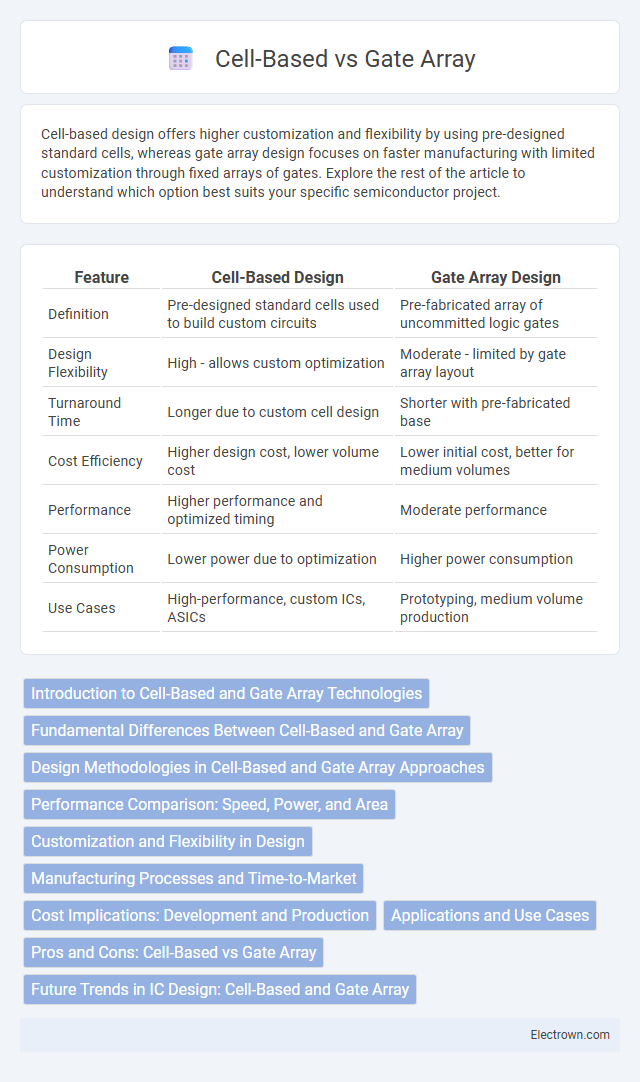
Cell-based design offers higher customization and flexibility by using pre-designed standard cells, whereas gate array design focuses on faster manufacturing with limited customization through fixed arrays of gates. Explore the rest of the article to understand which option best suits your specific semiconductor project.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cell-Based Design | Gate Array Design |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-designed standard cells used to build custom circuits | Pre-fabricated array of uncommitted logic gates |
| Design Flexibility | High - allows custom optimization | Moderate - limited by gate array layout |
| Turnaround Time | Longer due to custom cell design | Shorter with pre-fabricated base |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher design cost, lower volume cost | Lower initial cost, better for medium volumes |
| Performance | Higher performance and optimized timing | Moderate performance |
| Power Consumption | Lower power due to optimization | Higher power consumption |
| Use Cases | High-performance, custom ICs, ASICs | Prototyping, medium volume production |
Introduction to Cell-Based and Gate Array Technologies
Cell-based technology uses standard logic cells pre-designed and characterized for specific functions, allowing flexible and customized integrated circuit design with optimized performance and area. Gate array technology employs a prefabricated silicon wafer with unconnected transistors that are later customized through metal layer interconnections, resulting in faster production times and lower initial costs but less flexibility. Both approaches serve distinct purposes in semiconductor manufacturing, balancing design efficiency, cost, and scalability.
Fundamental Differences Between Cell-Based and Gate Array
Cell-based design utilizes pre-defined logic cells to create custom integrated circuits, offering high flexibility and optimization for specific applications. Gate array design relies on a fixed array of unconnected transistors or gates, where customization occurs by adding metal interconnections, leading to faster manufacturing but less design flexibility. The fundamental difference lies in cell-based's adaptable modular blocks versus gate array's fixed hardware with customizable wiring layers.
Design Methodologies in Cell-Based and Gate Array Approaches
Cell-based design methodologies utilize predefined functional blocks or standard cells, allowing designers to create custom integrated circuits with high flexibility and optimized performance. Gate array approaches employ a prefabricated array of uncommitted transistors or gates, enabling faster turnaround times by customizing only the interconnections during the final stages of fabrication. The cell-based method emphasizes modularity and scalability, while the gate array design reduces mask and fabrication costs, making each suitable for different production scales and timelines.
Performance Comparison: Speed, Power, and Area
Cell-based designs offer higher speed and better power efficiency due to customized transistor sizing and optimized routing, resulting in lower latency and reduced dynamic power consumption. Gate arrays typically consume more area and power because of pre-defined standard cell placements and fixed metal layers, leading to increased parasitic capacitance and slower signal propagation. Overall, cell-based approaches provide superior performance in speed and power metrics, while gate arrays trade off efficiency for faster manufacturing turnaround and lower non-recurring engineering costs.
Customization and Flexibility in Design
Cell-based design offers higher customization by allowing designers to create circuits from individual logic cells tailored precisely to your specifications, enabling unique functionality and optimization for performance or area. Gate array design provides moderate flexibility with a prefabricated array of gates that can be customized only at the final metal layer, resulting in faster production cycles but less design uniqueness. Choosing between cell-based and gate array depends on the desired balance between customization, time-to-market, and design flexibility.
Manufacturing Processes and Time-to-Market
Cell-based designs involve custom logic cells tailored for specific functions, enabling flexible manufacturing but requiring longer design and fabrication times. Gate array technology uses prefabricated silicon wafers with predefined transistor arrays, significantly reducing manufacturing complexity and accelerating time-to-market. Your choice depends on prioritizing rapid production with gate arrays or optimized performance and customization with cell-based processes.
Cost Implications: Development and Production
Cell-based design typically involves higher initial development costs due to custom cell library creation and extensive design verification but can lead to lower per-unit production costs for large volumes. Gate array design offers reduced development time and cost by using pre-fabricated wafers, making it more economical for moderate production runs. Your choice depends on balancing upfront design expenses against long-term manufacturing savings.
Applications and Use Cases
Cell-based design is ideal for customized integrated circuits in high-performance applications such as microprocessors and ASICs, where specific functionality and optimization are critical. Gate array technology suits medium-volume production with moderate customization, commonly used in communications, consumer electronics, and prototyping environments. Selecting between cell-based and gate array depends on factors like time-to-market, design flexibility, and production scale.
Pros and Cons: Cell-Based vs Gate Array
Cell-based design offers higher design flexibility and faster time-to-market due to pre-characterized standard cells, but it typically results in larger chip area and higher power consumption compared to gate arrays. Gate arrays provide better cost efficiency and more predictable manufacturing turnaround times, though their limited customization often leads to suboptimal performance and higher non-recurring engineering costs for complex designs. Choosing between cell-based and gate array technologies depends on prioritizing factors like customization level, production volume, design complexity, and time constraints.
Future Trends in IC Design: Cell-Based and Gate Array
Emerging trends in IC design highlight increasing adoption of cell-based methodologies due to their flexibility in customization and scalability for complex integrated circuits, while gate arrays continue to offer cost-effective solutions for moderate volumes with faster time-to-market. Advanced process nodes and AI-driven design tools enhance cell-based designs by optimizing power, performance, and area (PPA), making them favorable for sophisticated applications in AI and 5G technology. Gate arrays maintain relevance in applications requiring rapid prototyping and lower non-recurring engineering (NRE) costs, supporting future hybrid approaches combining both design styles.
Cell-Based vs Gate Array Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com