Dummy gates are inactive structures used in semiconductor manufacturing to ensure planarization and process uniformity, while active gates control the flow of current in transistors, directly impacting device performance. Explore the article to understand how these components influence your chip's functionality and fabrication process.
Table of Comparison
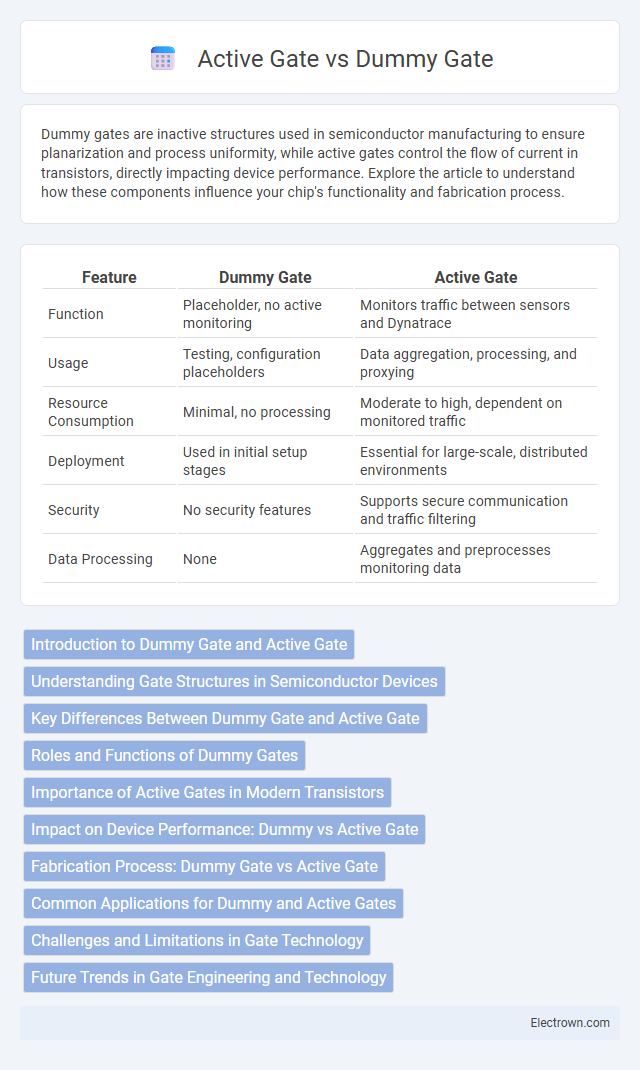
| Feature | Dummy Gate | Active Gate |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Placeholder, no active monitoring | Monitors traffic between sensors and Dynatrace |
| Usage | Testing, configuration placeholders | Data aggregation, processing, and proxying |
| Resource Consumption | Minimal, no processing | Moderate to high, dependent on monitored traffic |
| Deployment | Used in initial setup stages | Essential for large-scale, distributed environments |
| Security | No security features | Supports secure communication and traffic filtering |
| Data Processing | None | Aggregates and preprocesses monitoring data |
Introduction to Dummy Gate and Active Gate
Dummy gates are non-functional transistors used in semiconductor manufacturing to ensure uniformity in the fabrication process and improve overall device reliability. Active gates, in contrast, are functional transistors that form the core switching elements in integrated circuits, directly controlling current flow and signal processing. Understanding the differences between dummy and active gates can help optimize your chip design for both performance and manufacturability.
Understanding Gate Structures in Semiconductor Devices
Dummy Gate and Active Gate structures play critical roles in semiconductor devices, with the Active Gate directly controlling channel conductivity for transistor switching, while Dummy Gates serve as structural placeholders to improve device fabrication and performance. Your understanding of these gates influences insights into transistor scaling and device stability, as Dummy Gates help reduce variability and stress in gate dielectrics. Optimizing gate design ensures enhanced electrical characteristics and reliability in advanced integrated circuits.
Key Differences Between Dummy Gate and Active Gate
Dummy gates serve as non-functional filler structures in semiconductor devices, designed to maintain uniformity in the fabrication process and reduce variability in threshold voltage. Active gates, by contrast, control the transistor's switching behavior by forming the actual gate electrode over the channel region, enabling current flow regulation. Understanding these key differences helps optimize your chip design by balancing process stability with device performance.
Roles and Functions of Dummy Gates
Dummy gates serve as non-functional structures in semiconductor devices, ensuring uniform etching and planarization during manufacturing by mimicking the physical dimensions of active gates. They help maintain consistent stress distribution and electrical characteristics across the chip without conducting current or switching. Your design benefits from dummy gates by preventing edge effects and improving overall device reliability and performance.
Importance of Active Gates in Modern Transistors
Active gates in modern transistors enable precise control of electron flow by modulating the channel conductivity, which significantly enhances switching speed and energy efficiency compared to dummy gates. Unlike dummy gates that serve merely as structural placeholders, active gates utilize advanced materials such as high-k dielectrics and metal gates to improve gate capacitance and reduce leakage currents. These innovations are critical for sustaining transistor scaling in CMOS technology, enabling higher performance, lower power consumption, and improved reliability in integrated circuits.
Impact on Device Performance: Dummy vs Active Gate
Active gates significantly enhance device performance by providing effective control over the channel, reducing short-channel effects, and improving drive current and switching speed. Dummy gates, in contrast, serve primarily as structural placeholders without electrical functionality, leading to limited influence on device operation but helping maintain process uniformity. The inclusion of active gates directly correlates with higher transistor reliability and overall circuit efficiency compared to dummy gates.
Fabrication Process: Dummy Gate vs Active Gate
The fabrication process of dummy gates involves creating placeholder structures during early transistor formation to maintain uniformity and prevent pattern distortions, which are later replaced by active gate materials through a replacement gate process. In contrast, active gates are directly patterned and constructed with gate dielectric and conductive materials from the beginning, forming the functional channel control elements in transistors. Your choice between dummy and active gate fabrication methods significantly impacts device performance, process complexity, and scalability in advanced semiconductor manufacturing.
Common Applications for Dummy and Active Gates
Dummy gates are commonly used in semiconductor manufacturing to maintain uniform gate density and reduce patterning defects in CMOS processes. Active gates serve as the functional transistors in integrated circuits, enabling switching and amplification in applications such as microprocessors and memory devices. Both gate types contribute to fabrication stability, with dummy gates improving process uniformity and active gates ensuring circuit performance and functionality.
Challenges and Limitations in Gate Technology
Dummy Gate technology faces challenges such as increased parasitic capacitance and difficulty scaling in advanced nodes, which impact device performance and power efficiency. Active Gate designs provide improved electrical control but encounter limitations including higher fabrication complexity and cost due to additional doping and patterning steps. Both gate technologies struggle with variability issues and compatibility with emerging materials, hindering optimal integration into future semiconductor processes.
Future Trends in Gate Engineering and Technology
Future trends in gate engineering point to increased adoption of active gates, which integrate advanced sensors, IoT connectivity, and automation for enhanced security and remote control. Emerging technologies emphasize AI-driven access management, predictive maintenance, and energy-efficient designs, surpassing the simple mechanical function of dummy gates. The shift towards smart infrastructure accelerates the demand for active gates that provide real-time data analytics and seamless integration with smart home and city systems.
Dummy Gate vs Active Gate Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com