Monochrome OLED panels offer higher contrast and longer lifespan by using a single color, making them ideal for devices focused on clarity and energy efficiency, while RGB OLED displays provide vibrant full-color visuals suited for immersive multimedia experiences. Explore the rest of the article to understand which OLED technology best fits your needs and applications.
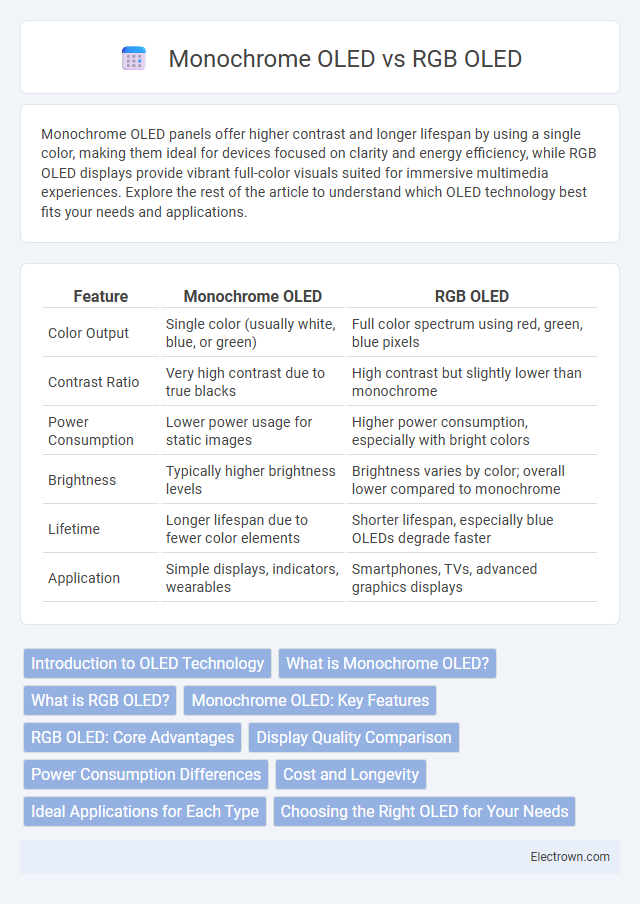
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Monochrome OLED | RGB OLED |
|---|---|---|
| Color Output | Single color (usually white, blue, or green) | Full color spectrum using red, green, blue pixels |
| Contrast Ratio | Very high contrast due to true blacks | High contrast but slightly lower than monochrome |
| Power Consumption | Lower power usage for static images | Higher power consumption, especially with bright colors |
| Brightness | Typically higher brightness levels | Brightness varies by color; overall lower compared to monochrome |
| Lifetime | Longer lifespan due to fewer color elements | Shorter lifespan, especially blue OLEDs degrade faster |
| Application | Simple displays, indicators, wearables | Smartphones, TVs, advanced graphics displays |
Introduction to OLED Technology
OLED technology uses organic compounds that emit light when an electric current passes through, enabling vibrant and energy-efficient displays. Monochrome OLEDs feature a single color emitter, offering higher brightness and longer lifespan, ideal for applications like wearable devices and simple displays. RGB OLEDs incorporate red, green, and blue emitters in each pixel, delivering full-color images with rich contrast and wide viewing angles, commonly used in smartphones, TVs, and advanced display panels.
What is Monochrome OLED?
Monochrome OLED displays utilize organic light-emitting diodes to produce images in a single color, typically white or various shades of gray, providing higher brightness and better energy efficiency compared to RGB OLED screens. These displays are ideal for applications where simple, high-contrast visuals are required, such as smartwatches, fitness bands, and certain industrial devices. Understanding how Monochrome OLED works can help you choose the right display technology for low-power, high-clarity needs.
What is RGB OLED?
RGB OLED displays use individual red, green, and blue organic light-emitting diodes for each pixel, enabling full-color image reproduction with vibrant hues and high contrast ratios. This technology allows your device to render detailed visuals and dynamic color ranges, making it ideal for applications like smartphones, TVs, and wearable screens. Compared to monochrome OLEDs, RGB OLEDs provide richer graphics by combining these primary colors at varying intensities for true-to-life color accuracy.
Monochrome OLED: Key Features
Monochrome OLED displays feature a single-color emission, offering higher brightness and longer lifespan compared to RGB OLEDs due to reduced pixel complexity and power consumption. These displays excel in applications requiring sharp contrast and energy efficiency, such as fitness trackers and smartwatches. The simplified architecture of monochrome OLEDs results in better durability and less susceptibility to burn-in, making them ideal for extended-use devices.
RGB OLED: Core Advantages
RGB OLED displays deliver superior color accuracy and vibrancy by independently controlling red, green, and blue subpixels, enabling a broader color gamut and richer image quality compared to monochrome OLEDs. These displays offer enhanced visual detail and realistic color representation, making them ideal for applications requiring precise color fidelity such as high-end smartphones and professional monitors. Furthermore, RGB OLED technology supports dynamic content with smoother gradients and deeper contrast levels, improving overall viewing experience.
Display Quality Comparison
Monochrome OLED displays deliver higher contrast ratios and deeper blacks due to the absence of color filters, resulting in sharper and more vivid images for text and simple graphics. RGB OLED panels provide full-color reproduction with vivid hues but may exhibit slightly lower brightness and contrast compared to monochrome displays. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize crisp monochrome clarity or vibrant color depth for your specific application.
Power Consumption Differences
Monochrome OLED displays consume significantly less power than RGB OLEDs due to their simpler structure and fewer active subpixels, making them highly efficient for devices requiring extended battery life. RGB OLEDs light up red, green, and blue subpixels independently, which increases overall power usage, especially during bright or colorful image rendering. Your choice between these technologies can impact energy efficiency, with monochrome OLEDs ideal for low-power applications and RGB OLEDs suited for vibrant multimedia experiences.
Cost and Longevity
Monochrome OLED displays generally offer lower cost and superior longevity compared to RGB OLEDs due to their simpler structure and fewer subpixels, resulting in reduced manufacturing complexity and power consumption. RGB OLEDs, while providing vibrant color reproduction for applications like smartphones and TVs, tend to have shorter lifespans because the blue subpixel degrades faster, increasing replacement and maintenance expenses over time. Choosing a Monochrome OLED can optimize your device's durability and affordability when color is not a critical requirement.
Ideal Applications for Each Type
Monochrome OLED displays excel in applications requiring high contrast and low power consumption, such as wearable devices, digital watches, and industrial instrumentation, where displaying simple information clearly is crucial. RGB OLED screens are best suited for devices needing rich, vibrant colors and detailed images, including smartphones, tablets, and high-end TVs, providing an immersive visual experience. Your choice depends on whether the priority is energy efficiency and clarity or full-color graphics and multimedia performance.
Choosing the Right OLED for Your Needs
Monochrome OLED displays deliver higher brightness and longer lifespan compared to RGB OLEDs, making them ideal for applications requiring clear, high-contrast visuals such as digital watches or industrial instruments. RGB OLEDs provide vibrant full-color images, perfect for smartphones, tablets, and TVs where color accuracy and richness are critical. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize durability and clarity with monochrome or vivid, dynamic color reproduction with RGB OLED technology.
Monochrome OLED vs RGB OLED Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com