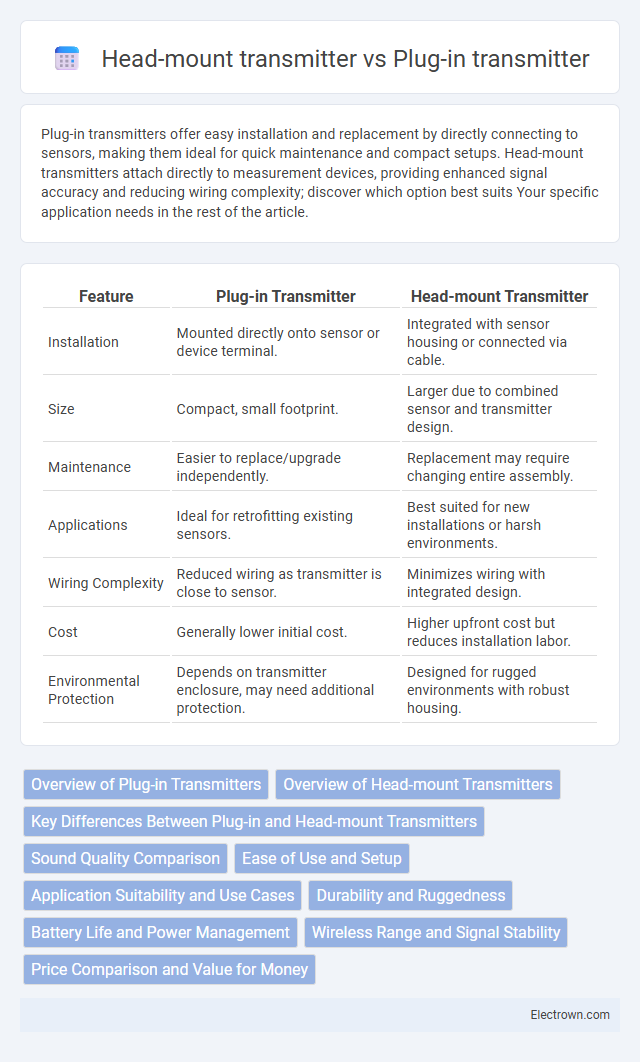
Plug-in transmitters offer easy installation and replacement by directly connecting to sensors, making them ideal for quick maintenance and compact setups. Head-mount transmitters attach directly to measurement devices, providing enhanced signal accuracy and reducing wiring complexity; discover which option best suits Your specific application needs in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Plug-in Transmitter | Head-mount Transmitter |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | Mounted directly onto sensor or device terminal. | Integrated with sensor housing or connected via cable. |
| Size | Compact, small footprint. | Larger due to combined sensor and transmitter design. |
| Maintenance | Easier to replace/upgrade independently. | Replacement may require changing entire assembly. |
| Applications | Ideal for retrofitting existing sensors. | Best suited for new installations or harsh environments. |
| Wiring Complexity | Reduced wiring as transmitter is close to sensor. | Minimizes wiring with integrated design. |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost. | Higher upfront cost but reduces installation labor. |
| Environmental Protection | Depends on transmitter enclosure, may need additional protection. | Designed for rugged environments with robust housing. |
Overview of Plug-in Transmitters
Plug-in transmitters are compact devices designed to attach directly to the sensor or process equipment, providing easy installation and maintenance without extensive wiring. These transmitters offer enhanced signal conditioning and digital communication capabilities, facilitating accurate measurement and real-time data transmission for various industrial applications. Your system benefits from plug-in transmitters by minimizing downtime and reducing installation complexity compared to head-mount transmitters.
Overview of Head-mount Transmitters
Head-mount transmitters are compact, self-contained devices designed to attach directly to process sensors, offering enhanced signal transmission with minimal wiring. Their integrated design reduces installation time and maintenance efforts compared to traditional plug-in transmitters, making them ideal for space-constrained or hazardous environments. These transmitters provide reliable, accurate data conversion and communication in industries such as chemical processing, oil and gas, and pharmaceuticals.
Key Differences Between Plug-in and Head-mount Transmitters
Plug-in transmitters attach directly to sensors, minimizing wiring complexity and enabling rapid installation, whereas head-mount transmitters are mounted separately, typically offering easier access for maintenance and calibration. Plug-in transmitters excel in compact setups and local signal processing, while head-mount transmitters provide enhanced isolation and are better suited for harsh environments due to their physical separation from the sensor. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right transmitter type for optimizing signal accuracy and system reliability in your industrial applications.
Sound Quality Comparison
Plug-in transmitters typically offer higher sound quality due to their direct connection to audio sources, minimizing signal loss and interference. Head-mount transmitters rely on built-in microphones that can introduce background noise and reduce clarity in complex acoustic environments. Both systems benefit from digital transmission, but the plug-in approach generally delivers superior fidelity for professional audio applications.
Ease of Use and Setup
Plug-in transmitters offer quick installation by connecting directly to existing devices, simplifying setup and reducing configuration time. Head-mount transmitters require initial calibration and secure attachment to the user, which may involve more detailed adjustments but provide hands-free operation. Ease of use favors plug-in transmitters for straightforward deployment, while head-mount transmitters excel in environments demanding mobility and continuous monitoring.
Application Suitability and Use Cases
Plug-in transmitters excel in applications requiring compact sensor integration and ease of installation, making them ideal for process control environments where space is limited. Head-mount transmitters, designed for direct attachment to sensors, offer superior ruggedness and are well-suited for harsh industrial settings involving temperature, pressure, and flow measurements. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize flexibility and quick deployment (plug-in) or durability and proximity to the sensor (head-mount) for optimized performance.
Durability and Ruggedness
Plug-in transmitters offer moderate durability, suitable for controlled environments but may be less resistant to harsh industrial conditions compared to head-mount transmitters. Head-mount transmitters are engineered for maximum ruggedness, featuring robust housings that withstand extreme temperatures, moisture, and vibration, making them ideal for demanding field applications. Your choice impacts long-term reliability, with head-mount transmitters providing superior resilience in tough environments.
Battery Life and Power Management
Plug-in transmitters typically offer longer battery life due to their larger internal batteries and more efficient power management systems, making them ideal for extended use without frequent recharging. Head-mount transmitters, while more compact and lightweight for ease of movement, often have shorter battery life and rely on smaller batteries that require more frequent replacement or charging. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize extended operational time or increased mobility during performance or recording sessions.
Wireless Range and Signal Stability
Plug-in transmitters typically offer limited wireless range due to their compact design and lower power output, making them ideal for short-distance communication in controlled environments. Head-mount transmitters provide enhanced signal stability and extended wireless range, benefiting from larger antennas and higher transmission power suitable for dynamic, mobile applications. Signal interference is minimized in head-mount units by advanced frequency management, whereas plug-in transmitters may experience more frequent dropouts in cluttered RF environments.
Price Comparison and Value for Money
Plug-in transmitters typically offer a lower upfront cost compared to head-mount transmitters, making them a budget-friendly choice for temporary or less demanding applications. Head-mount transmitters often provide enhanced durability, ergonomic design, and longer battery life, justifying their higher price with greater long-term value and user comfort. Evaluating total cost of ownership and performance needs is essential for determining which transmitter type delivers the best return on investment.
Plug-in transmitter vs Head-mount transmitter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com