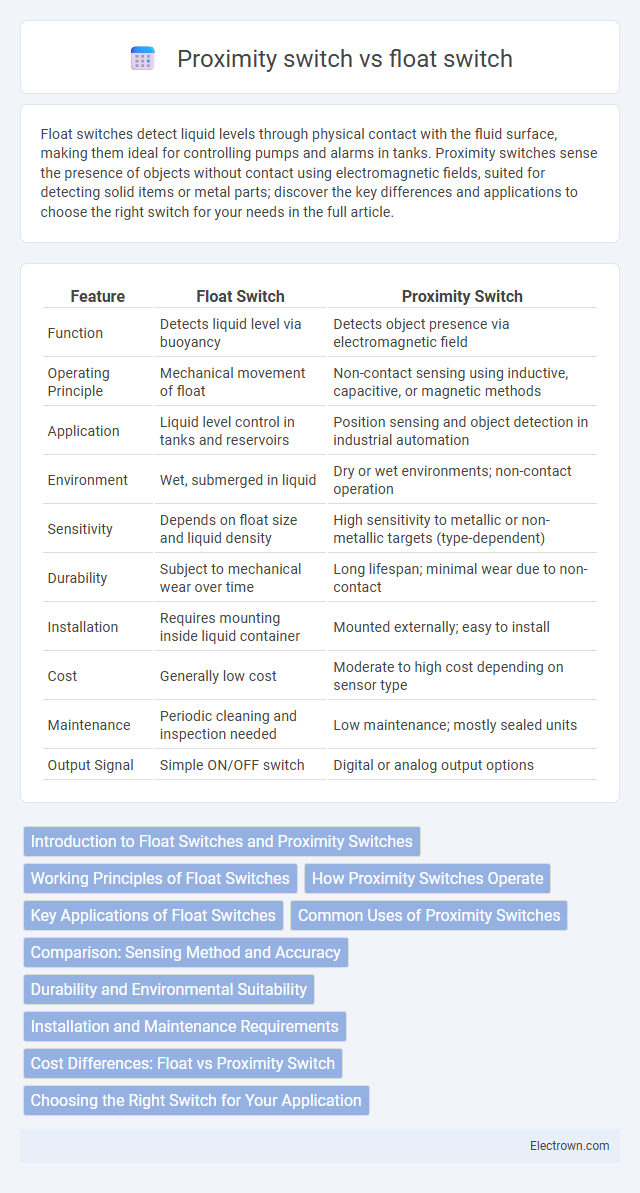
| Feature | Float Switch | Proximity Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Detects liquid level via buoyancy | Detects object presence via electromagnetic field |
| Operating Principle | Mechanical movement of float | Non-contact sensing using inductive, capacitive, or magnetic methods |
| Application | Liquid level control in tanks and reservoirs | Position sensing and object detection in industrial automation |
| Environment | Wet, submerged in liquid | Dry or wet environments; non-contact operation |
| Sensitivity | Depends on float size and liquid density | High sensitivity to metallic or non-metallic targets (type-dependent) |
| Durability | Subject to mechanical wear over time | Long lifespan; minimal wear due to non-contact |
| Installation | Requires mounting inside liquid container | Mounted externally; easy to install |
| Cost | Generally low cost | Moderate to high cost depending on sensor type |
| Maintenance | Periodic cleaning and inspection needed | Low maintenance; mostly sealed units |
| Output Signal | Simple ON/OFF switch | Digital or analog output options |
Introduction to Float Switches and Proximity Switches
Float switches detect liquid levels by using a buoyant sensor that rises or falls with the fluid, triggering an electrical switch to control pumps or alarms. Proximity switches operate without physical contact, sensing the presence of objects through electromagnetic fields, capacitance, or inductance, making them ideal for non-invasive level detection or position sensing. Both switches serve critical roles in automation and level measurement, with float switches suited for direct liquid interface and proximity switches preferred for solid object detection or sealed environments.
Working Principles of Float Switches
Float switches operate by utilizing a buoyant component that rises and falls with liquid levels, triggering an internal mechanical or magnetic switch to signal level changes. These switches rely on the displacement of the float to open or close electrical circuits, commonly used for liquid level detection in tanks, wells, and sumps. The simplicity and reliability of float switches make them ideal for controlling pumps, alarms, and other devices based on liquid presence or absence.
How Proximity Switches Operate
Proximity switches operate by detecting the presence of nearby objects without physical contact, using sensors such as inductive, capacitive, or ultrasonic technologies to trigger signals. These switches are ideal for applications requiring reliable detection in harsh environments since they function based on electromagnetic fields or sound waves rather than mechanical movement. Your choice between a float switch and a proximity switch should consider the need for non-contact operation and the type of materials or liquids involved in the application.
Key Applications of Float Switches
Float switches are predominantly used in liquid level detection for applications such as water tanks, sump pumps, and industrial fluid reservoirs. These devices provide reliable on/off control to prevent overflow or dry-run conditions in wastewater treatment plants, cooling systems, and chemical processing units. Their durability in harsh environments makes them essential for automation in marine, agricultural irrigation, and HVAC systems.
Common Uses of Proximity Switches
Proximity switches are commonly used in industrial automation for detecting the presence or absence of objects without physical contact, improving durability and reducing wear. They are frequently employed in conveyor systems, position sensing, and safety interlocks to ensure precise and reliable machine operations. Unlike float switches, proximity switches are ideal for detecting metal or other materials where fluid level measurement is not required.
Comparison: Sensing Method and Accuracy
Float switches use a physical float to detect liquid levels via buoyancy, providing reliable measurement in water and similar liquids but with limited precision and slower response times. Proximity switches employ magnetic, inductive, or capacitive sensing to detect the presence or absence of objects without direct contact, offering higher accuracy and faster response suitable for solid materials or metal surfaces. Choosing the right switch depends on your required sensing method and the accuracy necessary for your specific application.
Durability and Environmental Suitability
Float switches offer high durability in liquid environments, being corrosion-resistant and ideal for water, wastewater, and chemical tanks. Proximity switches, especially capacitive or inductive types, provide robust non-contact sensing with long-lasting performance in harsh industrial settings but may be less effective in turbulent liquids. Your choice depends on the specific environmental conditions and the required maintenance intervals for optimal system reliability.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Float switches require careful positioning within tanks to ensure accurate liquid level detection, often necessitating secure mounting and periodic cleaning to prevent debris buildup and ensure reliable operation. Proximity switches, typically installed near target objects or surfaces, demand precise alignment and calibration to maintain sensitivity, with minimal cleaning needed due to their non-contact sensing method. Maintenance for float switches tends to be more frequent due to mechanical parts subject to wear and environmental exposure, while proximity switches offer longer service intervals with fewer mechanical failures.
Cost Differences: Float vs Proximity Switch
Float switches generally offer a more cost-effective solution for liquid level detection due to their simple mechanical design and widespread availability. Proximity switches, incorporating advanced sensing technology like capacitive or ultrasonic sensors, typically come with higher initial costs but provide enhanced durability and fewer maintenance requirements in harsh environments. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including installation and long-term reliability, often favors float switches in budget-sensitive applications while proximity switches suit precision and longevity needs.
Choosing the Right Switch for Your Application
Choosing the right switch for your application depends on factors like liquid type, environmental conditions, and required sensitivity. Float switches are ideal for detecting liquid levels in tanks with stable, clean fluids, offering reliable mechanical operation. Proximity switches provide non-contact detection suitable for corrosive environments or when precision is critical in your automated system.
float switch vs proximity switch Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com