Triaxial accelerometers measure acceleration across three axes (X, Y, and Z), providing more comprehensive motion data compared to biaxial accelerometers, which capture movement on only two axes. Discover how choosing between these sensors can impact your project's accuracy and performance in the full article.
Table of Comparison
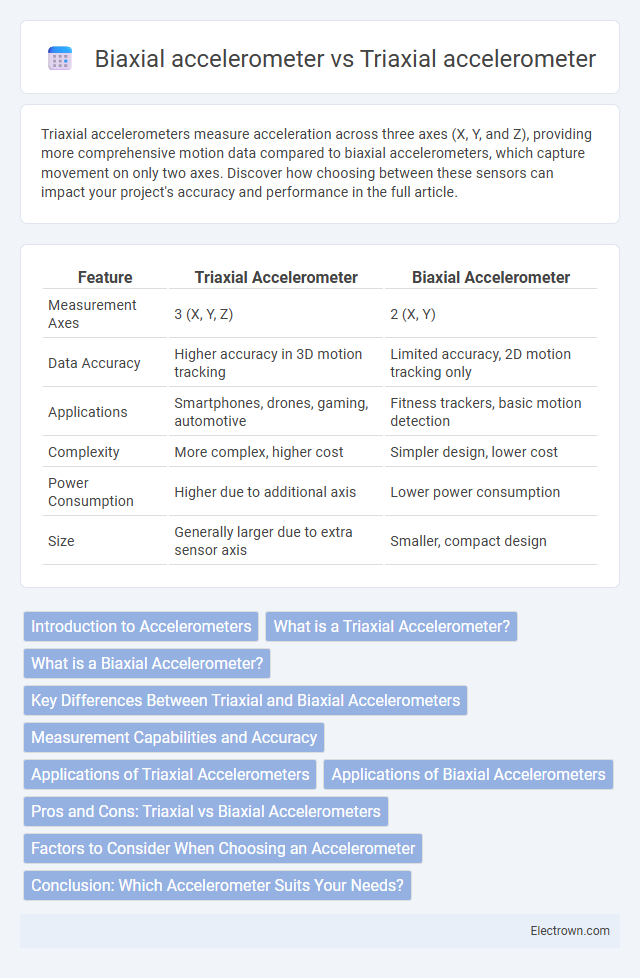
| Feature | Triaxial Accelerometer | Biaxial Accelerometer |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Axes | 3 (X, Y, Z) | 2 (X, Y) |
| Data Accuracy | Higher accuracy in 3D motion tracking | Limited accuracy, 2D motion tracking only |
| Applications | Smartphones, drones, gaming, automotive | Fitness trackers, basic motion detection |
| Complexity | More complex, higher cost | Simpler design, lower cost |
| Power Consumption | Higher due to additional axis | Lower power consumption |
| Size | Generally larger due to extra sensor axis | Smaller, compact design |
Introduction to Accelerometers
Triaxial accelerometers measure acceleration along three perpendicular axes (X, Y, and Z), providing comprehensive motion data, while biaxial accelerometers detect acceleration on only two axes. The added axis in triaxial models enables more precise monitoring of complex movements and vibrations, crucial for applications like wearable devices, robotics, and automotive safety systems. Biaxial accelerometers are often used in simpler contexts where motion occurs primarily in two dimensions, such as touchscreen orientation detection and basic tilt sensing.
What is a Triaxial Accelerometer?
A triaxial accelerometer measures acceleration forces along three perpendicular axes--X, Y, and Z--providing comprehensive data on movement and orientation in three-dimensional space. It captures dynamic and static acceleration, enabling precise detection of tilt, vibration, and shock in applications such as smartphones, automotive systems, and industrial machinery. Compared to biaxial accelerometers, which only detect acceleration along two axes, triaxial accelerometers offer enhanced accuracy and versatility in motion sensing and monitoring.
What is a Biaxial Accelerometer?
A biaxial accelerometer measures acceleration along two perpendicular axes, typically the X and Y axes, making it suitable for applications requiring detection of motion or tilt in a plane. Unlike triaxial accelerometers that capture movement across three axes (X, Y, and Z), biaxial sensors provide a more simplified, cost-effective solution for monitoring two-dimensional dynamic forces. Common uses include automotive stability control, robotics, and handheld device orientation where planar motion data is sufficient.
Key Differences Between Triaxial and Biaxial Accelerometers
Triaxial accelerometers measure acceleration along three orthogonal axes (X, Y, and Z), providing comprehensive motion data including vertical, lateral, and longitudinal movements, whereas biaxial accelerometers capture acceleration on only two axes, typically X and Y, limiting the scope of motion analysis. The enhanced dimensional sensing of triaxial accelerometers enables more accurate monitoring in applications such as vibration analysis, human motion tracking, and automotive crash detection compared to the simpler biaxial models. Power consumption and size may be higher for triaxial accelerometers due to their increased complexity, but they offer superior precision for complex motion detection tasks.
Measurement Capabilities and Accuracy
Triaxial accelerometers measure acceleration along three orthogonal axes (X, Y, and Z), providing comprehensive motion tracking and improved accuracy in dynamic environments compared to biaxial accelerometers, which measure only two axes. The added Z-axis measurement in triaxial sensors enables more precise orientation detection and vibration analysis, reducing errors from rotational movements and axis cross-talk. Consequently, triaxial accelerometers are preferred for applications requiring high-fidelity motion data, such as smartphones, robotics, and structural health monitoring.
Applications of Triaxial Accelerometers
Triaxial accelerometers provide three-dimensional acceleration data, making them essential in applications such as vehicle dynamics analysis, wearable fitness trackers, and structural health monitoring where precise motion detection is critical. These devices capture movement along the X, Y, and Z axes, enabling more comprehensive data compared to biaxial accelerometers, which only measure two axes. Your choice of a triaxial accelerometer enhances accuracy in navigation systems, robotics, and virtual reality environments by delivering richer motion insights.
Applications of Biaxial Accelerometers
Biaxial accelerometers are widely used in applications requiring the measurement of acceleration along two perpendicular axes, such as vehicle stability control, industrial machinery monitoring, and consumer electronics like smartphones for screen orientation detection. These sensors provide essential data for vibration analysis and impact detection where full triaxial data is unnecessary or cost-prohibitive. Your choice of a biaxial accelerometer can optimize performance and reduce complexity in systems focused on planar motion analysis.
Pros and Cons: Triaxial vs Biaxial Accelerometers
Triaxial accelerometers measure acceleration along three axes (X, Y, and Z), providing comprehensive motion data ideal for applications requiring precise 3D movement analysis, while biaxial accelerometers capture acceleration on only two axes, offering simpler, more cost-effective solutions with less complexity. Triaxial devices excel in fields like smartphones, drones, and fitness trackers due to their accuracy and versatility, but they tend to consume more power and are bulkier than biaxial sensors. Your choice depends on whether you need detailed spatial motion tracking or a lightweight, lower-power option.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Accelerometer
When choosing between a triaxial accelerometer and a biaxial accelerometer, consider the number of measurement axes required for accurate motion detection, with triaxial devices providing data along three perpendicular axes (X, Y, Z) for comprehensive spatial analysis compared to biaxial sensors measuring only two axes. Sensitivity requirements, application-specific vibration or shock levels, and the dimensionality of the monitored movement should guide the selection process. Additionally, factors such as power consumption, size constraints, and cost also influence the optimal choice between triaxial and biaxial accelerometers.
Conclusion: Which Accelerometer Suits Your Needs?
Triaxial accelerometers provide comprehensive motion detection across three axes, making them ideal for applications requiring precise 3D movement analysis, such as advanced robotics, automotive safety, and smartphone orientation tracking. Biaxial accelerometers capture acceleration on two axes and are suitable for simpler tasks like tilt sensing or basic vibration monitoring in cost-sensitive or space-constrained environments. Choosing between the two depends on the complexity of motion detection needed, with triaxial sensors offering greater versatility and biaxial units delivering efficient, targeted performance.
Triaxial accelerometer vs Biaxial accelerometer Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com