PT100 and PT1000 sensors differ primarily in resistance values and sensitivity, with PT100 offering 100 ohms at 0degC and PT1000 offering 1000 ohms, making PT1000 more sensitive to temperature changes and less prone to signal loss over long distances. Understanding these distinctions can help you choose the right sensor for accurate temperature measurement--explore the rest of the article to learn more.
Table of Comparison
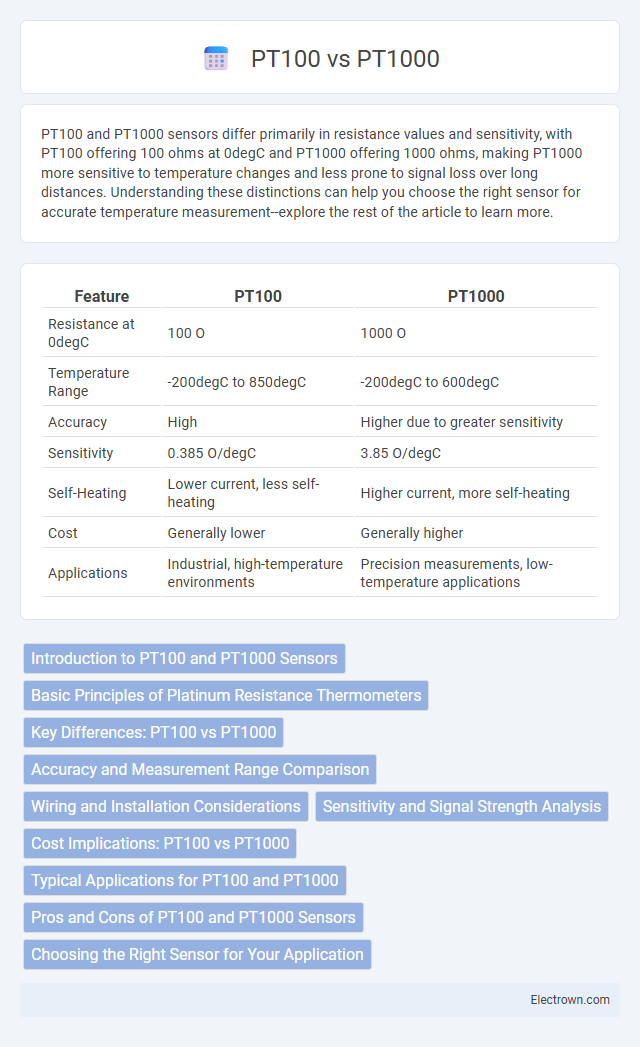
| Feature | PT100 | PT1000 |
|---|---|---|
| Resistance at 0degC | 100 O | 1000 O |
| Temperature Range | -200degC to 850degC | -200degC to 600degC |
| Accuracy | High | Higher due to greater sensitivity |
| Sensitivity | 0.385 O/degC | 3.85 O/degC |
| Self-Heating | Lower current, less self-heating | Higher current, more self-heating |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher |
| Applications | Industrial, high-temperature environments | Precision measurements, low-temperature applications |
Introduction to PT100 and PT1000 Sensors
PT100 and PT1000 sensors are platinum resistance temperature detectors (RTDs) that utilize the predictable change in electrical resistance of platinum with temperature to measure temperature accurately. PT100 sensors have a resistance of 100 ohms at 0degC, whereas PT1000 sensors feature a resistance of 1000 ohms at 0degC, offering higher sensitivity and reduced signal susceptibility to electrical noise. Both sensors provide reliable and precise temperature measurements across a wide temperature range, making them essential in industrial process control and scientific applications.
Basic Principles of Platinum Resistance Thermometers
Platinum resistance thermometers, including PT100 and PT1000 sensors, operate on the principle that platinum's electrical resistance changes predictably with temperature. PT100 sensors have a resistance of 100 ohms at 0degC, while PT1000 sensors have 1000 ohms at the same reference point, affecting sensitivity and accuracy. This resistance-temperature relationship follows a nearly linear pattern, making both types reliable for precise temperature measurements across various industrial applications.
Key Differences: PT100 vs PT1000
PT100 sensors have a resistance of 100 ohms at 0degC, while PT1000 sensors have a resistance of 1000 ohms at the same temperature, offering higher sensitivity and accuracy. PT1000 thermometers provide better noise immunity and lower wiring costs due to higher signal levels compared to PT100. Your choice between PT100 and PT1000 depends on the specific application's precision requirements and environmental conditions.
Accuracy and Measurement Range Comparison
PT100 sensors offer high accuracy within a standard measurement range of -200degC to 850degC, making them suitable for precision temperature monitoring in industrial applications. PT1000 sensors provide similar accuracy with a slightly narrower temperature range but feature higher resistance values, reducing signal interference over long cable runs. When selecting your sensor, consider the trade-off between measurement range and signal stability based on your specific temperature monitoring requirements.
Wiring and Installation Considerations
PT100 sensors typically require more wiring effort due to their lower resistance values, making them more susceptible to electrical noise and thus often necessitating 3-wire or 4-wire installations for accurate measurements. PT1000 sensors have higher resistance, which reduces wiring error sensitivity and allows for simpler 2-wire configurations in many cases, lowering installation complexity and cost. Proper selection between PT100 and PT1000 depends on the specific application environment and wiring layout to ensure precise temperature readings with minimal signal interference.
Sensitivity and Signal Strength Analysis
PT100 sensors have lower resistance values resulting in stronger signal levels but lower sensitivity compared to PT1000 sensors, which provide higher resistance and improved sensitivity for detecting small temperature changes. The increased resistance in PT1000 sensors reduces the impact of lead wire resistance, enhancing measurement accuracy and signal quality especially over long distances. Your choice between PT100 and PT1000 should consider the trade-off between signal strength and sensitivity based on the specific temperature measurement application.
Cost Implications: PT100 vs PT1000
PT100 sensors generally have higher initial costs due to their widespread industrial use and precision manufacturing standards, while PT1000 sensors are often more cost-effective for applications requiring higher sensitivity and lower power consumption. Your choice between PT100 and PT1000 impacts overall system expenses, as PT1000 wiring costs may be lower due to reduced current requirements and thinner cables. Cost implications also extend to calibration and maintenance, where PT1000 may offer savings by delivering more stable readings with less frequent calibration needs.
Typical Applications for PT100 and PT1000
PT100 sensors are commonly used in industrial applications requiring precise temperature measurement, such as HVAC systems, process control, and automotive diagnostics due to their accuracy and stability over wide temperature ranges. PT1000 sensors find typical applications in domestic heating systems, medical devices, and environmental monitoring where lower current and simplified wiring offer advantages. Your choice between PT100 and PT1000 depends on factors like measurement accuracy, wiring complexity, and environmental conditions.
Pros and Cons of PT100 and PT1000 Sensors
PT100 sensors offer high accuracy and stability over a wide temperature range, making them ideal for industrial applications, but they require more current and can be more expensive than PT1000 sensors. PT1000 sensors provide greater sensitivity and lower wiring costs due to higher resistance, which can improve signal quality in long-distance measurements; however, they may have slightly lower temperature accuracy compared to PT100. Your choice depends on the balance between precision needs and installation convenience.
Choosing the Right Sensor for Your Application
Selecting the appropriate temperature sensor between PT100 and PT1000 depends on measurement accuracy, environmental conditions, and application requirements. PT100 sensors offer higher accuracy and better stability at extreme temperatures, making them ideal for industrial processes with wide temperature ranges. PT1000 sensors provide higher resistance, resulting in improved signal-to-noise ratio and suitability for long-distance measurements in less demanding temperature environments.
PT100 vs PT1000 Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com