PWM output generates a variable voltage signal by switching between on and off states at a high frequency, making it ideal for controlling power to devices, while DAC output provides a true analog voltage that accurately represents a desired signal level. Understanding the differences between PWM and DAC outputs can help you choose the right method for precise voltage control or efficient power management; read on to explore their applications and advantages.
Table of Comparison
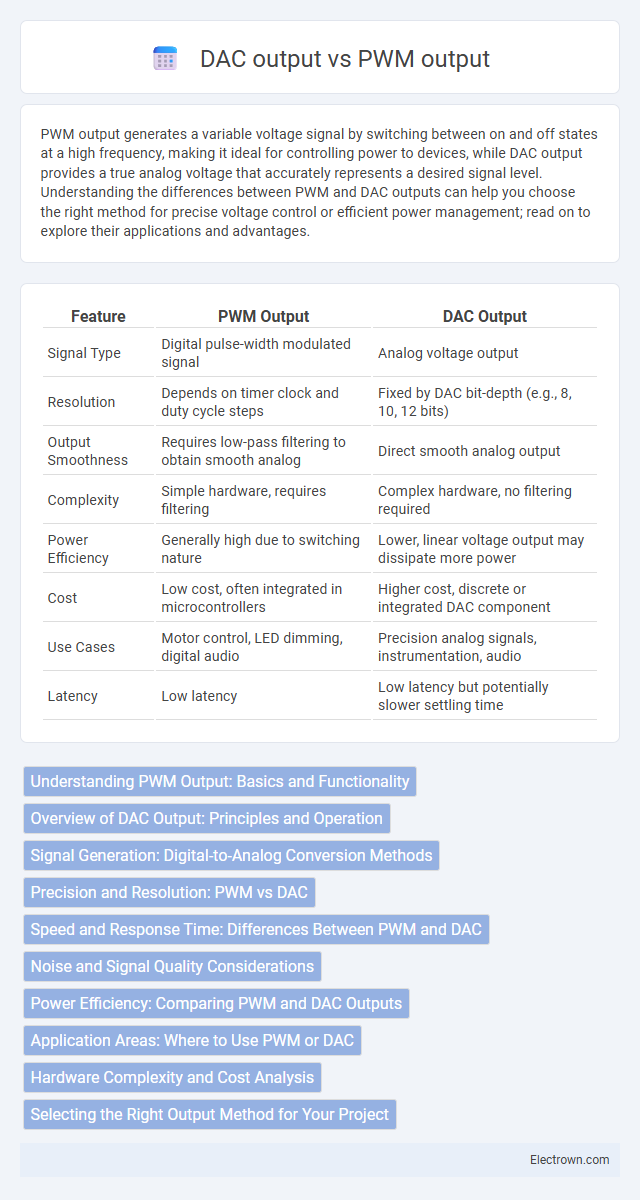
| Feature | PWM Output | DAC Output |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Type | Digital pulse-width modulated signal | Analog voltage output |
| Resolution | Depends on timer clock and duty cycle steps | Fixed by DAC bit-depth (e.g., 8, 10, 12 bits) |
| Output Smoothness | Requires low-pass filtering to obtain smooth analog | Direct smooth analog output |
| Complexity | Simple hardware, requires filtering | Complex hardware, no filtering required |
| Power Efficiency | Generally high due to switching nature | Lower, linear voltage output may dissipate more power |
| Cost | Low cost, often integrated in microcontrollers | Higher cost, discrete or integrated DAC component |
| Use Cases | Motor control, LED dimming, digital audio | Precision analog signals, instrumentation, audio |
| Latency | Low latency | Low latency but potentially slower settling time |
Understanding PWM Output: Basics and Functionality
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) output controls the effective voltage delivered to a load by varying the duty cycle of a fixed-frequency digital signal, enabling efficient power regulation without analog components. PWM signals toggle between on and off states rapidly, where the ratio of the on-time to the total period determines the average voltage perceived by the device. This digital modulation is commonly used in motor control, LED dimming, and power delivery systems due to its simplicity and ease of implementation.
Overview of DAC Output: Principles and Operation
DAC output converts digital signals into continuous analog voltages by utilizing binary-weighted resistor networks or sigma-delta modulation, ensuring precise voltage levels corresponding to digital input codes. PWM output generates analog-like signals by varying the duty cycle of a fixed-frequency square wave, relying on filtering to smooth the pulses into a steady voltage. Understanding these principles allows you to select the appropriate method for your application's resolution, speed, and complexity requirements.
Signal Generation: Digital-to-Analog Conversion Methods
PWM output generates analog voltage levels by modulating the duty cycle of a fixed-frequency digital signal, effectively creating a pulsed waveform that can be smoothed into an analog signal using a low-pass filter. DAC output directly converts a digital code into a precise analog voltage or current, providing a continuous and stable signal without the need for filtering. Signal generation via DACs offers higher accuracy and resolution, while PWM is favored for cost-effective, flexible analog approximations in embedded systems.
Precision and Resolution: PWM vs DAC
PWM output offers variable duty cycle control but typically has lower precision and resolution compared to DAC output, as it relies on digital pulses rather than true analog voltage levels. DAC output provides higher precision and finer resolution by converting digital values directly into smooth, continuous analog signals. Applications requiring accurate voltage control and minimal noise often prefer DACs over PWM for superior signal fidelity.
Speed and Response Time: Differences Between PWM and DAC
PWM output offers faster switching speeds with microsecond-level response times, making it ideal for applications requiring rapid signal changes. DAC output provides smoother, continuous analog signals but typically has slower response times due to conversion and settling delays. Your choice depends on whether speed and fast response or precise analog output quality are prioritized in your system design.
Noise and Signal Quality Considerations
PWM output generates signals with inherent high-frequency switching noise, which can affect signal quality without proper filtering. DAC output provides cleaner analog signals with lower noise levels, resulting in superior signal fidelity for sensitive applications. You can improve PWM signal quality by adding low-pass filters, but DACs remain the preferred choice for low-noise, high-precision analog output.
Power Efficiency: Comparing PWM and DAC Outputs
PWM output achieves higher power efficiency by rapidly switching between fully on and off states, minimizing energy loss as heat, whereas DAC output relies on analog voltage levels that often dissipate power in resistive elements. PWM signals enable efficient power delivery in applications such as motor control and LED dimming by controlling the duty cycle without continuous current draw. DAC outputs, while providing smoother signal representation, typically consume more power due to constant voltage regulation and linear operation.
Application Areas: Where to Use PWM or DAC
PWM output is ideal for applications requiring efficient power control and simple digital signaling, such as motor speed regulation, LED dimming, and switching power supplies. DAC output excels in precision analog signal generation needed in audio systems, waveform synthesis, and instrumentation where smooth voltage variations are crucial. Your choice depends on whether your application prioritizes power efficiency and digital control (PWM) or high-resolution and stable analog output (DAC).
Hardware Complexity and Cost Analysis
PWM output circuits typically exhibit lower hardware complexity and cost due to their reliance on simple digital components such as timers and switches, which reduce the need for precision analog circuitry. DAC output systems require more sophisticated components, including resistors, capacitors, and operational amplifiers, increasing both design complexity and production expenses. Your choice between PWM and DAC should consider these factors alongside performance requirements to optimize budget and implementation simplicity.
Selecting the Right Output Method for Your Project
Choosing between PWM output and DAC output depends on the project's accuracy and complexity requirements. PWM signals offer cost-effective, simple digital control suitable for applications like motor speed or LED brightness but require filtering for smooth analog voltage. DAC output delivers precise, noise-free analog voltages ideal for audio, instrumentation, and control systems demanding high resolution and linearity.
PWM output vs DAC output Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com