Pipelined ADCs offer a balance of speed and resolution by processing signals in stages, making them ideal for high-precision applications, whereas Flash ADCs prioritize maximum conversion speed with lower resolution through parallel comparators. Explore the detailed comparison to determine which ADC suits Your specific application needs.
Table of Comparison
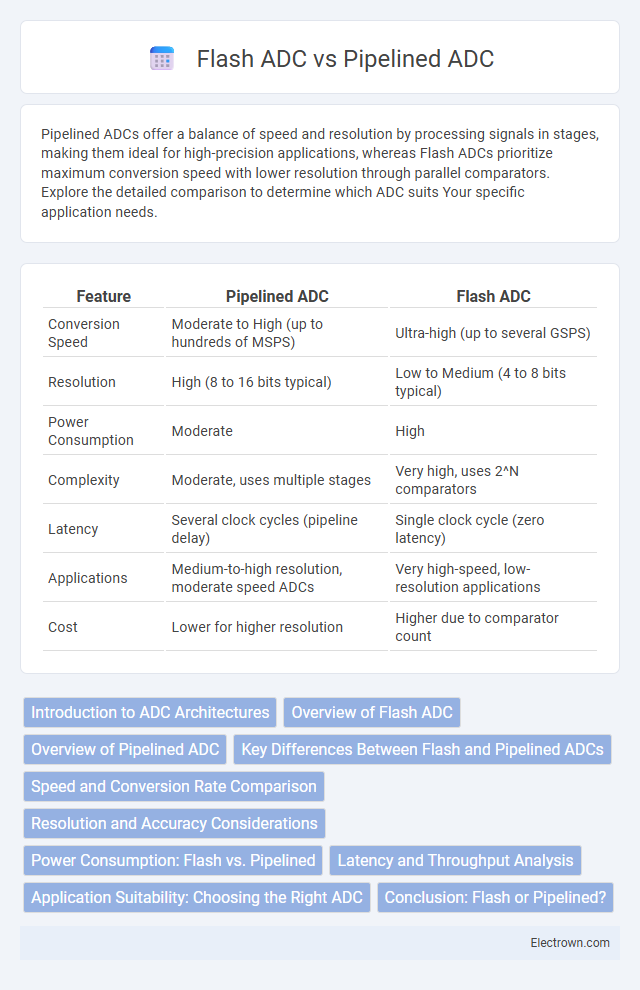
| Feature | Pipelined ADC | Flash ADC |
|---|---|---|
| Conversion Speed | Moderate to High (up to hundreds of MSPS) | Ultra-high (up to several GSPS) |
| Resolution | High (8 to 16 bits typical) | Low to Medium (4 to 8 bits typical) |
| Power Consumption | Moderate | High |
| Complexity | Moderate, uses multiple stages | Very high, uses 2^N comparators |
| Latency | Several clock cycles (pipeline delay) | Single clock cycle (zero latency) |
| Applications | Medium-to-high resolution, moderate speed ADCs | Very high-speed, low-resolution applications |
| Cost | Lower for higher resolution | Higher due to comparator count |
Introduction to ADC Architectures
Pipelined ADCs gradually convert analog signals into digital form through multiple stages, balancing speed and resolution for medium-to-high applications. Flash ADCs use a parallel array of comparators for ultra-fast conversions but consume more power and area, making them ideal for very high-speed tasks. Your choice depends on whether throughput or precision is the priority in your system design.
Overview of Flash ADC
Flash ADCs, known for their ultra-fast conversion speeds, use a parallel array of comparators to simultaneously compare the input voltage against reference levels, enabling conversion times in the nanosecond range. This architecture excels in applications demanding high sampling rates, such as digital oscilloscopes and radar systems, but typically consumes more power and silicon area compared to pipelined ADCs. Flash ADCs offer low latency and exceptional speed, making them ideal for real-time signal processing where conversion speed outweighs resolution and power efficiency.
Overview of Pipelined ADC
Pipelined ADCs utilize a multi-stage architecture where each stage performs partial conversion and passes residual signals downstream, enabling high-resolution and moderate-speed digitization ideal for applications like digital imaging and communications. The pipeline structure efficiently balances power consumption and throughput, offering better linearity and lower power compared to Flash ADCs, which use parallel comparators for ultra-fast but power-hungry conversion. Understanding your system's speed, resolution, and power requirements helps determine if a pipelined ADC suits your application better than a Flash ADC.
Key Differences Between Flash and Pipelined ADCs
Flash ADCs offer ultra-high-speed conversion by using parallel comparators, enabling instantaneous analog-to-digital conversion ideal for applications requiring rapid sampling rates above 1 GSPS. Pipelined ADCs achieve a balance between speed and resolution through a staged process, providing higher resolution (up to 16 bits) with moderate latency and power consumption, making them suitable for high-resolution imaging and communication systems. The primary difference lies in Flash ADCs prioritizing speed with lower resolution and higher power use, whereas Pipelined ADCs emphasize resolution and efficiency with slightly slower throughput.
Speed and Conversion Rate Comparison
Pipelined ADCs offer moderate speed and high resolution, typically achieving conversion rates in the range of several mega samples per second (MSPS), making them suitable for applications requiring a balance between speed and accuracy. Flash ADCs, known for their ultra-high speed, can achieve conversion rates up to several giga samples per second (GSPS) by using parallel comparators, but often sacrifice resolution and consume more power. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize the ultra-fast conversion rates of Flash ADCs or the improved accuracy and power efficiency of Pipelined ADCs for high-speed data acquisition.
Resolution and Accuracy Considerations
Pipelined ADCs typically offer higher resolution ranging from 8 to 16 bits with improved accuracy due to their multi-stage architecture that allows for error correction and lower noise levels. Flash ADCs provide ultra-fast conversion speeds but are generally limited to lower resolutions, usually up to 8 bits, and may experience reduced accuracy from comparator offset errors and limited linearity. Your choice between pipelined and flash ADCs should balance the need for precise resolution against the requirement for high-speed data acquisition.
Power Consumption: Flash vs. Pipelined
Pipelined ADCs exhibit significantly lower power consumption compared to Flash ADCs due to their stepwise conversion process, which reduces the number of comparators and overall circuit complexity. Flash ADCs consume more power because all comparators operate simultaneously, leading to higher dynamic power dissipation, especially at high sampling rates. Consequently, pipelined ADCs are preferred in applications prioritizing energy efficiency without sacrificing moderate-to-high-speed performance.
Latency and Throughput Analysis
Pipelined ADCs exhibit lower latency compared to Flash ADCs due to their staged conversion process, allowing partial parallelism and faster settling times in each pipeline stage. Flash ADCs provide higher throughput with nearly instantaneous conversion by using a resistor ladder and parallel comparators but suffer from increased input capacitance and power consumption. Your choice depends on the application's emphasis on latency versus throughput, where pipelined ADCs balance speed and accuracy, while Flash ADCs excel in ultra-high-speed scenarios.
Application Suitability: Choosing the Right ADC
Pipelined ADCs are ideal for applications requiring medium-to-high resolution and moderate sampling rates, such as digital video, communications, and instrumentation. Flash ADCs excel in ultra-high-speed data conversion with lower resolution, making them suitable for radar systems, oscilloscopes, and high-frequency signal processing. Selecting the right ADC depends on balancing speed, resolution, power consumption, and the specific requirements of the target application.
Conclusion: Flash or Pipelined?
Flash ADCs offer ultra-fast conversion speeds ideal for applications requiring high sampling rates, but their complexity and power consumption increase exponentially with higher resolutions. Pipelined ADCs provide a balanced trade-off between speed and resolution, achieving moderate-to-high accuracy with more efficient power usage, making them suitable for high-resolution signal processing. The choice depends on the application's priority: Flash ADCs for maximum speed and Pipelined ADCs for optimized resolution and power efficiency.
Pipelined ADC vs Flash ADC Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com