UV-C LEDs emit short-wavelength ultraviolet light capable of effectively inactivating bacteria and viruses, making them ideal for disinfection purposes, while UV-A LEDs produce longer wavelengths primarily used in curing materials and detecting fluorescent substances. Discover how choosing between UV-C and UV-A LEDs can impact your application requirements by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
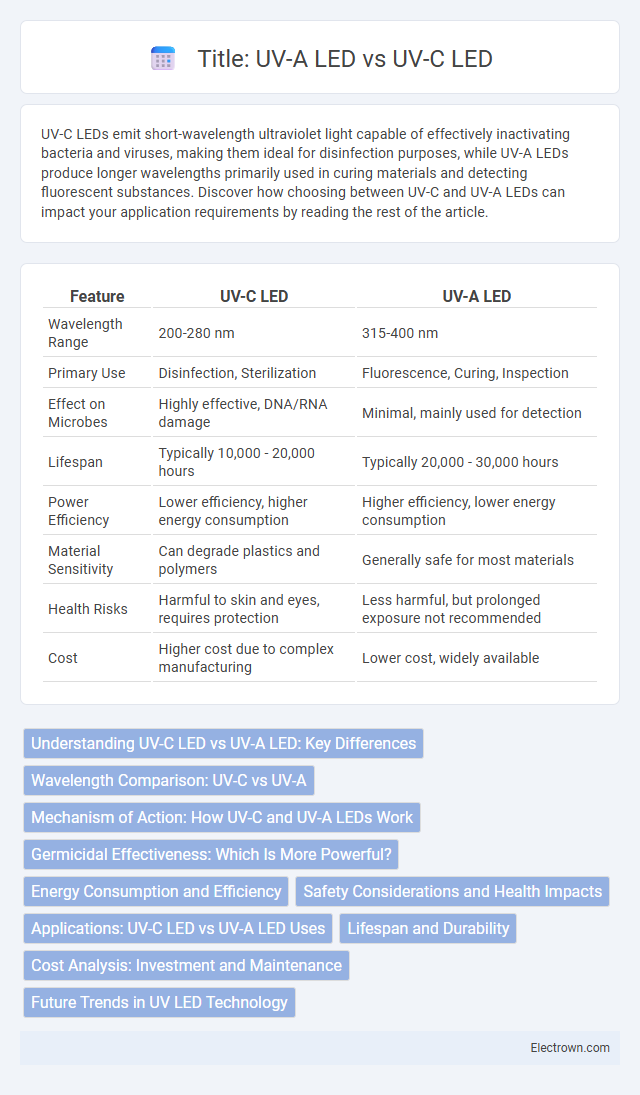
| Feature | UV-C LED | UV-A LED |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength Range | 200-280 nm | 315-400 nm |
| Primary Use | Disinfection, Sterilization | Fluorescence, Curing, Inspection |
| Effect on Microbes | Highly effective, DNA/RNA damage | Minimal, mainly used for detection |
| Lifespan | Typically 10,000 - 20,000 hours | Typically 20,000 - 30,000 hours |
| Power Efficiency | Lower efficiency, higher energy consumption | Higher efficiency, lower energy consumption |
| Material Sensitivity | Can degrade plastics and polymers | Generally safe for most materials |
| Health Risks | Harmful to skin and eyes, requires protection | Less harmful, but prolonged exposure not recommended |
| Cost | Higher cost due to complex manufacturing | Lower cost, widely available |
Understanding UV-C LED vs UV-A LED: Key Differences
UV-C LEDs emit short-wavelength ultraviolet light (200-280 nm) primarily used for germicidal applications by effectively disrupting DNA and RNA of microorganisms, while UV-A LEDs emit longer wavelengths (315-400 nm) commonly used in curing, fluorescence, and blacklight effects. The germicidal efficiency of UV-C LEDs makes them ideal for sterilization and water purification, whereas UV-A LEDs are favored for tasks requiring less intense UV exposure. Understanding these wavelength-driven functional differences helps you select the right LED technology for disinfection or specialized industrial processes.
Wavelength Comparison: UV-C vs UV-A
UV-C LEDs emit light within the 200-280 nm wavelength range, targeting germicidal applications due to their ability to disrupt microbial DNA and RNA. In contrast, UV-A LEDs operate between 315-400 nm, primarily used for curing, fluorescence, and phototherapy with lower energy than UV-C. The distinct wavelength ranges influence their effectiveness, with UV-C providing sterilization benefits while UV-A serves surface treatments and detection tasks.
Mechanism of Action: How UV-C and UV-A LEDs Work
UV-C LEDs emit light at wavelengths between 200-280 nm, causing direct damage to DNA and RNA strands of microorganisms, thereby inactivating them by preventing replication. UV-A LEDs operate within 315-400 nm wavelengths and primarily induce oxidative stress by generating reactive oxygen species (ROS) that damage cellular components. The distinct mechanisms of UV-C and UV-A LEDs influence their effectiveness in disinfection and sterilization applications.
Germicidal Effectiveness: Which Is More Powerful?
UV-C LEDs emit light within the 200-280 nm range, proven to be highly germicidal by effectively damaging the DNA and RNA of microorganisms, leading to their inactivation. UV-A LEDs, ranging from 315-400 nm, exhibit considerably lower germicidal effectiveness since their longer wavelengths cause less direct damage to microbial genetic material. Scientific studies consistently demonstrate that UV-C LEDs offer superior germicidal power compared to UV-A LEDs, making them the preferred choice for disinfection applications.
Energy Consumption and Efficiency
UV-C LEDs consume more energy compared to UV-A LEDs due to the higher energy required to generate shorter wavelengths around 260-280 nm for germicidal purposes. UV-A LEDs, emitting wavelengths between 315-400 nm, generally offer higher electrical-to-optical efficiency, resulting in lower energy consumption for applications like curing or sensing. Efficiency improvements in UV-C LED technology are ongoing, but UV-A LEDs remain more energy-efficient for comparable power outputs.
Safety Considerations and Health Impacts
UV-C LEDs emit short-wavelength ultraviolet light that effectively kills bacteria and viruses but can cause skin burns and eye damage with direct exposure, requiring strict safety measures and protective gear. UV-A LEDs have longer wavelengths, posing lower immediate harm but contributing to skin aging and potential long-term eye damage through cumulative exposure. When using UV LEDs, you should prioritize appropriate shielding and limited exposure to minimize health risks associated with each wavelength.
Applications: UV-C LED vs UV-A LED Uses
UV-C LEDs are primarily used for sterilization and disinfection in medical devices, water purification systems, and air sanitizers due to their ability to destroy bacteria and viruses. UV-A LEDs find applications in curing adhesives, forensic analysis, counterfeit detection, and dermatology treatments like phototherapy. Both UV-C and UV-A LEDs offer advantages in energy efficiency and compact design but differ significantly in wavelength and targeted applications.
Lifespan and Durability
UV-C LEDs typically have a shorter lifespan, averaging around 10,000 to 20,000 hours, due to the higher energy levels that accelerate material degradation. UV-A LEDs often last longer, with lifespans extending up to 50,000 hours, benefiting from lower energy outputs and less thermal stress. Durability in UV-C LEDs is challenged by their susceptibility to moisture and heat, whereas UV-A LEDs generally exhibit greater robustness in varying environmental conditions.
Cost Analysis: Investment and Maintenance
UV-C LED systems typically demand higher initial investment costs due to advanced semiconductor materials and complex manufacturing processes compared to UV-A LEDs, which are more affordable and widely available. Maintenance expenses for UV-C LEDs are generally lower because of their longer lifespan and reduced need for frequent replacements, whereas UV-A LEDs may incur more frequent maintenance despite lower upfront costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership favors UV-C LEDs in specialized applications requiring germicidal properties, while UV-A LEDs remain cost-effective for surface curing and inspection tasks.
Future Trends in UV LED Technology
UV-C LED technology is advancing rapidly with enhanced efficiency and durability, enabling broader applications in water purification, surface sterilization, and medical devices. UV-A LEDs continue to improve in wavelength precision and energy consumption, driving innovations in curing processes, counterfeit detection, and phototherapy. Emerging trends emphasize integrated smart UV LED systems with IoT connectivity and adaptive controls to optimize performance across diverse industrial and healthcare sectors.
UV-C LED vs UV-A LED Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com