Buck converters offer high efficiency and better thermal management for voltage regulation, making them ideal for applications requiring significant power conversion. Your choice between a buck converter and an LDO depends on factors like efficiency, noise sensitivity, and space constraints; continue reading to find out which solution best fits your needs.
Table of Comparison
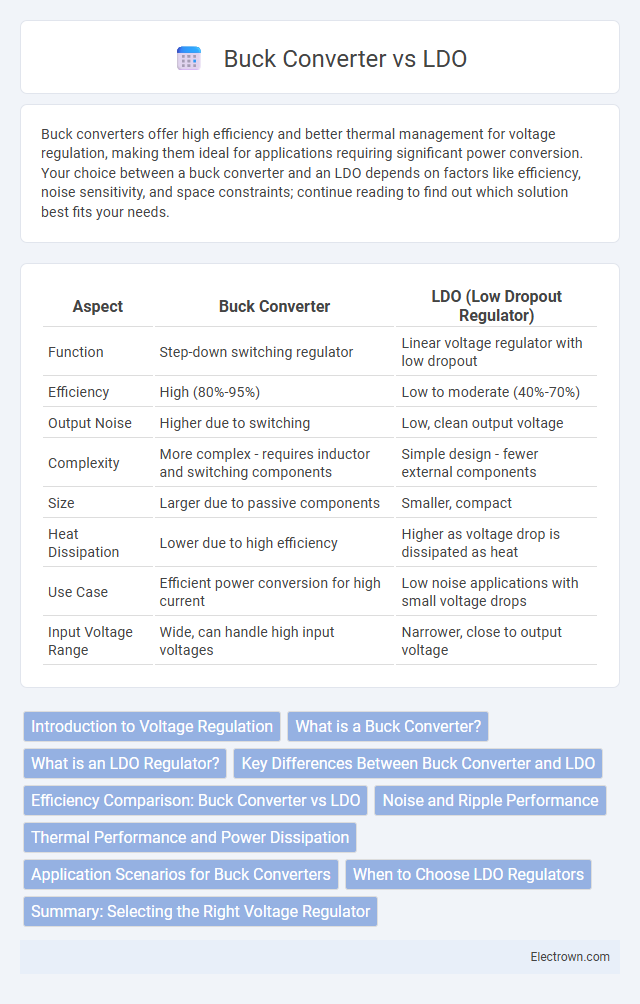
| Aspect | Buck Converter | LDO (Low Dropout Regulator) |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Step-down switching regulator | Linear voltage regulator with low dropout |
| Efficiency | High (80%-95%) | Low to moderate (40%-70%) |
| Output Noise | Higher due to switching | Low, clean output voltage |
| Complexity | More complex - requires inductor and switching components | Simple design - fewer external components |
| Size | Larger due to passive components | Smaller, compact |
| Heat Dissipation | Lower due to high efficiency | Higher as voltage drop is dissipated as heat |
| Use Case | Efficient power conversion for high current | Low noise applications with small voltage drops |
| Input Voltage Range | Wide, can handle high input voltages | Narrower, close to output voltage |
Introduction to Voltage Regulation
Buck converters and LDOs (Low Dropout Regulators) are essential components in voltage regulation, each offering distinct advantages based on application needs. Buck converters efficiently step down higher input voltages to lower output voltages with high power efficiency, making them ideal for battery-powered devices and power-intensive applications. Your choice between a buck converter and an LDO depends on factors like input voltage range, efficiency requirements, and noise sensitivity.
What is a Buck Converter?
A Buck Converter is a DC-DC power supply component designed to step down voltage efficiently by switching elements like transistors and inductors. It operates using pulse-width modulation (PWM) to regulate output voltage while minimizing power loss, making it ideal for applications requiring high efficiency and thermal management. Compared to Linear Dropout Regulators (LDOs), Buck Converters provide better energy efficiency at the cost of increased circuit complexity and electrical noise.
What is an LDO Regulator?
An LDO (Low Dropout) regulator is a type of linear voltage regulator designed to provide a stable output voltage with a very small input-to-output voltage difference. It excels in applications requiring low noise and minimal voltage ripple, making it ideal for sensitive analog and RF circuits. Your choice of an LDO regulator ensures efficient power management when the input voltage closely matches the output voltage, offering simplicity and low electromagnetic interference compared to switching regulators like buck converters.
Key Differences Between Buck Converter and LDO
Buck converters operate by switching elements to efficiently step down voltage with higher power efficiency, while LDOs use linear regulation resulting in simpler design but lower efficiency. Buck converters generate switching noise and require inductors, whereas LDOs provide cleaner output with minimal noise suitable for sensitive analog circuits. Your choice depends on factors like input-output voltage differential, efficiency requirements, and noise sensitivity in your application.
Efficiency Comparison: Buck Converter vs LDO
Buck converters offer significantly higher efficiency than LDOs, often achieving 80-95% efficiency by switching energy at high frequency and minimizing power loss. LDOs, on the other hand, provide simplicity and low noise but typically operate at 40-60% efficiency, especially when the voltage difference between input and output is large. For applications demanding power efficiency and longer battery life, choosing a buck converter will optimize Your device's performance.
Noise and Ripple Performance
Buck converters typically generate higher noise and ripple due to their switching operation, which can range from tens to hundreds of millivolts depending on the design and load conditions. LDO (Low Dropout) regulators provide superior noise and ripple performance with output voltage ripple often below a few millivolts, making them ideal for sensitive analog and RF applications. The choice between buck converters and LDOs depends on the priority between efficiency and noise-sensitive performance, where LDOs excel in low noise environments despite their lower efficiency.
Thermal Performance and Power Dissipation
Buck converters exhibit superior thermal performance and lower power dissipation compared to Low Dropout Regulators (LDO) due to their high efficiency switching operation, often achieving efficiencies above 85-95%. LDOs, operating via linear regulation, dissipate excess voltage as heat, resulting in higher thermal stress and limited efficiency, especially with large voltage drops and high load currents. Efficient thermal management in buck converters enables compact designs with reduced heat sinks, while LDOs typically require larger heat dissipation components to maintain safe operating temperatures.
Application Scenarios for Buck Converters
Buck converters are widely used in scenarios requiring efficient voltage step-down from higher DC levels, such as battery-powered devices, portable electronics, and power supply modules for microprocessors. They are ideal for applications demanding high current output and energy efficiency, including electric vehicles, industrial automation, and telecommunications equipment. Compared to LDO regulators, buck converters excel in managing thermal dissipation and extending battery life in power-sensitive applications.
When to Choose LDO Regulators
LDO regulators are ideal when low noise, fast transient response, and simple design are required, especially in low voltage and low current applications. They provide clean, stable output voltage with minimal ripple, making them suitable for sensitive analog and RF circuits. LDOs are preferred when the input voltage is only slightly higher than the output voltage, maximizing efficiency and reducing power dissipation.
Summary: Selecting the Right Voltage Regulator
Buck converters provide high efficiency by stepping down voltage with minimal power loss, making them ideal for applications requiring significant voltage reduction and battery-powered devices. LDO regulators offer simplicity, low noise, and fast transient response, suitable for low dropout voltage scenarios and sensitive analog circuits. Selecting the right voltage regulator depends on factors like efficiency requirements, noise sensitivity, output voltage, and system complexity to optimize overall performance.
Buck Converter vs LDO Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com