Class AB amplifiers combine the low distortion of Class A with the efficiency of Class B, making them ideal for high-fidelity audio applications, while Class D amplifiers use pulse-width modulation to achieve higher efficiency and compact design, suitable for portable and power-sensitive devices. Explore the differences in performance, efficiency, and sound quality to determine which amplifier class best meets Your audio needs.
Table of Comparison
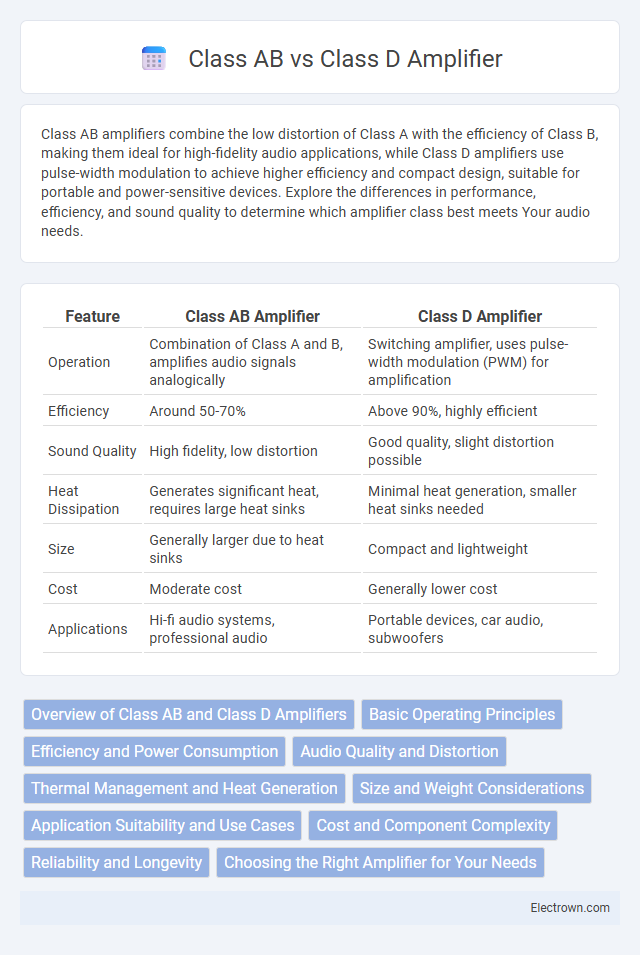
| Feature | Class AB Amplifier | Class D Amplifier |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Combination of Class A and B, amplifies audio signals analogically | Switching amplifier, uses pulse-width modulation (PWM) for amplification |
| Efficiency | Around 50-70% | Above 90%, highly efficient |
| Sound Quality | High fidelity, low distortion | Good quality, slight distortion possible |
| Heat Dissipation | Generates significant heat, requires large heat sinks | Minimal heat generation, smaller heat sinks needed |
| Size | Generally larger due to heat sinks | Compact and lightweight |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Generally lower cost |
| Applications | Hi-fi audio systems, professional audio | Portable devices, car audio, subwoofers |
Overview of Class AB and Class D Amplifiers
Class AB amplifiers combine the low distortion of Class A with the efficiency of Class B, making them ideal for high-fidelity audio applications with moderate power consumption. Class D amplifiers use pulse-width modulation to switch outputs rapidly, resulting in much higher efficiency and cooler operation, suitable for compact, energy-saving designs. Your choice depends on whether sound quality or power efficiency is your primary concern.
Basic Operating Principles
Class AB amplifiers combine the efficiency of Class B with the low distortion of Class A by using complementary transistors that conduct more than half but less than the entire input signal cycle. Class D amplifiers operate as switching devices that rapidly switch on and off, using pulse-width modulation to amplify signals with high efficiency and minimal heat dissipation. Understanding these basic operating principles helps you choose the right amplifier based on your audio quality and power efficiency needs.
Efficiency and Power Consumption
Class AB amplifiers typically offer efficiency levels around 50-70%, balancing linearity and power usage, but they consume more power and generate greater heat compared to Class D amplifiers. Class D amplifiers operate at higher efficiency rates, often exceeding 90%, by using pulse-width modulation to minimize power loss and reduce energy consumption. This efficiency advantage leads to lower heat dissipation and longer battery life in portable and high-power applications.
Audio Quality and Distortion
Class AB amplifiers deliver superior audio quality with low distortion levels, offering a balanced and natural sound ideal for high-fidelity listening. Class D amplifiers, while more energy-efficient and compact, may introduce higher distortion and noise, which can affect audio clarity but have improved significantly with modern designs. Your choice depends on whether audio fidelity or efficiency is more critical for your application.
Thermal Management and Heat Generation
Class AB amplifiers generate more heat due to their continuous conduction of current through output transistors, necessitating efficient thermal management with large heat sinks and cooling systems. Class D amplifiers operate with switching transistors, producing significantly less heat and allowing for more compact and energy-efficient designs. Your choice impacts system reliability and performance, especially in environments where heat dissipation is critical.
Size and Weight Considerations
Class D amplifiers are significantly smaller and lighter than Class AB amplifiers due to their high efficiency and reduced heat dissipation, making them ideal for portable and space-constrained applications. Class AB amplifiers require larger heat sinks to manage heat output, resulting in bulkier and heavier units. Choosing a Class D amplifier can improve your setup's portability without sacrificing power output.
Application Suitability and Use Cases
Class AB amplifiers offer superior sound quality with low distortion, making them ideal for high-fidelity home audio systems and professional studio equipment. Class D amplifiers excel in energy efficiency and compact size, which suits portable devices, car audio systems, and subwoofers where power consumption and heat dissipation are critical. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize audio precision or efficient power use in specific applications.
Cost and Component Complexity
Class AB amplifiers generally have higher component complexity due to their use of both transistor types operating in the linear region, which results in increased heat dissipation and the need for larger heat sinks, raising the overall cost. In contrast, Class D amplifiers utilize switching technology with fewer passive components, significantly reducing heat generation and enabling smaller, less expensive heat sinks, which lowers both manufacturing costs and physical size. The reduced component count and higher efficiency of Class D amplifiers make them more cost-effective for applications requiring compactness and energy savings.
Reliability and Longevity
Class AB amplifiers are known for their robust reliability and longer lifespan due to their simpler analog design and reduced heat generation during operation. Class D amplifiers, while highly efficient and compact, may face longevity challenges related to higher switching frequencies and potential stress on components like inductors and capacitors. Proper thermal management and quality components significantly enhance the durability of both Class AB and Class D amplifiers in high-performance audio applications.
Choosing the Right Amplifier for Your Needs
Class AB amplifiers deliver high-fidelity audio with low distortion, ideal for audiophiles seeking superior sound quality in home audio systems. Class D amplifiers offer high efficiency and compact size, making them perfect for portable devices and automotive audio where power conservation and heat management are critical. Selecting the right amplifier depends on balancing audio performance requirements with energy efficiency and form factor constraints.
Class AB vs Class D Amplifier Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com