Folded cascode amplifiers offer higher voltage swing and better output impedance, making them suitable for low-voltage applications, while telescopic cascode amplifiers provide superior gain and bandwidth but with reduced output voltage range. Explore the rest of the article to understand which architecture best fits Your design needs.
Table of Comparison
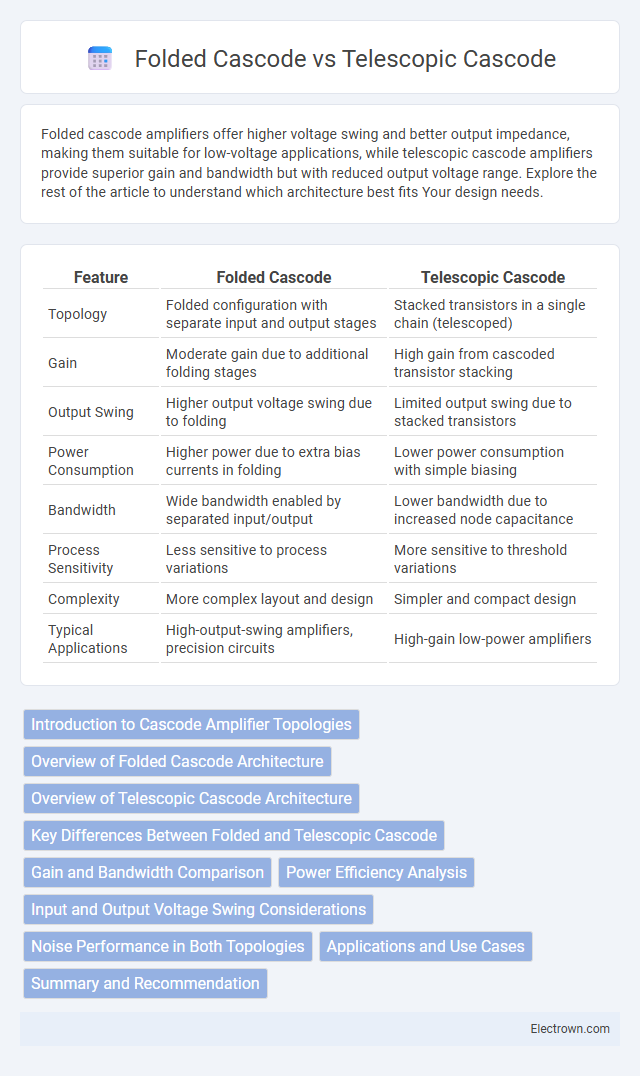
| Feature | Folded Cascode | Telescopic Cascode |
|---|---|---|
| Topology | Folded configuration with separate input and output stages | Stacked transistors in a single chain (telescoped) |
| Gain | Moderate gain due to additional folding stages | High gain from cascoded transistor stacking |
| Output Swing | Higher output voltage swing due to folding | Limited output swing due to stacked transistors |
| Power Consumption | Higher power due to extra bias currents in folding | Lower power consumption with simple biasing |
| Bandwidth | Wide bandwidth enabled by separated input/output | Lower bandwidth due to increased node capacitance |
| Process Sensitivity | Less sensitive to process variations | More sensitive to threshold variations |
| Complexity | More complex layout and design | Simpler and compact design |
| Typical Applications | High-output-swing amplifiers, precision circuits | High-gain low-power amplifiers |
Introduction to Cascode Amplifier Topologies
Cascode amplifier topologies, including Folded Cascode and Telescopic Cascode, are essential in achieving high gain and bandwidth in analog circuits. The Folded Cascode structure improves output voltage swing and input common-mode range by folding the signal path, making it suitable for low-voltage applications. The Telescopic Cascode offers higher gain and lower power consumption but with restricted output voltage swing, ideal for high-frequency designs.
Overview of Folded Cascode Architecture
The Folded Cascode architecture features a design where input devices are implemented in one polarity, typically NMOS, and the cascode devices are folded using opposite polarity, typically PMOS, allowing for a wider output voltage swing and better suitability for low-voltage applications. This architecture improves gain and bandwidth by reducing the Miller effect and provides enhanced power supply rejection compared to telescopic cascode amplifiers. Its configuration enables better flexibility in input common-mode range and output voltage range, making it ideal for low-voltage analog circuits and mixed-signal systems.
Overview of Telescopic Cascode Architecture
The Telescopic Cascode architecture features a multi-stage cascode arrangement that enhances gain and bandwidth by stacking transistors vertically to reduce parasitic capacitances and improve output impedance. This design offers superior frequency response and lower power consumption compared to traditional folded cascode configurations, making it ideal for high-speed, low-power amplifiers. Your circuit performance benefits from the compact layout and efficient transistor usage inherent in the telescopic cascode topology.
Key Differences Between Folded and Telescopic Cascode
The key differences between folded cascode and telescopic cascode amplifiers lie in their voltage swing and output impedance characteristics. Folded cascode designs provide higher output voltage swing and better power supply rejection by folding the current path, making them suitable for low-voltage applications. Telescopic cascode amplifiers offer higher gain and lower noise but have limited output voltage swing due to their stacked transistor structure, impacting your design choices based on performance priorities.
Gain and Bandwidth Comparison
Folded cascode amplifiers typically offer higher bandwidth due to their lower input capacitance and better frequency response compared to telescopic cascode amplifiers, which achieve higher gain through improved gain stage stacking and reduced output conductance. Your choice depends on whether maximizing gain or bandwidth is more critical: telescopic cascodes excel in gain but may sacrifice bandwidth, while folded cascodes provide broader bandwidth at slightly reduced gain. Both topologies employ cascode structures to enhance gain, but folded cascodes trade off gain for improved output voltage swing and frequency performance.
Power Efficiency Analysis
Folded cascode amplifiers generally offer better power efficiency compared to telescopic cascode designs due to their ability to operate at lower supply voltages while maintaining high gain and bandwidth. The telescopic cascode achieves higher gain and lower noise but typically consumes more power because of its stacked transistor configuration, which limits headroom and demands higher voltage levels. In power-sensitive applications, the folded cascode's flexibility in biasing and improved voltage swing make it a preferable choice for achieving lower power dissipation without sacrificing performance.
Input and Output Voltage Swing Considerations
Folded cascode amplifiers offer a wider input voltage range since their input transistor operates with a lower voltage headroom, making them ideal when your signal requires larger voltage swings at the input. Telescopic cascode amplifiers provide higher gain and better output voltage swing due to stacking transistors, but this reduces the output voltage headroom, limiting the maximum output swing. Choosing between folded and telescopic cascode architectures depends largely on balancing your design requirements for input voltage range and output swing capabilities.
Noise Performance in Both Topologies
Folded cascode amplifiers typically exhibit higher input-referred noise due to the additional transistor stages in the signal path, which contribute more flicker and thermal noise compared to telescopic cascode designs. Telescopic cascode topologies generally offer superior noise performance by minimizing the number of noise-generating transistors and providing better intrinsic gain, which enhances signal integrity. Your choice between these two should consider the noise requirements of your application, with telescopic cascodes being preferable for low-noise high-gain scenarios.
Applications and Use Cases
Folded cascode amplifiers are commonly used in low-voltage, low-power applications such as portable devices and battery-operated systems due to their ability to handle low supply voltages while maintaining high gain. Telescopic cascode amplifiers are favored in high-frequency and high-gain applications like RF circuits and precision analog front-ends because of their superior bandwidth and noise performance. Folded cascodes enable easier integration with input common-mode voltage variations, while telescopic cascodes are ideal where maximum output swing and linearity are critical.
Summary and Recommendation
Folded cascode amplifiers offer improved output voltage swing and reduced power supply requirements compared to telescopic cascodes, making them suitable for low-voltage, low-power applications. Telescopic cascode designs typically provide higher gain and better noise performance but have limited output swing and require higher voltage headroom. For applications prioritizing low voltage operation and increased output range, folded cascode is recommended; telescopic cascode is preferred when maximum gain and noise minimization are critical.
Folded Cascode vs Telescopic Cascode Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com