Arbitrary waveform generators (AWGs) produce complex, custom waveforms with high precision, while function generators typically output standard signals such as sine, square, and triangle waves. Understanding the differences in capabilities between these devices can help you choose the right tool for your signal testing needs--explore the rest of the article to learn more.
Table of Comparison
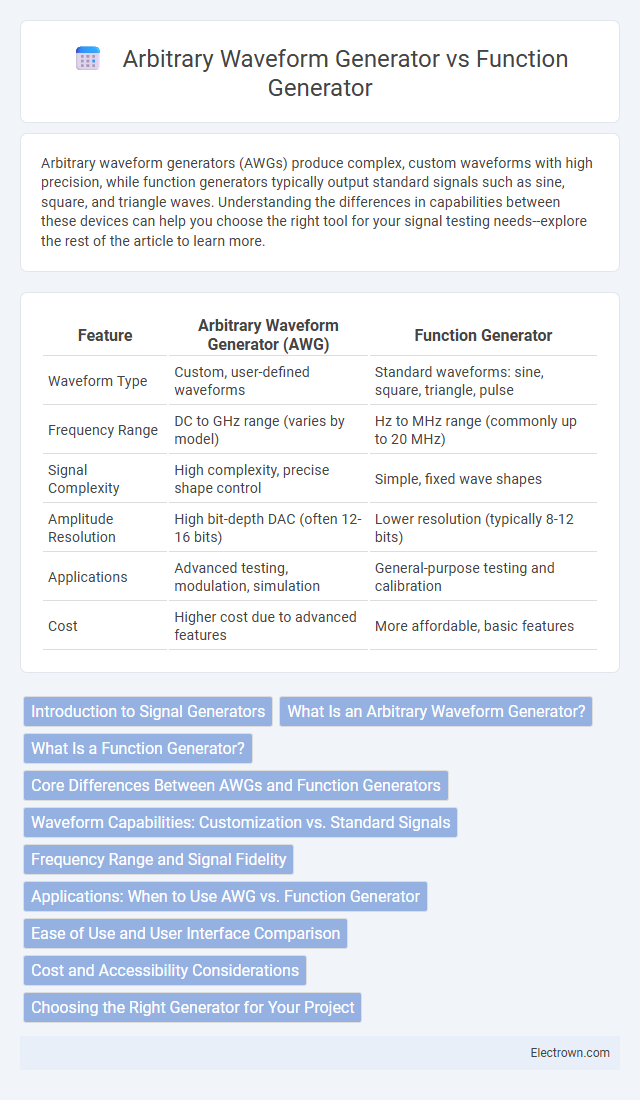
| Feature | Arbitrary Waveform Generator (AWG) | Function Generator |
|---|---|---|
| Waveform Type | Custom, user-defined waveforms | Standard waveforms: sine, square, triangle, pulse |
| Frequency Range | DC to GHz range (varies by model) | Hz to MHz range (commonly up to 20 MHz) |
| Signal Complexity | High complexity, precise shape control | Simple, fixed wave shapes |
| Amplitude Resolution | High bit-depth DAC (often 12-16 bits) | Lower resolution (typically 8-12 bits) |
| Applications | Advanced testing, modulation, simulation | General-purpose testing and calibration |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced features | More affordable, basic features |
Introduction to Signal Generators
Signal generators are essential devices in electronic testing and development, with arbitrary waveform generators (AWGs) and function generators being two primary types. AWGs offer precise control over waveform shapes, enabling the creation of complex, non-standard signals for advanced testing, while function generators typically produce standard waveforms like sine, square, and triangle waves. The choice between AWG and function generator depends on the required signal complexity, frequency range, and application specificity in fields such as telecommunications and circuit design.
What Is an Arbitrary Waveform Generator?
An arbitrary waveform generator (AWG) produces complex, user-defined waveforms by digitally synthesizing signals with precise control over amplitude, frequency, and phase, enabling the creation of non-standard waveforms for advanced testing. Unlike function generators that typically output basic waveforms such as sine, square, and triangle waves, AWGs allow the creation of customized, intricate signals needed in applications like communications, radar, and automated testing. High sampling rates and waveform memory in AWGs ensure accurate reproduction of sophisticated signal patterns essential for modern electronic system development.
What Is a Function Generator?
A function generator is a versatile electronic test instrument that produces standard waveforms such as sine, square, triangle, and sawtooth signals over a range of frequencies, commonly used for testing and calibration in laboratories and signal analysis. It generates repetitive waveforms with fixed and predictable shapes, suitable for routine applications like circuit testing and troubleshooting. Unlike arbitrary waveform generators, function generators have limited waveform customization, focusing on common predefined waveforms rather than fully user-defined signal shapes.
Core Differences Between AWGs and Function Generators
Arbitrary Waveform Generators (AWGs) produce customizable and complex waveforms defined by digital data, enabling precise signal modeling and advanced testing scenarios. Function generators typically output standard waveforms such as sine, square, triangle, and sawtooth with limited customization and resolution. AWGs offer higher sampling rates and deeper memory for waveform storage compared to the simpler signal generation and frequency sweep capabilities of function generators.
Waveform Capabilities: Customization vs. Standard Signals
Arbitrary waveform generators (AWGs) offer extensive customization, enabling you to design and output complex, user-defined waveforms beyond basic shapes. Function generators typically provide a limited set of standard signals such as sine, square, and triangle waves, suitable for general testing but less flexible. Your choice depends on whether precise waveform tailoring or standard signal generation is a higher priority for your application.
Frequency Range and Signal Fidelity
Arbitrary waveform generators (AWGs) typically offer a broader frequency range, often extending into hundreds of megahertz or gigahertz, allowing for precise waveform customization with high signal fidelity. Function generators usually provide a narrower frequency range, typically up to a few megahertz, with standard waveforms and less accurate signal reproduction. Your choice depends on the need for complex, high-frequency signals versus simple waveform generation with moderate fidelity.
Applications: When to Use AWG vs. Function Generator
Arbitrary waveform generators (AWGs) are ideal for applications requiring precise and complex signal creation, such as testing advanced communication systems, simulating sensor outputs, or developing custom-modulated waveforms. Function generators excel in scenarios needing standard waveforms like sine, square, triangle, or pulse signals, commonly used for basic signal testing, component characterization, and educational labs. Choose AWGs when high waveform customization and fidelity are critical, and select function generators for straightforward, routine waveform generation tasks.
Ease of Use and User Interface Comparison
Arbitrary waveform generators (AWGs) typically feature advanced touchscreen interfaces and customizable menus, providing greater flexibility but requiring a steeper learning curve compared to function generators. Function generators prioritize simplicity with straightforward knob controls and basic digital displays, making them more accessible for quick waveform selection and basic modulation tasks. Users seeking detailed signal customization may prefer AWGs despite their complexity, while those needing rapid setup and ease-of-use may opt for function generators.
Cost and Accessibility Considerations
Arbitrary waveform generators (AWGs) generally have a higher cost compared to function generators due to their ability to produce complex, customized signals, making them ideal for advanced testing environments. Function generators offer more accessible pricing and simpler operation, suitable for routine waveform generation tasks in educational or basic lab settings. Your choice depends on budget constraints and the level of waveform complexity required for your applications.
Choosing the Right Generator for Your Project
Selecting between an arbitrary waveform generator (AWG) and a function generator depends on the complexity and precision required by your project. AWGs offer high flexibility with customizable waveforms ideal for advanced testing and simulation scenarios, while function generators provide standard waveforms like sine, square, and triangle pulses suitable for general-purpose applications. Evaluating the waveform complexity, frequency range, and signal integrity needs ensures the optimal choice for accurate and efficient signal generation.
arbitrary waveform generator vs function generator Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com