Hot wire anemometers measure airflow velocity by detecting changes in heat loss from a heated wire, offering high sensitivity and rapid response ideal for low-speed air measurements. Vane anemometers, on the other hand, use a rotating vane to gauge airflow, providing durability and ease of use in outdoor or industrial environments; explore the full comparison to understand which device best suits Your airflow measurement needs.
Table of Comparison
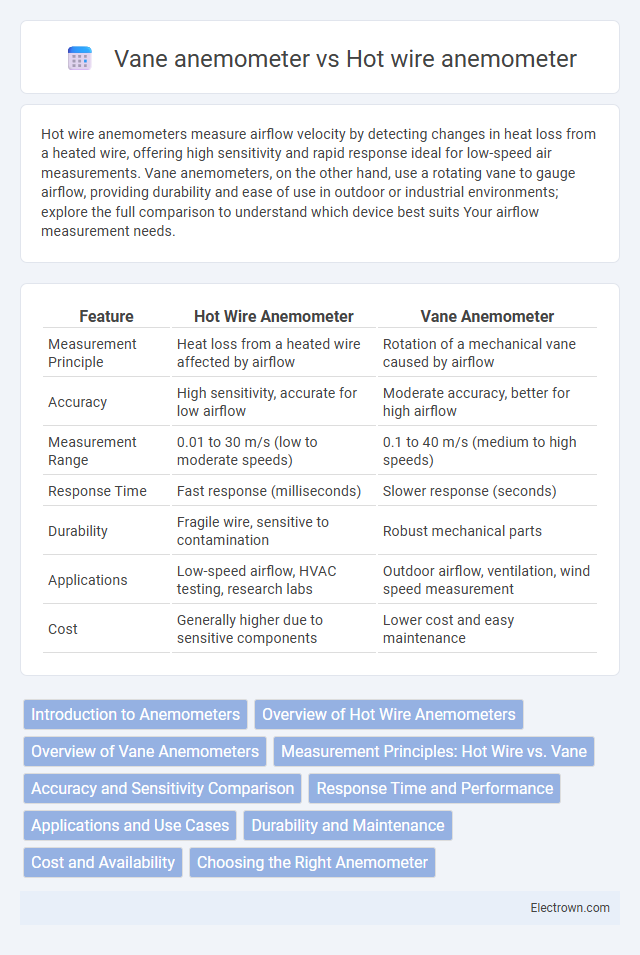
| Feature | Hot Wire Anemometer | Vane Anemometer |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Principle | Heat loss from a heated wire affected by airflow | Rotation of a mechanical vane caused by airflow |
| Accuracy | High sensitivity, accurate for low airflow | Moderate accuracy, better for high airflow |
| Measurement Range | 0.01 to 30 m/s (low to moderate speeds) | 0.1 to 40 m/s (medium to high speeds) |
| Response Time | Fast response (milliseconds) | Slower response (seconds) |
| Durability | Fragile wire, sensitive to contamination | Robust mechanical parts |
| Applications | Low-speed airflow, HVAC testing, research labs | Outdoor airflow, ventilation, wind speed measurement |
| Cost | Generally higher due to sensitive components | Lower cost and easy maintenance |
Introduction to Anemometers
Hot wire anemometers measure airflow velocity by detecting changes in electrical resistance of a heated wire cooled by the passing air, offering high sensitivity and rapid response for low-speed or turbulent flows. Vane anemometers use a rotating propeller or fan connected to a speed sensor, providing direct and reliable measurement of average wind speed in outdoor or industrial settings. Your choice between these anemometers depends on measurement precision, flow characteristics, and environmental conditions.
Overview of Hot Wire Anemometers
Hot wire anemometers measure air velocity by detecting changes in electrical resistance caused by the cooling effect of air flowing over a heated wire, providing high sensitivity and fast response times ideal for low-velocity airflow measurements. These devices are extensively used in aerodynamic research, HVAC system diagnostics, and environmental monitoring due to their precision and ability to capture turbulent air movements. Your choice between a hot wire and vane anemometer depends on the specific airflow characteristics and accuracy requirements of your application.
Overview of Vane Anemometers
Vane anemometers measure air velocity using a rotating fan or propeller that spins proportionally to the airflow, providing direct readings of wind speed. These devices are durable and effective for higher air velocities, making them suitable for HVAC system diagnostics and environmental monitoring. Unlike hot wire anemometers, vane anemometers are less sensitive to temperature variations but offer lower precision at very low airflow speeds.
Measurement Principles: Hot Wire vs. Vane
Hot wire anemometers measure airflow velocity by detecting heat loss from a heated wire exposed to the air stream, relying on convective heat transfer principles. Vane anemometers assess wind speed by mechanically rotating a propeller or fan, with rotation rate proportional to the airflow velocity. The hot wire method offers higher sensitivity and rapid response to turbulence, while vane anemometers provide straightforward, robust readings suitable for general airflow measurement.
Accuracy and Sensitivity Comparison
Hot wire anemometers offer superior accuracy and sensitivity compared to vane anemometers, as they measure air velocity based on heat loss from a heated wire, allowing detection of very low airflow rates with high precision. Vane anemometers rely on mechanical rotation, which can cause lag and reduced sensitivity in low-speed or turbulent airflows, resulting in less accurate measurements. You should choose a hot wire anemometer for detailed airflow analysis requiring precise and sensitive data, especially in low-velocity environments.
Response Time and Performance
Hot wire anemometers deliver superior response times, detecting rapid fluctuations in airflow with millisecond precision due to their thermal sensing technology. Vane anemometers, equipped with mechanical rotors, exhibit slower response times, generally less effective in capturing sudden changes or low turbulence airflow. Performance-wise, hot wire anemometers excel in accuracy and sensitivity for low-speed and variable airflow measurements, whereas vane anemometers perform reliably in steady, higher-velocity environments but lack fine temporal resolution.
Applications and Use Cases
Hot wire anemometers excel in measuring low-velocity airflow and turbulence in laboratory experiments, HVAC system diagnostics, and aerodynamic research where high sensitivity and rapid response are crucial. Vane anemometers are widely used in field applications such as industrial ventilation assessments, environmental monitoring, and outdoor airflow measurements due to their durability and ease of use. The choice between hot wire and vane anemometers depends on the precision required, environmental conditions, and the velocity range of the airflow being measured.
Durability and Maintenance
Hot wire anemometers require delicate sensor wires that can be easily damaged by dust and physical contact, leading to higher maintenance needs and lower overall durability. Vane anemometers feature robust mechanical components designed to withstand harsh environments and rough handling, offering greater longevity and easier maintenance. Selecting between the two depends on application conditions, with vane anemometers preferred for demanding industrial settings and hot wire anemometers suited for precise, clean airflow measurements.
Cost and Availability
Hot wire anemometers typically have a higher cost due to their sensitive thermal sensors and precise measurement capabilities, making them less common in general retail. Vane anemometers are more affordable and widely available, favored for their durability and straightforward mechanical design suitable for routine airflow measurement. Your choice depends on budget constraints and the specific accuracy requirements of your airflow monitoring tasks.
Choosing the Right Anemometer
Choosing the right anemometer depends on measurement needs and environment; hot wire anemometers excel in detecting low air velocities with high sensitivity, ideal for laboratory and HVAC system testing. Vane anemometers offer durability and straightforward use, suitable for outdoor applications and higher airflow measurements. Consider factors such as precision, response time, and physical conditions to select an anemometer that ensures accurate airflow data.
Hot wire anemometer vs Vane anemometer Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com