Optical pyrometers measure high temperatures by detecting the intensity of visible light emitted from an object, while infrared thermometers determine temperature by sensing infrared radiation without direct contact. To understand which device best suits Your temperature measurement needs, explore the detailed comparison in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
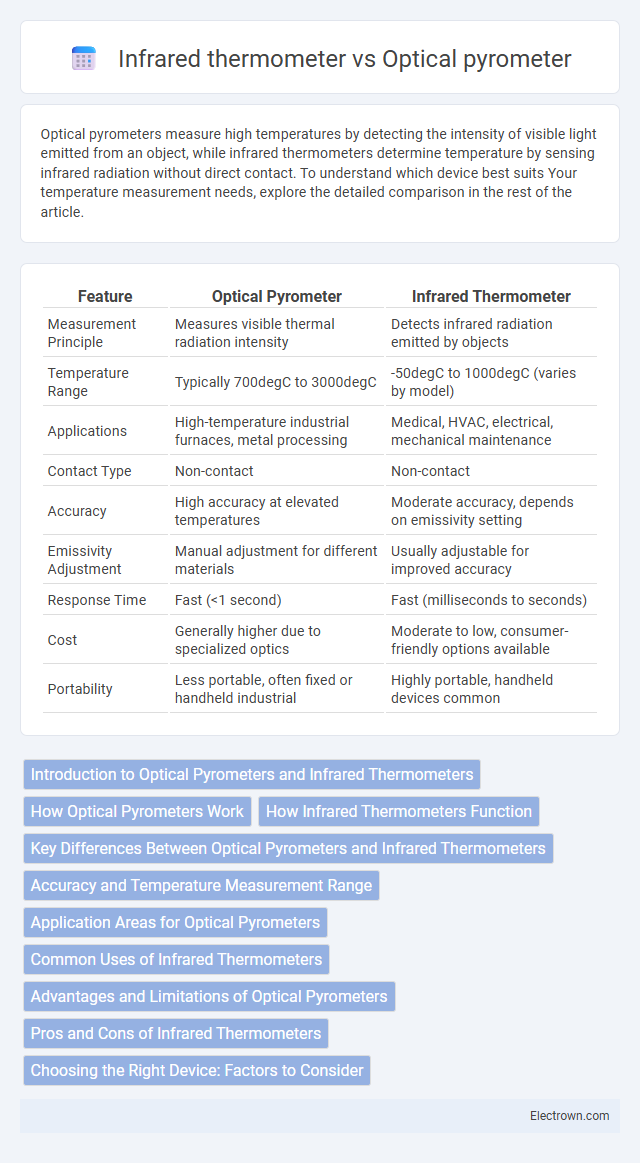
| Feature | Optical Pyrometer | Infrared Thermometer |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Principle | Measures visible thermal radiation intensity | Detects infrared radiation emitted by objects |
| Temperature Range | Typically 700degC to 3000degC | -50degC to 1000degC (varies by model) |
| Applications | High-temperature industrial furnaces, metal processing | Medical, HVAC, electrical, mechanical maintenance |
| Contact Type | Non-contact | Non-contact |
| Accuracy | High accuracy at elevated temperatures | Moderate accuracy, depends on emissivity setting |
| Emissivity Adjustment | Manual adjustment for different materials | Usually adjustable for improved accuracy |
| Response Time | Fast (<1 second) | Fast (milliseconds to seconds) |
| Cost | Generally higher due to specialized optics | Moderate to low, consumer-friendly options available |
| Portability | Less portable, often fixed or handheld industrial | Highly portable, handheld devices common |
Introduction to Optical Pyrometers and Infrared Thermometers
Optical pyrometers measure temperature by analyzing the visible light emitted from a hot object, making them ideal for extremely high-temperature applications such as steel manufacturing. Infrared thermometers detect infrared radiation emitted by objects, offering non-contact temperature readings suitable for various industrial and medical uses. Your choice depends on the temperature range and measurement precision required for specific tasks.
How Optical Pyrometers Work
Optical pyrometers measure temperature by detecting the intensity of visible light emitted from a hot object, using a calibrated scale to compare the brightness of the target to a reference filament. These devices rely on the principle of blackbody radiation and require a clear line of sight to the object without physical contact, enabling temperature measurement of extremely hot surfaces. Unlike infrared thermometers that sense thermal infrared radiation, optical pyrometers focus on visible wavelengths, making them ideal for applications involving high-temperature metals and furnaces.
How Infrared Thermometers Function
Infrared thermometers function by detecting the infrared radiation emitted by an object's surface, converting this energy into an electrical signal to calculate temperature without direct contact. They operate using a lens to focus infrared light onto a detector, which measures the intensity of the radiation to determine accurate surface temperature quickly. Unlike optical pyrometers, infrared thermometers provide rapid temperature readings and are effective for measuring moving or inaccessible objects.
Key Differences Between Optical Pyrometers and Infrared Thermometers
Optical pyrometers measure temperature by comparing the brightness of a hot object to a calibrated light source, making them ideal for extremely high temperatures and industrial metal processing. Infrared thermometers detect emitted infrared radiation from surfaces, offering quick, non-contact temperature readings suitable for a broad temperature range and diverse applications. Your choice depends on the specific temperature range, measurement accuracy requirements, and the material being measured.
Accuracy and Temperature Measurement Range
Optical pyrometers deliver high accuracy for measuring extremely high temperatures, often ranging from 700degC to over 3000degC, making them ideal for industrial applications like metal forging. Infrared thermometers offer versatility with a broader temperature measurement range, typically from -50degC to 1000degC, while providing precise readings for moderate temperature surfaces. Accuracy in optical pyrometers depends on the emissivity settings and distance, whereas infrared thermometers require proper surface emissivity and environmental conditions for optimal precision.
Application Areas for Optical Pyrometers
Optical pyrometers are widely used in high-temperature industrial processes such as steel manufacturing, glass production, and ceramic firing where direct contact measurement is impractical. These devices measure thermal radiation accurately at extreme temperatures, making them essential for monitoring molten metals and furnaces. Unlike infrared thermometers, optical pyrometers perform well in environments with high emissivity and intense heat without interfering with the process.
Common Uses of Infrared Thermometers
Infrared thermometers are commonly used in various industries for non-contact temperature measurements, including HVAC system diagnostics, electrical equipment inspections, and food safety monitoring. These devices enable quick detection of hot spots in machinery and prevent overheating, enhancing maintenance efficiency. Unlike optical pyrometers, infrared thermometers are versatile for surface temperature measurement across diverse materials and environments.
Advantages and Limitations of Optical Pyrometers
Optical pyrometers offer the advantage of measuring high temperatures without contact, making them ideal for monitoring molten metals and furnaces where direct contact is impossible. Their limitations include sensitivity to emissivity variations and the need for a clear line of sight, which can affect accuracy in environments with smoke or dust. You should consider these factors when choosing between an optical pyrometer and an infrared thermometer for precise temperature measurements.
Pros and Cons of Infrared Thermometers
Infrared thermometers provide non-contact temperature measurement, making them ideal for hazardous or hard-to-reach environments, and offer rapid results with minimal surface interference. However, their accuracy can be affected by factors such as distance-to-spot ratio, emissivity variations, and environmental conditions like dust or steam. Unlike optical pyrometers, infrared thermometers cannot measure temperature through transparent surfaces like glass, limiting their usability in certain industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Device: Factors to Consider
Selecting between an optical pyrometer and an infrared thermometer depends on factors such as temperature range, surface emissivity, and measurement distance. Optical pyrometers excel in extremely high-temperature environments and are ideal for measuring glowing objects without contact, while infrared thermometers offer versatility for moderate temperatures and quick spot checks. You should evaluate the specific application requirements, including accuracy needs and environmental conditions, to choose the most effective device.
Optical pyrometer vs Infrared thermometer Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com